Visible spectrum, Properties of light, Types of Light reflection and Formation of shadow
Light is one of the forms of energy, Light energy is the only form of energy that can be seen, Light energy that can be seen is called the visible spectrum, There are many sources of light such as the Sun (The main source of light on Earth), candles, Kerosene lamps & electric lamps, but the moon is not considered as a source of light as it reflects the sunlight falls on its surface.
Properties of light
- Travelling of light in straight lines.
- Transmitting of light through different materials.
- Light reflection.
- Light refraction.
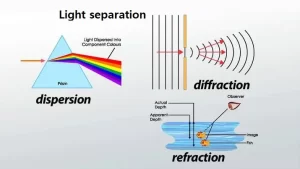
- Light separation (splitting of light).
Laser is a light beam that travels long distances without fainting, Laser lights are used in means of communication, medicine, and computers.
Travelling of light in straight lines
As a result of travelling of light in straight lines, Some Phenomena happen such as the Formation of images through narrow holes and the formation of shadows.
Formation of shadow
When you darken the room and put your hand between a wall and a torch, a darkened area that is called shadow is formed on the wall, Shadow is the darkened area which is formed as a result of the falling of light on an opaque object, The shadow formation is an evidence that light travels in straight lines.
The shadow area is changed by changing the position of the object with respect to the light source, The nearer object to the light source has a bigger shadow, The Shadow of an opaque body is formed when the light falls on it because the light travels in straight lines.
Formation of images through narrow holes
The idea of photographic cameras is based on the idea of the formation of images through narrow holes, where a minimized and inverted image is formed, Formation of images through narrow holes is due to the travelling of light in straight lines.
Transmitting of light through different materials
Light transmits through different materials with variable degrees, Materials can be classified according to their ability to transmit light into Transparent materials, Semi-transparent ( translucent ) materials, and Opaque materials.
Transparent materials allow the most light to pass through and the objects can be seen clearly (in full detail) through them, Such as Clear glass, Air, Clear water, and transparent plastic.
Semi-transparent ( translucent ) materials are the materials that allow some light to pass through and the objects can be seen through them less clearly than the transparent ones, Such as Frosted glass and Tissue paper.
Opaque materials are materials that do not allow light to pass through and objects can not be seen through them, Such as Rocks, Aluminium foil, Wood & Cartoon, Opaque materials are used to cover the windows of darkened photographic rooms.
Our bodies are opaque materials because they do not allow the light to transmit through and the objects can not be seen behind them and we can not see through the foil sheet because the foil sheet is an opaque material.
Clear glass is a transparent material because it allows most light to pass through and the objects can be seen clearly through it.
Light reflection
Light reflection is the bouncing (returning back) of light rays when the light falls on a reflecting surface, Light reflection occurs in the presence of a source of light and a reflecting surface.
We can see the surrounding objects, When the light falls on the object, Light reflection occurs and reaches our eyes causing the vision of these objects.
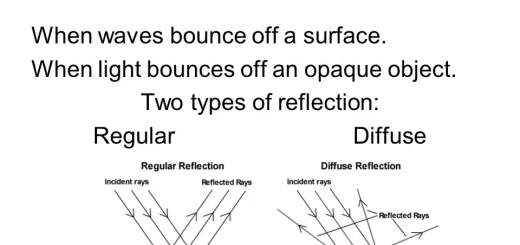
Types of Light reflection
Light reflection can be divided into regular reflection and irregular reflection :
Regular reflection is the reflection of light when it falls on a smooth and shiny reflecting surface, where the light rays are reflected directly in one direction, such as reflection of light when it falls on a mirror surface and reflection of light when it falls on a glass surface.
Irregular reflection is the reflection of light when it falls on a rough reflecting surface, where the light rays are reflected & scattered in different directions, like the reflection of light when it falls on any rough surface as the piece of white paper (which contains the protrusions and tiny holes).
When you look in a mirror, you can see your image due to the regular light reflection, where the distance between your body and the mirror is equal to the distance between your image and the mirror.
We can not see in the dark because there is no light falling on the objects and reflecting on our eyes causing vision, We can see your image in the plane mirror due to the light reflection.
Light refraction
Light refraction is the change in the direction of light rays when light passes through the separating surface between two different transparent media due to the change in the light speed.
The pencil appears broken when you put it in a transparent cup of water due to the refraction of light, The reflected light rays from the part of the pencil above the water travel through the air only, So, they do not refract.
But, the light rays that are reflected from the part of the pencil inside the water travel firstly through the water, then through the air, The light speed through air is faster than that through the water, So, this change in the speed of light rays causes their refraction (changing in their direction) and seeing the pencil broken.
Light separation (splitting of light)
Light separation is the separation (splitting) of white light into seven spectrum colours, White light consists of seven spectrum colors, so, we can separate it into seven colours by using the glass prism.
Sunlight (white light) is formed of seven spectrum colours which are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet, White light can be also analyzed into seven spectrum colours by the drops of rain water forming rainbow, that appears in the sky during rainfall, So, the drops of rain water act as a glass prism.
The formation of spectrum colours is due to the splitting of white light into seven spectrum colors.
Light refraction effects, Law of light refraction, Mirage and Apparent positions of objects
Light wave properties, Analysis of white light, Spectrum colours and Light intensity
Types & Laws of light reflection, Regular and Irregular reflection of light
Light refraction, Snell’s law, Factors affect the absolute refractive index of a medium