Transparent and translucent objects, Seeing coloured objects and mixing coloured lights
We can use the glass prism to separate the white light into seven spectrum colours, which are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet When the seven light colours are mixed together, the white light is produced again, But mixing coloured dyes gives colours that are different from those produced by mixing coloured lights.
Seeing the coloured objects
First: Seeing the coloured transparent and translucent objects
The transparent and translucent objects allow the light to pass through them, When the white light strikes the coloured transparent or translucent object, this object absorbs all colours of light (spectrum colours), but it permits its colour only to pass through it.
So, The colours of the transparent and translucent objects are the same colours of the transmitted light through.
Example: Green transparent glass bottle that appears as it absorbs all light colours and allows the green light only to transmit through it.
The red transparent ruler appears red when white light falls on it because it absorbs all light colours that fall on it and allows the red light only to transmit through it.
Second: seeing the coloured opaque objects
The opaque objects do not allow the light to transmit through them, The opaque objects are divided into White objects, Black objects, and Coloured objects.
Seeing the white opaque objects
When white light strikes a white opaque object, this object reflects all light colours, So, it appears in the same colour of light that falls on it.
We wear white clothes in summer because white clothes reflect all light colours that fall on them causing a decrease in the feeling of heat.
Seeing the black opaque objects
When white light strikes a black opaque object, this object absorbs all light colours and does not reflect any color, so, it appears black.
We must wear black (dark) clothes in winter because black clothes absorb all light colours that fall on them causing the feeling of warmth.
Seeing the coloured opaque objects
When the white light strikes a coloured opaque object, this object absorbs all light colours and reflects its colour only, So, the colour of the coloured opaque object is the colour of the reflected light.
The banana fruit seems yellow when sunlight falls on it because the banana fruit absorbs all light colours and reflects the yellow colour only.
Third: Seeing the coloured opaque object through coloured transparent objects
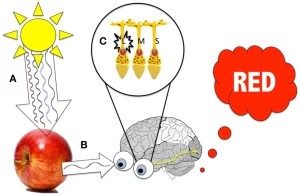
Look at a red apple through a red transparent glass sheet, a green or blue transparent glass sheet.
The apple appears red when you look at it through the red transparent glass sheet, The apple appears in no colour (black) when you look at it through the green or blue transparent glass sheet.
The apple appears red through the red transparent glass sheet because the apple absorbs all light colours that fall on it and reflects the red light only.
The reflected red light strikes the red transparent glass sheet and transmits through it then reaches our eyes.
The apple appears in no colour (black) through the green or the blue transparent glass sheet, because the reflected red light from the apple is absorbed by green or blue transparent glass and does not transmit through them.
The opaque object is seen in its real colour when you look at it through a transparent object that has the same colour.
Mixing the coloured lights
There are two types of coloured lights which are primary coloured lights and secondary coloured lights.
Primary coloured lights are coloured lights that can not be produced by mixing two other colour lights, Such as Red, green, and blue coloured lights.
On mixing all the primary coloured lights, white light is produced, On mixing any two of the primary coloured lights, a secondary coloured light is produced.
Secondary coloured lights are coloured lights that are produced by mixing two of the primary coloured lights, Such as yellow, Magenta, and cyan coloured lights.
Red + Green → Yellow
Red + Blue → Magenta
Blue + green → Cyan
We must use three coloured projector sets (red, green, and blue) to study the effect of mixing the primary coloured lights.
Red light is a primary coloured light because it can not be produced by mixing any of the other coloured lights.
Magenta is called a secondary coloured light because it is produced by mixing two of the primary coloured lights which are red and blue.
Light wave properties, Analysis of white light, Spectrum colours, and Light intensity
Types and Laws of light reflection, Regular and Irregular reflection of light
Light refraction, Snell’s law, Factors affect the absolute refractive index of a medium


nice job really helpful good efforts
Thank you very much for your comment