The states of matter (solid, liquid, gas & plasma)
The states of matter
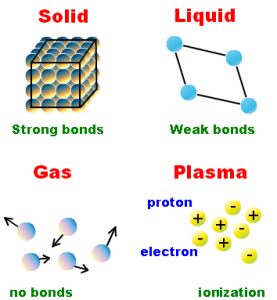
All matters have a mass and take up space, the state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on, and there are four states of matter observable in our life which are solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
The solid-state
The solid is the state in which matter maintains a definite (fixed) volume and shape, the motion of its particles is limited motion (oscillatory motion), they are packed closely together.
The intermolecular forces between the solid particles are very strong that the particles can not move freely, they can only vibrate, Some examples of solid-state such as iron, aluminum, and copper.
The solid has very small intermolecular spaces, it can transform into a liquid through the melting process, the liquid can change into a solid by freezing process, and the solid can change into a gas by a sublimation process.
The liquid state
The liquid is the state in which matter adapts to the shape of its container but varies only slightly in volume, the liquid state has definite volume and indefinite shape if the temperature and pressure are constant.
The motion of the liquid particles is more free, the intermolecular spaces between its particles are relatively large, and the intermolecular forces are relatively weak, Examples of liquid state such as the water, alcohol, the oil, the milk, and the juice.
The liquid can be changed to gas by heating at constant pressure to the substance’s boiling point or through reduction of pressure at a constant temperature, and it is called the evaporation process.
The gaseous state
The gas is the state in which matter expands to occupy the volume and shape of its container and it has indefinite shape and indefinite volume, The motion of gas molecules is completely free (unlimited), the intermolecular spaces are very large and the intermolecular forces are very weak or almost not existed.
The plasma state
The plasma does not have definite shape or volume, it is electrically conductive, it produces magnetic fields and electric currents, and respond strongly to electromagnetic forces.
Lighting, electric sparks, the fluorescent lights, neon lights, plasma televisions, some types of flame and the stares are examples of illuminated matter in the plasma state.
The gas is usually changed to the plasma in one of two ways when there is a huge voltage difference between two points, or by exposing it to extremely high temperatures.