Properties of Noble (inert) gases, Features and Applications of Inert gases
Inert gases are the elements in which the outermost electron shells are completely filled with electrons, so they don’t participate in any chemical combination in ordinary conditions.
Inert gases
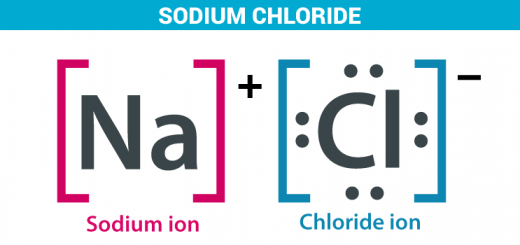
Noble gases do not form positive or negative ions in ordinary conditions, The elements of the atoms with which all the shells completely filled are called inert gases or noble gases or rare gases.
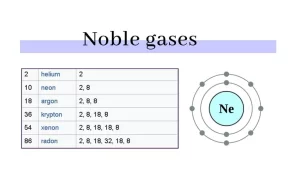
Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe), and Radon (Rn) are inert gases, The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties under standard conditions.
The noble gases are odorless, colorless, monoatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity, and each molecule consists of one single atom (monoatomic).
The noble gases have weak interatomic force, they have low melting and boiling points, and they are all monoatomic gases under the standard conditions, The noble gases are located in the far-right column of the periodic table, they are in group (0) or group (18).
They have a valence of zero, their atoms cannot combine with other elements to form compounds, The noble gases have full valence electron shells, they are stable and do not tend to form chemical bonds.
Noble gases are commonly used in lighting because of their lack of chemical reactivity, and they glow in distinctive colours when they are used inside gas-discharge lamps such as neon lights.
Some noble gases have direct application in medicine, and the noble gases are used in the excimer lasers.
Properties of inert gases
Inert gases are also known as noble gases, They are a group of elements in Group 18 of the periodic table. Noble gases include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). These gases share several unique properties:
Physical Properties
- Colorless, Odorless, and Tasteless: Noble gases are colorless, odorless, and tasteless in their natural state.
- Low Boiling and Melting Points: Inert gases exist as gases under standard conditions due to weak intermolecular forces.
- Monatomic: Inert gases exist as single atoms rather than molecules, making them unique among elements.
- Low Density: Inert gases are lighter than many other gases, especially helium, which is the lightest after hydrogen.
- Non-Flammability: Inert gases are non-flammable, as they do not readily react with other substances.
Chemical Properties
- High Stability: Noble gases have full outer electron shells (except helium, which has a full 1s shell with two electrons), making them chemically stable and unreactive under normal conditions.
- Low Reactivity: Their lack of chemical reactivity is due to their complete valence electron configuration. However, under extreme conditions, some (like xenon and krypton) can form compounds, especially with highly electronegative elements like fluorine and oxygen.
- Insolubility: Inert gases have low solubility in water, though solubility increases slightly with molecular weight.
- Nonpolar Nature: Noble gases are nonpolar because they are monoatomic and do not form bonds under typical conditions.
Applications of Inert gases
- Helium can be used in balloons and cryogenics, and it is used as a coolant in nuclear reactors.
- Neon is known for its use in neon lights and signs.
- Argon is widely used in welding and as an inert gas shield in industrial processes.
- Krypton and Xenon are utilized in lighting (e.g., flash photography, high-intensity lamps) and as anesthetics in some cases.
- Radon: Though radioactive, it has applications in cancer treatment and radiotherapy.
You can follow science online on YouTube from this link: Science online
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Chemical combination, Properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Noble (inert) gases
Classification of elements in Long-form periodic table, Ionization Energy, and Oxidation numbers
Radius property, Ionization potential, Electron affinity & Electronegativity
Modern periodic table and classification of Elements
Theories explaining the covalent bond, Octet rule & Overlapped orbitals concept