General properties of halogens in the modern periodic table
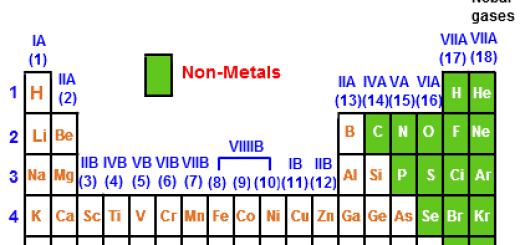
Halogens are located on the right side of the modern periodic table before the inert gases, The halogens are elements of group 7 A (17) in p-block, and Halogens are mono-valent elements as their outermost energy levels have (7) electrons. Each element of the halogens replaces the element below it in its salt solution.
Halogens
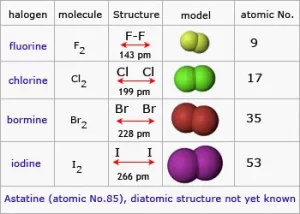
Halogens exist in the form of diatomic molecules (they are formed of two atoms), The halogens tend to gain one electron during the chemical reaction and convert into negative ion which has one negative charge. The physical state of the halogens is graduated from the gas to the liquid to the solid. Fluorine and Chlorine are gases, Bromine is a liquid, and Iodine is a solid.
Halogens react with the metals forming the salts, So, they are called halogens which means “Forming the salts”. Halogens are active elements, therefore, they do not exist in nature in the elementary state, but they are found combining with the other elements forming the chemical compounds (except Astatine (At) which is prepared artificially).
They are a group of nonmetallic elements found in Group 17 (VIIA) of the periodic table. The group includes fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). These elements share common properties due to their similar electronic configuration but also exhibit trends in properties as you move down the group.
Physical Properties of Halogens
States at Room Temperature:
- Fluorine: Pale yellow gas.
- Chlorine: Greenish-yellow gas.
- Bromine: Reddish-brown liquid.
- Iodine: Dark gray solid (sublimes to violet vapor).
- Astatine: Solid (rare and radioactive, physical appearance less well studied).
The color of halogens deepens down the group due to increasing molecular size and electron cloud polarizability (e.g., fluorine is pale yellow, while iodine vapor is violet).
Melting and Boiling Points: Increase down the group as molecular size and van der Waals forces increase. Fluorine and chlorine have low melting/boiling points, while iodine and astatine are higher.
Halogens are more soluble in organic solvents (e.g., chloroform, carbon tetrachloride) than in water. Fluorine reacts violently with water, while others dissolve to form halogen acids or hypohalous acids. The density increases down the group, with heavier halogens (bromine, iodine, astatine) being denser.
Chemical Properties of Halogens
They are highly reactive nonmetals, with reactivity decreasing down the group: Fluorine is the most reactive element in the periodic table.
Fluorine > Chlorine > Bromine > Iodine > Astatine.
They have very high electronegativity values, with fluorine being the most electronegative element. The electronegativity decreases down the group. They are strong oxidizing agents due to their high affinity for electrons. Oxidizing power decreases down the group.
They exist as diatomic molecules in their elemental form (e.g., F₂, Cl₂). They react with metals to form ionic halides (e.g., NaCl, MgBr₂). They form covalent compounds with nonmetals (e.g., HCl, PCl₅).
They react with hydrogen to form hydrogen halides (e.g., HCl, HF), which dissolve in water to produce strong acids (except HF, which is a weak acid). More reactive halogens can displace less reactive halogens from their compounds (e.g., Cl₂ + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br₂). They combine with each other to form interhalogen compounds (e.g., ClF, BrF₅).
- Fluorine is exceptionally reactive; and forms compounds with nearly all elements. Causes violent reactions with many substances, including water.
- Chlorine is used in disinfectants and bleaching agents (e.g., Cl₂ in water purification).
- Bromine is liquid at room temperature; and used in flame retardants and certain dyes.
- Iodine is essential for thyroid function in humans (iodized salt). Exhibits sublimation (solid to vapor transition).
- Astatine is radioactive and extremely rare; least studied halogen.
Halogens applications
- Fluorine is used in toothpaste (as fluoride) and Teflon production.
- Chlorine is used in water purification, PVC production, and as a disinfectant.
- Bromine is used in Flame retardants and pharmaceuticals.
- Iodine is used in Antiseptics and dietary supplements.
- Astatine is used in Research in nuclear medicine (due to its radioactivity).
Halogens play vital roles in both industrial and biological systems due to their unique chemical properties.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Classification of elements in Long-form periodic table, Ionization Energy and Oxidation numbers
The graduation of the electronegativity of the elements in the periodic table
The lanthanides and actinides in the modern periodic table
Modern periodic table and classification of Elements
Graduation of the properties of the elements in the modern periodic table