Properties and Kinds of molecules, Relation between temperature of matter and its physical state
The molecule is the building unit of matter, It is the smallest part of matter which can exist freely & it has the properties of matter, Matter in any state (solid, liquid or gaseous) is composed of small building units called “Molecules“, Air is considered as matter because air has a mass and occupies a certain space when you open a perfume bottle in a closed room for a while, the odour of the perfume spreads all over the room.
Matter and molecules
When you put a suitable amount of perfume in a glass beaker, then determine its mass by using a sensitive balance, Leave the beaker on one side of the room for a period of time, then move to the other side of the room, and determine the mass of the beaker again.
You will notice that the odour of the perfume spreads all over the room, and the mass of the beaker decreases, The matter of the perfume is divided into tiny (small) particles which can’t be seen by the naked eye or by a microscope.
The particles of the perfume are called “molecules that spread all over the room keeping the properties of perfume, The odour of perfume spreads all over the room when the bottle is opened because the molecules of the perfume are in continuous motion and they keep the properties of the perfume.
Properties of the molecules of matter
Molecules of matter are in a state of continuous motion, There are intermolecular spaces among the molecules of matter and there are attraction forces among the molecules of matter.
A drop of ink spreads through water because the molecules of ink are in continuous motion in all directions among water molecules, When you leave the perfume bottle open, you smell it all over the room because the molecules of the perfume are in a continuous motion and they keep the properties of perfume.
There are intermolecular spaces among the molecules of matter, Intermolecular spaces are the spaces that are found among the molecules of matter, The disappearance of a little amount of table salt when it is put in a beaker containing water for a period of time because molecules of table salt spread in the intermolecular spaces among water molecules.
When we put a small amount of potassium permanganate in a glass containing water, the colour of the water changes into violet because the molecules of ink or potassium permanganate are in continuous motion in all directions among water molecules, The molecules of solid matter have limited vibrational motion, while the motion of liquids is more free and that of gases is completely free.
When you put 300 cm³ of water in a graduated cylinder and 200 cm³ of ethyl alcohol to the water, the volume of the mixture will be less than 500 cm³, Some of the ethyl alcohol molecules are distributed in the intermolecular spaces that are found among water molecules.
It is difficult to break a piece of iron because the attraction force among molecules is very strong in solids (such as iron and aluminium), It is easy to divide an amount of water into portions because the attraction force among molecules is weak in liquids (such as water, alcohol and oil)
There are intermolecular forces (attraction forces) among the molecules of matter, Intermolecular force is the force that binds the molecules of matter together, The intermolecular forces among the molecules of gases are almost not existed.
Solid substances have definite shape and volume because the intermolecular spaces among their molecules are very narrow and the intermolecular force is very strong, so the molecules are relatively fixed in their positions.
The liquid matter takes the shape of its container because the intermolecular spaces among its molecules are relatively large and the intermolecular force among its molecules is weak, Gases have indefinite shapes and volumes because the intermolecular spaces among their molecules are very large and the intermolecular force among their molecules is very weak.
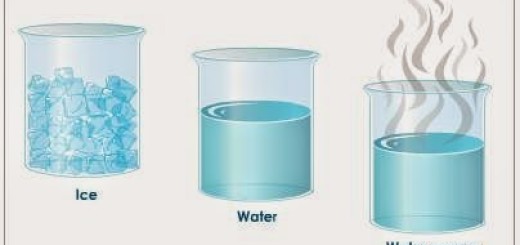
The relation between the temperature of matter & its physical state
Melting process is the change of matter from the solid state to the liquid state by heating, On heating the solid substance, Its molecules gain thermal energy, so, the speed of its molecules increases and at the melting point, the intermolecular force weakens, the intermolecular spaces increase and they become more freely leading to the change of matter from the solid-state into the liquid state, and this is known as Melting.
On heating the liquid substance, Its molecules gain more energy, So, the speed of its molecules increases and at the boiling point, the molecules overcome the intermolecular forces (become more free), the intermolecular spaces increase and they escape in the form of vapour, this process is known as Vaporization.
The vaporization process is the change of matter from the liquid state to the gaseous state by heating, The melting process reverses the freezing process, while the vaporization process reverses the condensation process.
The latent heat of melting is the amount of heat required to change 1 kg of a substance from the solid-state to the liquid state without a change in the temperature (although heating is continued), The latent heat of vaporization is the amount of heat required to change 1 kg of a substance from the liquid state to the gaseous state without a change in the temperature (although heating is continued).
Kinds of molecules
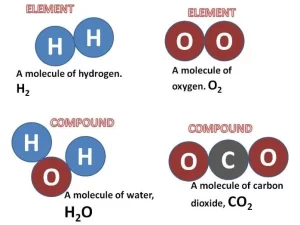
A drop of water is composed of millions of water molecules, this means that molecules are very tiny and can’t be seen by the naked eye or by the microscope, the molecules of the same substance are similar in properties, but they differ from other substances, The molecules are composed of tiny structural units called “Atoms“, Kinds of molecules are the element molecule & compound molecule.
The element molecule
The element molecule is formed of similar atoms (one or more atoms) that combine together, The element is the simplest pure form of matter which can’t be analyzed chemically into a simpler form by simple chemical methods.
Elements molecules formed of only one atom (Monoatomic) such as Liquids such as Mercury, Nobel (Inert) gases are Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon, Elements molecules formed of two atoms (Diaatomic) such as Liquids as Bromine, Active gases are oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen chlorine, and fluorine.
The molecule of active gases are diatomic, while molecules of noble gases are monoatomic, Mercury is the liquid element which is composed of one atom, while bromine is the liquid element which is composed of two atoms, The molecule of helium differs from the molecule of hydrogen because helium is an inert gas & its molecule is monoatomic, while hydrogen is active gas & its molecule is diatomic.
The compound molecule
The compound molecule is formed of different atoms that combine together, The compound is a substance that is formed from the combination of atoms of two or more different elements with constant weight ratios, Examples of some known compounds:
Hydrogen chloride molecule consists of two atoms of two different elements.
Hydrogen atom + chlorine atom → Hydrogen chloride molecule
A water molecule consists of three atoms of two different elements
Two hydrogen atoms + one oxygen atom → Water molecule
Ammonia molecule consists of four atoms of two different elements.
Three hydrogen atoms + One nitrogen atom → Ammonia molecule
The properties of molecules of substances are different from each other because molecules of various substances differ from each other in the number of atoms, kind of atoms, and way of combination between atoms.
Molecules of elements differ from molecules of compounds because the molecule of an element consists of similar atoms, but the molecule of a compound consists of different atoms, Oxygen is an element, while hydrogen chloride is a compound because the oxygen molecule is formed of two similar atoms, while hydrogen chloride molecule is formed of two different atoms.
Atomic structure of matter, Energy levels, Electronic distribution & chemical activity
What are the kinds of molecules?
Chemical combination, Types of bonds (Chemical bonds & Physical bonds)
The coordinate bond, Physical bonds (hydrogen bond and the metallic bond)