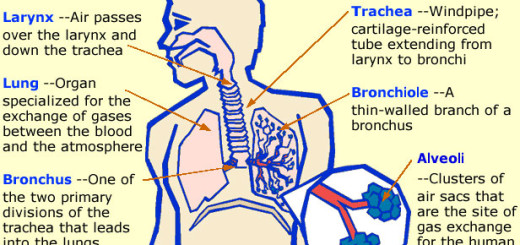
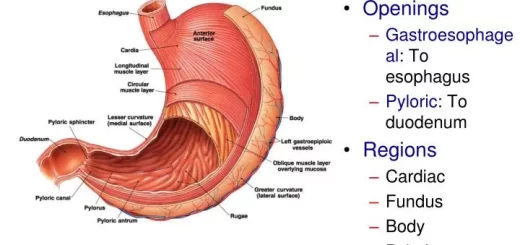
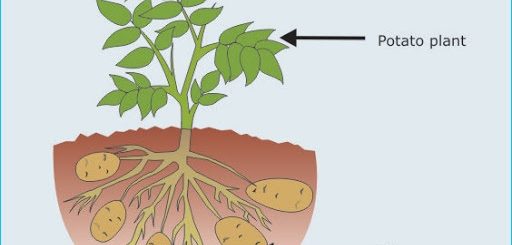
Structure of the plant cell and function of plant cell organelles
The plant tissue (as the epidermis tissue of the onion leaf) is composed of small units known as the plant cells, where each cell contains many components, The plant cell is the eukaryotic cell which differs in several key aspects from the cells of the other eukaryotic organisms.
The cell wall
The cell wall is the wall that surrounds the plant cell from outside, It supports the plant cell and gives it a definite shape.
The plasma (cell) membrane
The plasma membrane is the membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm, and it controls the substances that enter or leave the cell.
The cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a fluid that fills the cell and all the cell components are suspended in it, All the biological operations of the cell occur in the cytoplasm.
The nucleus
The nucleus organizes the biological operations in the cell and it is responsible for cell division.
The green plastids (the chloroplasts)
The chloroplasts are responsible for making food by the photosynthesis process.
The sap vacuole
The sap vacuole of the plant is much larger than animals and has the same functions, The sap vacuole stores important substances, and it also helps support the plant.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Diversity of cells, Cell theory, Role of scientists in discovering cell & its structure
Parts of cell & How can the cell perform its functions?
Excretion in plants, Importance & types of transpiration for the plant
Differentiation of cells and diversity of plant tissues
Histology, Molecular structure of the cell membrane, Cell function & structure