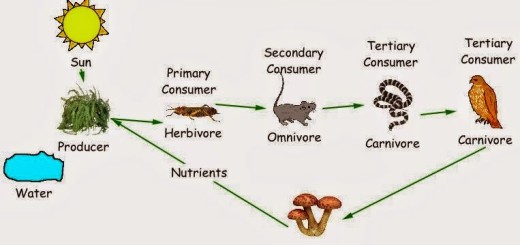
The structure and the function of the heart in the circulatory system
The circulatory system is the system that transports the digested food, oxygen gas, and water to all the body cells and carries the wastes away from the body cells to special organs to get rid of them.
The circulatory system
The circulatory system helps in maintaining the body health and it consists of the heart, the blood vessels, and the blood.
The heart
The heart is a muscular hollow organ equals to about the size of your fist, and it is located inside the chest cavity between the two lungs, The heart pumps blood continuously throughout the body, the four chambers of the heart are always full of the blood, and connected to the blood vessels.
The heart consists of four chambers located on two sides (the right side and the left side), The upper chamber on each side is called the “atrium”, and the lower chamber is called the “ventricle”.
There is a wall that separates the right side of the heart and the left side of the heart, to prevent the mixing of the blood on both sides.
There is a valve between each atrium and ventricle to allow the blood to flow from the atrium to the ventricle and prevent its returning back.
The heart normally pumps 4.5 to 5 liters of blood per minute and this rate increases up to three times when exercising, The heart is about 350 grams in a man weighing 70 Kg.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Heart function, structure, Valves, Borders, Chambers & Surfaces
Human Transport System, Structure of human circulatory system (heart, blood vessels and blood)
Blood pressure, structure, functions & Mechanism of blood clotting
The types and functions of the blood vessels in the circulatory system