The structure and importance of the nervous system
The human nervous system
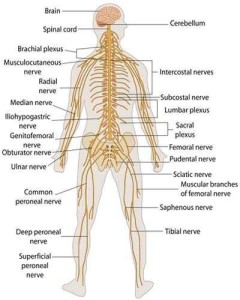
The nervous system is a communication and controlling body system, It consists of the brain, the spinal cord and the nerves, and it is the most important system inside your body.
The nervous system controls and regulates all the vital operations of the body because it receives the information from the environment and from the body, then it interprets this information and makes the body respond to it.
The nervous system is responsible for knowing if the things are hot or cold, sweet or bitter, rough or smooth, The nervous system adjusts the responses that require the emotions, so, it makes you sad or happy, angry or calm.
The nervous system oversees and regulates the multiple functions performed by the human body such as moving, feeding, digestion, breathing, thinking and others.
The structure of the nervous system
The nervous system consists of two major systems which are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
The neuron
The building unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell that is called the neuron, and it consists of two main parts which are the cell body and the axon, The cell body contains a nucleus, the cytoplasm and the plasma membrane.
There are some branches extending from the neuron’s body called the dendrites, The dendrites are connected to the neighbouring neurons to form the synapse (the synaptic areas).
The axon is a cylindrical axis covered with a fatty layer called myelin sheath, and it ends with nerve endings called the axon terminals, The axon terminals are connected to the muscles or form a synapse with other neurons.
The nerve cell’s axons are grouped together forming the nerve fibre. and the nerve fibres are grouped together forming the nerve.
Autonomic nervous system, Reflex action types & Autonomic ganglia function
Functions of Sympathetic nervous system & Role of the sympathetic in emergencies
Nervous system in man, Nerve cells types & Nature of nerve impulse
Nervous system (Central nervous system, Peripheral nervous system & Autonomic nervous system)
Human Transport System, Structure of human circulatory system (heart, blood vessels and blood)