The structure and function of the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system is the nerves which emerge from the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord), It consists of the cranial nerves and the spinal nerves and the cranial nerves are 12 pairs of nerves emerge from the brain.
The spinal nerves are 31 pairs of nerves emerge from the spinal cord, the peripheral nervous system consists of the sensory neurons running from the stimulus receptors that inform the central nervous system and the motor neurons running from the central nervous system to the muscles and the glands.
The peripheral nervous system is subdivided into the sensory-somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system, The sensory-somatic nervous system consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
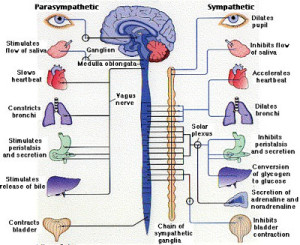
The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between the central nervous system and the various internal organs such as the hearts, the lungs, the viscera and the glands.
The autonomic nervous system has two subdivisions which are the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
The peripheral nervous system function
The peripheral nervous system delivers the sensory information and the kinetic responses between the central nervous system and all the parts of the body.
Autonomic nervous system, Reflex action types & Autonomic ganglia function
Functions of Sympathetic nervous system & Role of the sympathetic in emergencies
Nervous system in man, Nerve cells types & Nature of nerve impulse
Nervous system (Central nervous system, Peripheral nervous system & Autonomic nervous system)