The role of the muscles in performing the movement
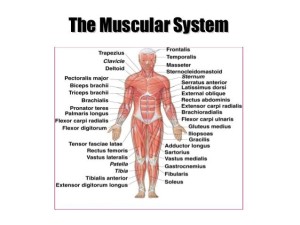
The muscular system
The muscular system is the engine that moves our body, where the muscles generate the mechanical energy and the movement to the body due to the ability of the muscular cells to contract and relax.
The muscles are fixed to the bones by the long strips called the tendons, So, when the muscles contract and relax, they move the bones.
The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body, It attached to the bones of the skeletal system which are about 650 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person’s body weight.
The human body contains 650 muscles, the biggest muscle in size is at the bottom of the body while the smallest muscle is in the ear, The human use 200 muscles during the walking.
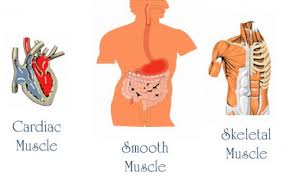
The types of muscles
There are two types of muscles which are the voluntary muscles and the involuntary muscles, the voluntary muscles are the muscles that can move willingly, and you can control its movement.
The voluntary muscles such as the limbs muscles, the trunk muscles, the face muscles and the abdominal wall muscles.
The involuntary muscles are the muscles that can move automatically and you can not control or even aware of their movement.
The involuntary muscles such as the gastrointestinal tract, the blood vessels, and the bladder muscles.
The role of the muscles in the movement of the forearms
The front muscle contracts and the back muscle relaxes, this causes the bending (moving up) of the arm by the help of the elbow joint.
The front muscle relaxes and the back muscle contracts, this causes extending (move down) of the arm by the help of the elbow joint.
The effect of the contraction or the relaxation of the muscles is transferred to the elbow joint bones by the tendons that link between the muscles and the bones.
Muscular system, Structure of skeletal muscle, Muscles properties & functions
Skeletal system, Axial skeleton (vertebral column, Skull & thoracic cage)
Skeletal system, Appendicular skeleton structure and importance
Mechanism of muscle contraction, motor unit, muscle fatigue & Huxley’s theory of sliding filaments