Asexual reproduction by grafting in the plants
Grafting is a technique used by the farmers and scientists to attach the tissue of one plant to the tissue of another, It allows for the asexual reproduction of plants, It is used in viticulture (grape growing) and the citrus industry, The scions capable of producing a particular fruit variety are grafted onto the rootstock with specific resistance to disease.
Reproduction by grafting
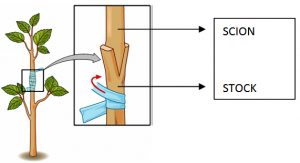
In reproduction by grafting, a part of a plant that contains more than one bud known as the scion (graft) is selected to be placed on a branch of another plant known as the stock.
Grafting is an advanced technique that the botanists, the farmers, the gardeners, and the hobbyists use to add living tissue from one plant to another, The plant tissues have the ability to grow new vascular tissue and the process of grafting takes advantage of this ability.
The vascular tissue of the main plant joins with the vascular tissue of the added plant keeping the new tissue alive and growing, and this is a way for the plants to reproduce asexually.
In grafting, two plants are used to develop a new plant with combined traits from the two parent plants, In grafting, the scion is the above-ground part of one plant, The scion is attached to the stock which is the rooted part of the second plant.
Grafting has long been used to produce novel varieties of roses, the citrus species, and other plants, In grafting, Two plant species are used part of the stem of the desirable plant to be grafted onto a rooted plant called the stock.
The stock and the scion are cut at an oblique angle (any angle other than a right angle), Then they are placed in close contact with each other and they are held together, Matching up these two surfaces is extremely important because these will be holding the plant together.
The vascular systems of the two plants grow and fuse forming a graft, After a period of time, the scion starts producing the shoots, eventually bearing the flowers and the fruits.
There is grafting by attachment such as the mango trees, in which the scion is attached to the stock, and there is grafting by wedge such as in the large trees, in which the scion in the form of a wedge (pencil-shaped ) is inserted into a cleft in the stock.
The scion and the stock are tightly tied together, where the scion feeds on the juice of the stock, The produced fruits by grafting belong to the type of the scion, this kind of reproduction is used only between highly similar plant species such as the orange and naring (or bitter orange), and between the apples and the pears.
Advantages of grafting
Grafting helps to induce fruitfulness without the need for completing the juvenile phase, Juvenility is the natural state through which a seedling plant must pass before it can become reproductive, Grafting of mature scions onto the rootstocks can result in fruiting in as little as two years.
Grafting provide sturdiness to the plant grafting, It provides a strong, tall trunk for certain ornamental shrubs and trees, A graft is made at the desired height on a stock plant with a strong stem, It is used to raise standard roses which are the rose bushes on a high stem and it is also used for some ornamental trees such as certain weeping cherries.
Grafting induces dwarfing or cold tolerance or other characteristics to the scion, Most apple trees in modern orchards are grafted on to dwarf or semi-dwarf trees planted at high density, They provide more fruit per unit of land and higher quality fruit.
Grafting causes the disease and pest resistance, In the areas where the soil-borne pests or pathogens would prevent the successful planting of the desired cultivar, the use of pest/disease tolerant rootstocks allows the production from the cultivar that would be unsuccessful, A major example is the use of rootstocks in combating Phylloxera.
Grafting changes the cultivars, It is used to change the cultivar in a fruit orchard to a more profitable cultivar, It may be faster to graft a new cultivar onto existing limbs of established trees than to replant an entire orchard.
Grafting causes ease of propagation as the scion is difficult to propagate vegetatively by other means such as by cuttings, In this case, cuttings of an easily rooted plant are used to provide a rootstock, In some cases, the scion may be easily propagated but grafting may still be used because it is commercially the most cost-effective way of raising a particular type of plant.
Grafting is used to speed maturity of hybrids in the fruit tree breeding programs, Hybrid seedlings may take ten or more years to flower and fruit on their own roots, Grafting can reduce the time to flowering and shorten the breeding program.
Grafting maintains the consistency, The apples are notorious for their genetic variability, even differing in multiple characteristics such as the size, the color, and the flavor of fruits located on the same tree, The consistency is maintained by grafting a scion with desired fruit traits onto a hardy stock.
Grafting is used to repair the damage to the trunk of a tree that would prohibit the nutrient flow such as the stripping of the bark by the rodents that completely girdles the trunk, So, a bridge graft may be used to connect the tissues receiving flow from the roots to the tissues above the damage that have been severed from the flow.