Harmful effects of toxic chemicals in the environment
Toxic chemicals are substances that can be poisonous or cause health effects, They don’t break down easily in the environment, they can build up the tissues of small organisms, and they can move up through the food chain.
Toxic chemicals
Chemicals can be toxic because they can harm us when they enter or contact the body, and they can threaten human health, The motor vehicle emissions of nitrogen and sulphur oxides cause acid rain which poisons the fish and other aquatic organisms in the rivers and lakes.
Carbon dioxide gas causes the greenhouse effect and climate change, Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) cause the destruction of ozone in the stratosphere and they create the possibility of serious environmental damage from ultraviolet radiation.
Oil drilling and transport, mining, and maritime operations all result in the accidental introduction of toxic materials into the marine environment, the leakage from the storage tanks and the pipelines, and the seepage from the waste dumps.
Toxic materials or substances can poison people and other lives, they can cause illness and even death if swallowed or absorbed through the skin, where pesticides, weed killers, and many household cleaners are toxic, they occur as a result of a variety of human activities.
Industries and sewage treatment plants discharge wastes that contain toxic substances directly into the waterways, These direct pipeline discharges are called point sources.
Fuel combustion from means of transport and power plants contains numerous chemicals that drift in the atmosphere and rain down upon or absorb into the surface of the ocean and other bodies of water.
Toxic chemicals can be found in our soil, water, air, and bodies, This contamination has seriously affected the health of humans and wildlife everywhere.
Sources of radioactive contamination are the plutonium processing plants, nuclear power plants, nuclear submarines, and nuclear waste dumps, When they are incinerated and discharged, they can cause marine pollution.
Disinfecting products are flushed into the sewage systems and out through the treatment plant discharge, and they are washed from the houses and the septic tanks into the groundwater and streams.
Effects of some toxic chemicals
- Arsenic is a potent poison, Many water supplies close to mines are contaminated by it, Arsenic causes harm by disrupting metabolism at the cellular level, and Arsenic can cause fetal death and malformations in many mammal species.
- Cadmium can be toxic to freshwater organisms, shellfish can concentrate cadmium in levels that are harmful to people who eat them, zinc can kill young salmon as they swim out of their nest gravel, and it can kill many adult fish species.
- Many petrochemicals can poison fish, and kill their eggs and larvae, they are toxic to algae and invertebrates, and they can cause changes in the metabolism, reduced feeding, and poor shell formation, They can reduce the reproductive success of invertebrates.
- Petrochemicals can damage the skin, lungs, liver, and kidneys of birds and mammals as well as increase vulnerability to deadly infections by suppressing the immune system, they can damage plants, and they stop seed germination.
- Pesticide DDT builds up in the food chain and can last for decades in the environment, DDT is linked to the decline of the bald eagle, the peregrine falcon, and other birds because it makes their eggshells too thin, and decreases the survival of the chicks.
- Lead can impair brain development and learning in children and can affect behavior, high blood pressure, reproduction, and growth in both children and adults.
- Mercury is very toxic, It is mostly known as a neurotoxin which means that it harms the brain and nervous system, and it is linked to kidney and liver damage and possibly cancer.
What are chemical toxins in the environment?
Toxic chemicals in the environment can come from industrial activities, agriculture, household products, and natural sources. These chemicals can accumulate in air, water, soil, and living organisms, leading to harmful effects on human health and ecosystems.
Common Toxic Chemicals and Their Effects
1. Heavy Metals (Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Arsenic)
Sources: Industrial waste, mining, batteries, contaminated water.
Effects:
- Lead: Neurological damage, developmental disorders.
- Mercury: Brain and kidney damage, birth defects.
- Cadmium: Lung and kidney damage, cancer.
- Arsenic: Skin lesions, cancer, cardiovascular diseases.
2. Pesticides (DDT, Organophosphates, Glyphosate)
Sources: Agricultural runoff, insecticides, herbicides.
Effects:
- Nervous system disorders.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Increased cancer risk.
- Reproductive and developmental problems.
3. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
Sources: Electrical equipment, industrial waste, contaminated fish
Effects:
- Liver damage.
- Hormonal disruption.
- Cancer risk.
- Impaired immune system.
4. Dioxins and Furans
Sources: Waste incineration, industrial processes, burning plastics.
Effects:
- Skin disorders (chloracne).
- Cancer.
- Reproductive and immune system damage.
5. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Sources: Paints, solvents, fuel emissions, household cleaners
Effects:
6. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)
Sources: Non-stick cookware, water-resistant products, firefighting foam.
Effects:
7. Microplastics and Nanoplastics
Sources: Plastic waste, cosmetics, synthetic clothing.
Effects:
- Potential digestive and hormonal disruption.
- Bioaccumulation in the food chain.
- Cellular toxicity.
Environmental Impact
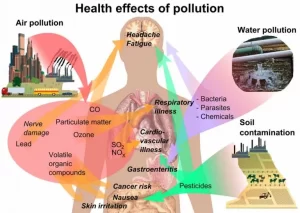
- Air Pollution: Chemicals like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) contribute to acid rain and respiratory diseases.
- Water Contamination: Industrial chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and pesticides contaminate drinking water and aquatic life.
- Soil Degradation: Heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants reduce soil fertility and affect food safety.
- Wildlife Toxicity: Biomagnification of toxic chemicals in the food chain harms top predators like birds and marine mammals.
Preventive Measures
- Reduce industrial emissions and adopt cleaner technologies.
- Use eco-friendly and biodegradable products.
- Enforce stricter regulations on chemical disposal.
- Promote awareness and sustainable practices.
The positive and negative effects of cars
What are the disadvantages of carbon dioxide?
What are the bad effects and health risks of smoking?
Positive and negative effects of chemical pesticides
Dangers and bad effects of burning plastics and rubber on humans and global warming
The erosion of the ozone layer and the protection from the ozone layer pollutants
Types, importance, negative effects of chemical reactions, Sulphur & Carbon oxides harms
Air pollution causes, types, effects, solutions & How to prevent air pollution




Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful post. Thank you for supplying this info.
You are welcome