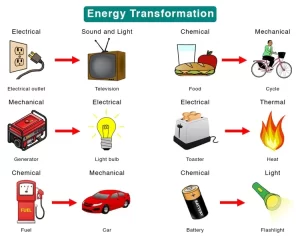
Forms of energy, their changes and 20 Energy transformation examples in daily life
If you look around you, you will notice that everything needs the energy to do its functions. You need food to obtain the energy that helps you to work, move, play, …..etc, Your car needs fuel to obtain the energy that causes the motion of its engines.
Do you know what is the meaning of energy?
The energy
Energy is the ability to do work. The chemical energy stored in food is broken down by our bodies and converted into thermal and kinetic energy to keep us warm and moving. Your phone uses electrical energy to power all its functions, from the screen (light energy) to the vibrations (kinetic energy).
Cars use the chemical energy in gasoline, which goes through a series of transformations. Burning the gasoline creates thermal energy, which in turn heats water and converts it to steam. This high-pressure steam spins a turbine, generating kinetic energy that ultimately moves the car (mechanical energy).
A light bulb uses electrical energy to create heat energy, which then produces light energy (with some bulbs being more efficient than others).
The forms of energy
-
There is potential energy stored in the spring of the toy car.
- There is kinetic energy produced by the electric fan and the washing machine.
-
There is light energy produced by the electric lamp or the Sun.
-
There is heat energy produced by the heater.
-
There is electric energy produced by the dry cell (battery) and the solar cells.
-
There is chemical energy stored in the battery.
-
There is sound energy produced by the piano and the radio.
Examples of some changes in the energy
The potential energy changes into kinetic energy as in the spring of the children’s toys.
The kinetic energy can change into sound energy as in the violin, the guitar, and when you knock on the door.
The kinetic energy changes into heat energy, When you rub your hands, when you hammer on a piece of iron, and when you remove a nail from a piece of wood.
The kinetic energy changes into electric energy as in the dynamo.
The electric energy changes into light energy as in the electric lamp, which lights, when the electric current passes through it.
The electric energy changes into kinetic energy as in the electric fan, the electric motor, and the washing machine.
The electric energy changes into the sound energy as in the recorder or the radio.
The light energy changes into heat energy as in the solar heater.
The light energy changes into electric energy as in the solar cells.
The chemical energy changes into electric energy as in the battery.
Energy transformation examples in everyday life
Appliance Power: When you turn on a toaster, electrical energy from the outlet flows through the wires and converts into thermal energy (heat) to brown your bread. A blender uses electrical energy to convert into kinetic energy to spin the blades, which chops up your ingredients.
Transportation: A car engine burns gasoline (chemical energy) which creates an explosion, The engine burns the fuel, releasing the chemical energy and converting that chemical energy into thermal energy. This thermal energy then expands gases which push on pistons, creating mechanical energy that moves the wheels (kinetic energy).
Electronics: A light bulb seems simple, but it involves a two-step transformation. Electrical energy is converted into heat energy, which then excites atoms in the filament, causing them to glow and produce light. This filament also emits light energy, illuminating your surroundings. Your smartphone uses electrical energy for various functions. Some of this energy is stored in the battery, while some is converted into light energy for the display or sound energy for the speakers.
Body in Motion: The food we eat contains chemical energy. Our bodies break down this chemical energy and convert it into thermal energy (to maintain body heat) and kinetic energy (to allow us to move). Our bodies use this energy to perform actions, converting it into kinetic energy for movement.
Bells and Whistles: Electronic devices like smartphones rely on electrical energy. This energy can be used for various functions, transforming into light for the screen, sound for the speakers, or heat for processing power.
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download the Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Energy resources and forms, Potential energy, Kinetic energy and Mechanical energy
Potential energy, Kinetic energy and Law of conservation of mechanical energy
Energy, Finding the Kinetic energy and Potential energy of an object