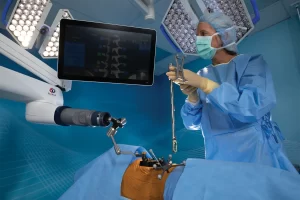
Robotic-assisted spine surgery importance, risks, and Is robotic spine surgery better?
Robotic surgery utilizes smaller incisions than traditional open surgery. This translates to less muscle disruption, blood loss, and post-operative pain for the patient. Smaller incisions generally mean a lower risk of surgical site infections.
Robotic-assisted spine surgery
Robotic-assisted spine surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses a robotic arm to assist the surgeon in performing the delicate tasks involved in spinal fusion surgery. The robot is controlled by the surgeon, who can use it to place screws and rods in the spine precisely. Due to the minimally invasive nature of the surgery, patients may experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times when compared to traditional open surgery.
Minimally invasive surgery provides treatment for many spinal injuries and disorders such as:
- Anterior cervical disc excision and fusionholy-family-spine.
- Artificial disc replacement.
- Hydrodiscectomy.
- Kyphoplasty.
- Laparoscopic anterior lumbar interbody fusion.
- Lumbar laminectomy.
- Microdiscectomy.
- Minimally invasive lumbar fusion.
- Posterior lumbar instrumented fusion.
Common procedures of robotic-assisted spine surgery
- Spinal Fusion: This is a procedure to permanently join two or more vertebrae together. It is used to treat a variety of conditions, such as spinal deformity, instability, and pain. For conditions like scoliosis or degenerative disc disease, surgeons can use robots for precise placement of hardware (screws and rods) to stabilize the spine and fuse vertebrae together.
- Disc Replacement: Robotic assistance can precisely place artificial discs to replace damaged ones in the spine.
- Spinal Decompression: In cases where spinal stenosis (narrowing) compresses nerves, robotic assistance can help surgeons remove bone or disc material to create more space for nerves.
- Vertebral Fracture Repair: Robots can help surgeons repair fractures in the spine with more accuracy and stability.
- Tumor Resection: Robotic arms can be used to assist in the removal of tumors in the spine.
- Revision Surgery: Reoperating on a previously fused spine can be complex. Robotic assistance can provide surgeons with better visualization and accuracy for placing hardware during these procedures.
It’s important to note that robotic-assisted spine surgery is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It is not always the best option for every patient, and there are still some potential risks involved.
Advantages of Robotic-Assisted Spine Surgery
Robotic arms provide steady movements and excellent visualization, leading to more accurate placement of implants (screws, rods) during spinal fusion surgery. This translates to potentially better outcomes and a reduced risk of complications like nerve damage or misplaced hardware.
Robotic surgery often uses smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. This can result in less blood loss, reduced tissue damage, less post-operative pain for the patient, and faster healing for the patient, leading to shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times. This can lead to a quicker return to daily activities.
Fluoroscopy (X-ray imaging) is used minimally during robotic surgery due to the 3D pre-operative planning and real-time guidance. This reduces radiation exposure for both the surgeon and the patient. Robotic systems provide surgeons with magnified 3D views of the surgical site, enhancing their ability to visualize critical structures and navigate the complex anatomy of the spine.
The robotic system allows surgeons to operate in a more comfortable position, reducing fatigue and potentially improving surgical precision over long procedures. Smaller incisions translate to a lower risk of infection following surgery, a significant benefit for any surgical procedure.
Disadvantages of Robotic-Assisted Spine Surgery
Robotic surgery currently has a higher cost associated with it compared to traditional open surgery due to the cost of the robotic system itself, the disposable surgical components used with the robot, and potentially longer OR time. This can translate to higher out-of-pocket expenses for patients.
Robotic spine surgery is not yet as widely available as traditional open surgery. It may not be accessible at all hospitals or surgical centers. There may be limitations depending on your location and healthcare provider. Surgeons need specialized training to operate the robotic systems.
Surgeons need specialized training to operate effectively with robotic systems. While the robot is a tool, the surgeon’s skill and experience remain crucial for a successful outcome. While experienced surgeons can leverage the benefits of the technology, it may not be suitable for all surgeons yet.
Robotic-assisted surgery may not be appropriate for all types of spine surgery, particularly very complex procedures or those requiring significant soft tissue manipulation. Not all spine surgeries require the enhanced precision of robotics. For simpler procedures, traditional surgery may be equally effective and more cost-effective.
For certain, straightforward spine surgeries, the benefits of robotic assistance may not outweigh the traditional open-surgery approach. Consulting with a qualified surgeon is crucial to determine if robotic surgery is the best option for your specific case.
Robotic spine surgery is a relatively new technology. The surgery relies on the proper functioning of the robotic system. While malfunctions are rare, any technical issues could prolong surgery or require conversion to a traditional open approach, potentially adding to OR time.
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download the application on Google Play from this link: Science Online Apps on Google Play
Use of robotics in minimally invasive spine surgery and benefits from robotic assistance
Robotic Surgery vs. Laparoscopic Surgery, Robot-assisted surgery features, benefits and drawbacks
Surgical robot types, advantages, disadvantages, How is robotic surgery different from traditional
Healthcare robotics, Nursing care robots review, types, advantages, disadvantages and uses
Robot-Assisted Heart Surgery types, benefits, risks, Robotic heart vs. open-heart surgery
Interventional radiology types, Robotic endovascular systems advantages and disadvantages