What is PET/CT, Positron emission tomography scan (PET) uses, risks and importance
The PET scan is an effective way to help identify cancer, heart disease, and brain disorders, Your doctor can use this information to help diagnose, monitor or treat your condition, PET scans are used in detecting cancer, Revealing whether your cancer has spread, checking whether a cancer treatment is working, and finding a cancer recurrence.
PET scans
Positron emission tomography scan (PET) can help reveal the metabolic or biochemical function of your tissues and organs, It uses a radioactive drug (tracer) to show both normal and abnormal metabolic activity, It can detect abnormal metabolism of the tracer in diseases before the disease shows up on other imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
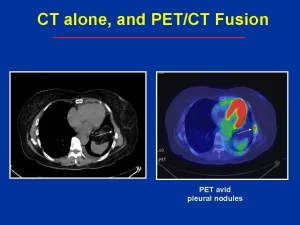
The tracer is most injected into a vein within your hand or arm, The tracer will collect into areas of your body that have higher levels of metabolic or biochemical activity, which pinpoints the location of the disease, The PET images can be combined with CT or MRI and are called PET-CT or PET-MRI scans. PET scans should be interpreted carefully because noncancerous conditions can look like cancer, and some cancers do not appear on PET scans.
Many types of solid tumors can be detected by PET-CT and PET-MRI scans, including Brain, Breast, Cervical, Colorectal, Esophageal, Head and neck, Lung, Lymphatic system, Pancreatic, Prostate, Skin, and Thyroid. PET/CT can offer information from a single imaging session about the cells, structures, and functioning of body tissues and organs, providing a more robust diagnosis than either scan can produce independently.
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is an imaging test that combines two different types of imaging scans during a single procedure with one machine, It combines two distinctive technologies to reveal important information about the form and function of cells and organs inside the body.
PET scan is a nuclear imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers that are ingested or injected and absorbed by body tissues, PET scans will show areas of greater absorption (where more chemical activity is occurring in the body), which may indicate disease, It can offer details about how well blood or oxygen travels throughout the body, how well sugar is processed, and more, It may reveal cancerous tissue not revealed by a CT scan.
CT scan utilizes X-rays taken from different angles and processed by a computer to create a 3D, cross-sectional image of the body, Computed tomography produces more accurate and precise images than X-rays, It can reveal the size, shape, and location of a tumor, as well as the blood vessels feeding it.
When you arrive for your PET scan, you may be asked to: Change into a hospital gown, and empty your bladder, A member of your healthcare team injects the radioactive drug (tracer) into a vein in your arm or hand, You may briefly feel a cold sensation moving up your arm, You can rest and remain silent in a reclining chair. After the test you can carry on with your day as usual, unless your doctor tells you otherwise, You’ll need to drink plenty of fluids to help flush the tracer from your body.
Advantages of Pet Scans
Pet Scans can study bodily functions through biochemical processes, the scans can detect diseases before the symptoms and signs show hence they are more effective compared to the other imaging tests, Since it studies the metabolic functions of the patient, PET imaging can be used as an alternative to biopsy and other exploratory surgeries conducted to determine how far a disease has spread.
Positron emission tomography scan can differentiate between non-cancerous and cancerous tumors, It is the most precise medical tool to help minimize the number of unnecessary surgeries done because of inaccurate staging data and diagnosis, It is effective for diagnosing early stages of certain neurological illnesses such as Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and other mental illnesses.
PET scans are the best options for those people scared of getting an infection from medical procedures, As compared to other forms of CT scans, Because nuclear medicine tests use only a small dose of the radiotracer, they have relatively low radiation exposure, Which is acceptable for diagnostic tests, so, the potential benefits of a test outweigh the very low radiation risk.
The PET scan can show how well certain parts of your body are working, rather than simply showing what they look like, PET scans are used for investigating confirmed cases of cancer to determine how far cancer has spread and how well it’s responding to treatment. PET scans are used to help plan operations, such as a coronary artery bypass graft or brain surgery for epilepsy, They can help diagnose some conditions that affect the normal workings of the brain, such as dementia.
Nuclear medicine tests offer unique information that is unattainable using other imaging procedures, This information includes details on the function and anatomy of body structures, Nuclear medicine scan is less expensive and may yield more precise information than exploratory surgery, By identifying changes in the body at the cellular level, PET imaging may detect the early onset of disease before it is evident on other imaging tests such as CT or MRI.
Advantages of PET/CT Scans
PET/CT Scans offer double the diagnostic clarity, The PET scan and CT scan show different things, but combined patients reap twice the diagnostic benefits. Alone, the PET scan will show areas of increased activity within the body – while the CT scan alone produces detailed images of tissues and organs inside the body, PET/CT scans can help differentiate between a cancerous and noncancerous mass in the body.
PET/CT Scan is a relatively painless procedure that measures both anatomy and metabolic function within the patient’s body as images are captured in a single scan, The actual scan only takes about half an hour to complete. PET/CT scan is nondisruptive and easy, Aside from the initial injection of the radioactive material, the test is noninvasive and requires no recovery or downtime afterward, Patients may immediately assume normal activities after a PET/CT scan.
PET/CT scan offers greater detail with a higher level of accuracy; because both scans are performed at the same time without the patient having to change positions, there is less room for error, It presents greater convenience for the patient who undergoes CT and PET at one time rather than two different times.
Disadvantages of PET/CT Scans
Pregnant women must not undergo PET/CT scans because the radioactive tracers used may be dangerous to the baby, although the amount of radiation received is negligible. You should not expose your unborn baby to radiation if you are pregnant, You should not expose your child to radiation if you are breastfeeding.
Diabetics may undergo the PET/CT scan, but with certain precautions, Because the radioactive material is combined with glucose and injected into the patient, this can be a concern for some diabetic patients, Before having the PET/CT scan, the diabetic patient’s blood sugar level will be evaluated, and the glucose serum blood test might be administered, This can increase the time required to complete the testing.
Although it is a new procedure, it is quite expensive compared to other forms of medical imaging, Pet Scans require a cyclotron which is an expensive machine used to create radioisotopes that are used to produce the radioactive rays required for imaging.
Allergic reactions to radiotracers are rare and mild, Always tell the nuclear medicine personnel about any allergies you may have. Describe any problems you may have had during previous nuclear medicine tests, The radiotracer injection may cause slight pain and redness. This should rapidly resolve.
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Common procedures of Interventional Radiology and the best Interventional Radiologists
Computed Tomography (CT) types, uses, advantages & disadvantages
Cone beam CT vs. Fan beam CT, CBCT advantages, disadvantages & uses
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses, advantages and disadvantages