Uterine fibroid embolization risks, importance and Minimally invasive procedure specialists
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a minimally invasive treatment used to stop serious pelvic bleeding, The cause of bleeding could be uterine fibroids (noncancerous tumors inside the uterus), trauma, malignant gynecological tumors, or hemorrhage following childbirth, among other conditions, The terms uterine artery embolization and uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) are mistakenly used to mean the same thing.
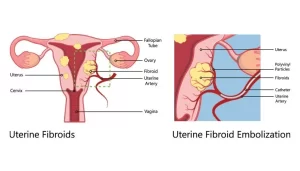
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE)
It is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat fibroid tumors of the uterus which can cause heavy menstrual bleeding, pain in the pelvic region, and pressure on the bladder or bowel, It uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to guide the delivery of embolic agents to the uterus and fibroids, These agents block the arteries that provide blood to the fibroids and cause them to shrink.
UFE is a procedure to shrink noncancerous tumors in the uterus called uterine fibroids, You do not need to stay in the hospital. Many types of particles are used for uterine fibroid embolization, These substances have safely been used by doctors for many years. The interventional radiologist doctor specializes in treating conditions without using major surgery, he uses small tools plus imaging tests, These tests may be X-rays, CT scans, MRI, fluoroscopy, or ultrasound.
Fibroid tumors are also known as myomas, they are benign tumors that arise from the muscular wall of the uterus, It is extremely rare for them to turn cancerous, UFE is a minimally-invasive alternative to hysterectomy or myomectomy, It is performed instead of a major surgery, this procedure requires minimal or no hospital stay and a shorter recovery.
During uterine fibroid embolization, The thin tube called the catheter is inserted through the blood vessel in the leg or wrist and guided by fluoroscopic (X-ray) images to the blood vessels that feed the fibroids of the uterus, Tiny particles are injected to stop blood flow to the fibroids, When blood flow to the fibroids is blocked, patients return home while the fibroids shrink gradually.
UFE is a very effective procedure with an approximate success rate of 85%, Most individuals who undergo the procedure have a dramatic improvement in their symptoms and a decrease in the size of their uterine fibroids, Fibroid embolization does not require surgery, decreasing hospital stay and recovery time.
Why might I need uterine artery embolization?
The interventional radiologist may recommend this procedure if you have low blood count (anemia) from uterine bleeding due to fibroids, when there is fullness or pain in your belly, An enlarged uterus, and infertility, When your belly that is larger than normal, Bladder pressure that makes you feel like you need to urinate often, Pressure on the bowel that causes constipation and bloating, When you feel pain during sexual intercourse, and pain in your back or legs, which may be caused by the fibroids pressing on nerves.
How does uterine artery embolization (UAE) work?
Blocking agents are introduced into particular blood vessels, These agents are guided to the uterine arteries through a tube (catheter) with the use of fluoroscopy, a form of X-ray that captures moving images, When blood vessels are blocked, bleeding can be brought under control, and tumors or fibroids can be made to shrink by cutting their blood supply, Surrounding healthy tissue is not affected because it continues to be fed by other unblocked vessels.
Advantages of uterine fibroid embolization
Uterine fibroid embolization is performed under local anesthesia, It is much less invasive than open or laparoscopic surgery to remove individual uterine fibroids (myomectomy) or the whole uterus (hysterectomy), Patients who undergo uterine fibroid embolization notice decreased bleeding, pelvic pain and pressure, and other symptoms of uterine fibroids, as well as an overall improvement in physical and emotional well-being.
Uterine fibroid embolization is a minimally invasive alternative treatment option to surgery, the patients will return to normal activities quickly, There is no surgical removal of the uterus and virtually no blood loss or bleeding afterwards, UFE reduces the need for hormone therapy that is sometimes used to treat fibroids.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) reduces the period of recovery, It needs only a tiny incision, making it less invasive than other treatments such as myomectomy (surgical removal of uterine fibroids) or hysterectomy (removal of the entire uterus), Nearly 90 percent of women treated with UAE for fibroids experience partial or full relief of symptoms.
Disadvantages of uterine fibroid embolization
Insertion of the catheter can damage other blood vessels, and an allergic reaction to X-ray contrast dyes could occur that can affect the woman’s breathing or blood pressure. In about 1% to 5% of women, menstrual cycles will shut down permanently following uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), Some women will go through menopause (amenorrhea) after the procedure, this usually occurs in women over the age of 45.
The embolic agent may lodge in the wrong blood vessel and deprive normal tissue of its oxygen supply, UFE may not be recommended if your fibroids are very large. There are possible complications of this procedure such as abnormal bleeding (hemorrhage), Injury to the uterus, Infection of the uterus or the puncture site in the groin, Collection of blood under the skin (hematoma) at the puncture site in the groin, Injury to the artery being used, Blood clots, and Infertility.
Some women have postembolization syndrome, Symptoms include pelvic pain and cramping, Nausea and vomiting, Low-grade fever, Fatigue, and discomfort. Medicine to help with nausea may also be used, The younger a woman is at the time of UFE, the greater the chances that symptoms could return, and a hysterectomy might eventually be needed.
What happens during uterine artery embolization?
You may have uterine fibroid embolization as an outpatient or may need to stay overnight in a hospital. The way the test is done may vary depending on your condition and your healthcare provider’s practices. You will remove any jewelry or other objects that may get in the way of the procedure, You will remove clothing, You will be given a gown to wear, and An IV line will be started in your arm or hand.
You may be given antibiotic medicine before the procedure, You will lie on your back on the procedure table, and the nurse will put a long thin tube (catheter) into your bladder to drain urine, Medical staff will watch your heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and blood oxygen level during the procedure.
The interventional radiologist will clean the groin area with an antiseptic solution, He will put a small tube into your groin area, This will be used as a guide to put the catheter in the area to be blocked off (embolized). The doctor will inject contrast dye into the catheter. The contrast dye will help the interventional radiologist find the artery to be blocked off.
The interventional radiologist will use X-rays to help find the blood vessels that supply blood to each fibroid, He will put a tiny catheter into the groin (femoral) artery, He will inject very small particles into the blood vessels, He will take more X-ray images to make sure the arteries are blocked, Some doctors will use one groin site to treat both the left and right uterine arteries if needed, Other doctors may use two groin sites, The sheath and catheter will be removed after the embolization is done.
What happens after uterine artery embolization?
In the hospital
Medical staff will put pressure on the insertion site in the groin to stop bleeding, This usually takes about 20 minutes, You will be taken to the recovery room, and the nurse will watch your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing, You will need to lie flat for a few hours, when your vital signs are stable, You may have cramping in your belly after the procedure, You may get pain medicine through a device connected to your IV line.
You will be encouraged to get out of bed within a few hours, You should do coughing and deep breathing exercises as your nurse tells you to, You will take liquids to drink a few hours after the procedure, and your diet may be changed to more solid foods as you can eat them.
At home
You should keep the groin incision clean and dry, Your healthcare provider will give you specific bathing instructions, If adhesive strips are used, they should be kept dry, They will fall off within a few days, You may have aching at the incision site and in your abdominal and pelvic muscles, This is true after you stand for long periods, you can take a pain reliever for soreness as recommended by your doctor.
You should take recommended medicines, Your doctor will recommend walking and limited movement, You will need to avoid strenuous activity. You should include fiber and plenty of fluids in your diet, Your doctor may recommend a mild laxative, You should not use a douche or tampons, or have sexual intercourse until your healthcare provider says you can do so, Also you should not go back to work until your healthcare provider says it is OK.
Additional Considerations
Who is a Candidate?: Women with symptomatic fibroids, such as heavy bleeding, pain, or pressure. Women who prefer a minimally invasive treatment or wish to avoid hysterectomy.
When UFE May Not Be Suitable: Women planning future pregnancies (discuss fertility implications with a specialist). Patients with certain uterine or pelvic conditions or very large fibroids.
Alternatives to UFE
- Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids.
- Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus.
- Hormonal therapy: Temporary symptom relief.
- MRI-guided focused ultrasound: Non-invasive fibroid ablation.
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Common procedures of Interventional Radiology and the best Interventional Radiologists
Interventional radiology types, Robotic endovascular systems advantages & disadvantages
Computed Tomography (CT) types, uses, advantages & disadvantages
Cone beam CT vs. Fan beam CT, CBCT advantages, disadvantages & uses
Artificial intelligence in radiology decision support systems, Medical Imaging & Healthcare
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses, advantages and disadvantages
Thyroid nodules, Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy importance & risks
Uterine fibroid embolization risks, importance & Minimally invasive procedure specialists