Refractory ascites symptoms, cause, types and treatment of refractory ascites in cirrhosis
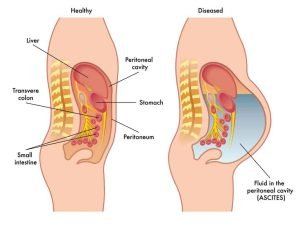
Refractory ascites (RA) do not recede or recur shortly after therapeutic paracentesis, despite sodium restriction and diuretic treatment. Every year, 5–10% of patients with liver cirrhosis and with an accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity develop RA while undergoing standard treatment.
Refractory ascites
The ascites that cannot be mobilized by medical therapy (sodium restriction and maximum or maximally-tolerated doses of diuretics) or the early recurrence of ascites (ie. after therapeutic paracentesis).
Types of refractory ascites
- Diuretic-resistant ascites: Lack of response to sodium restriction and maximal diuretic treatment or the early recurrence of ascites.
- Diuretic-intractable ascites: The development (hepatorenal of the diuretic-induced syndrome, hepatic complications encephalopathy, hyponatremia (serum Na concentration <120 mmol/L), and hypo-or hyperkalemia and severe muscle cramps) that precludes the use of an effective diuretic dosage.
Treatment of refractory ascites in cirrhosis
1. Serial LVB (large volume paracentesis)
- It is the common treatment option.
- Usually, total paracentesis is performed in selected patients to minimize the number of paracenteses.
- However, LVP is a symptomatic, non-causative treatment, that commonly requires hospitalization, neither prevents the recurrence of ascites nor influences survival, and worsens malnutrition.
2. Transjugular portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
- TIPS functions as a side-to-side portocaval anastomosis between the high-pressure portal vein side and low-pressure hepatic vein side.
- The decrease in portal hypertension results in a secondary decrease in the activation of RAAS leading to an increased sodium excretion. TIPS can be considered in patients with frequent requirements of LVP (> 3 months), or in those in whom paracentesis is ineffective.
Complications
- Shunt dysfunction.
- Increased risk for hepatic encephalopathy (30%).
- TIPS is contraindicated in severe liver failure, concomitant active infection, progressive renal failure, and severe cardiopulmonary disease.
Peritoneovenous shunt (PVS) (Denver shunt)
- PVS is an implantable device that carries the ascites into the systemic circulation through a surgically placed subcutaneous plastic cannula with a one-way pressure valve.
- PVS is considered for patients with refractory ascites who are not candidates for paracenteses, transplantation, or TIPS.
Complications
- Shunt occlusion.
- Peritonitis.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation.
- Bleeding.
4. ALFA pamp
- ALFA pump is a subcutaneously- implanted battery-operated, low-flow pump system that transports fluid from the peritoneal cavity to the bladder.
- ALFA pump offers an alternative option for patients who have refractory ascites in whom TIPS and transplantation are contraindicated.
- ALFA pump is safe and effective and improves the nutritional state of patients.
- Transient AKI (acute kidney injury) episodes are reversible with volume expansion.
5. Cell-Free and Concentrated Ascites Reinfusion Therapy (CART)
- CART comprises three processes: collection of ascites by paracentesis, removal of cell components from ascites by filtration, and concentration of ascitic fluid and reinfusion of fluid.
- CART has no effect on renal function, reduces albumin administration and stabilizes sodium concentration.
- Contraindication In the case of SBP.
6. Tunneled peritoneal drainage catheter
- Tunneled peritoneal drainage catheter is a one-way valve tunneled catheter covered with a polyester cuff connected to a vacuumed bottle.
- Patients are trained to manage these catheter systems at home using removing ascites on a daily schedule or whenever discomfort occurs.
Adverse events:
- Catheter-induced problems.
- bacterial peritonitis.
7. Systemic vasoconstrictors
Administration of vasoconstrictors (with albumin infusion) such as oral midodrine (al-adrenergic agonist) or intravenous terlipressin (vasopressin analog) may ameliorate the splanchnic arterial vasodilatation and thereby improve renal perfusion and filtration and sodium excretion.
8. Vaptans (aquaretics)
- Vaptans are specific vasopressin V2-receptor antagonists that induce release of Solute free water into the urine and correct’ dilutional hyponatremia (aquaretics).
- Vaptans may be helpful for refractory ascites patients, to reduce ascites volume and the need for paracentesis, without the generation of more adverse events by increasing the diuretic dose.
Adverse effects of vaptans
- Overcorrection of sodium.
- Dehydration.
- Renal injury and hepatic toxicity.
9. Liver Transplantation
- Represents the definitive treatment of refractory ascites.
- Refractory ascites are considered an exception to the MELD score in the allocation of priority patients with cirrhosis on the waiting list.
You can subscribe to Science Online on Youtube from this link: Science Online
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science Online Apps on Google Play
Ascites cause, grades, symptoms, diagnosis and Treatment of cirrhotic ascites
Cardio-Pulmonary problems in Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatopulmonary syndrome
Gastro-esophageal varices cause, treatment, and therapy of variceal bleeding
Liver Cirrhosis causes, symptoms, treatment & stages, Liver Biopsy and treatment of PHTN
Viral hepatitis, HDV symptoms, Treatment of acute HCV, Occult hepatitis C and HEV
Acute Hepatitis Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment, Chronic hepatitis and Liver biopsy
Liver development, congenital anomalies, function & Pancreas development