Hepatic Artery Embolization Importance and risks of Embolization therapy for Liver cancer
Embolization is the therapy to treat liver tumors by blocking their blood supply, Because liver tumours thrive on highly oxygenated blood from the hepatic artery, blocking that supply may kill it. Embolization may not be a good option for hepatitis or cirrhosis. People getting this type of treatment do not stay in the hospital overnight.
Embolization therapy for Liver cancer
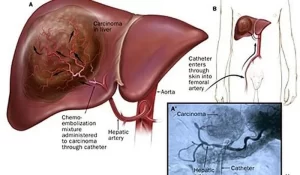
Tumour embolization is called transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), It is a procedure to shrink a liver tumour by cutting off its blood supply, The Interventional radiologist puts a thin, flexible tube, called the catheter, into an artery in your groin or in your arm, The catheter was guided into the liver artery (the hepatic artery) that supplies blood to the tumour.
The Interventional radiologist sent small particles (like grains of sand) through the catheter into the hepatic artery, This mixture blocks the artery and will stop blood from getting to the liver tumour, Procedures commonly done include chemoembolization and radioembolization.
Hepatic Artery Embolization
The liver has 2 blood supplies, Most normal liver cells are fed by the portal vein, whereas cancer in the liver is fed by the hepatic artery, Blocking the part of the hepatic artery that feeds the tumor helps kill off the cancer cells, but it leaves most of the healthy liver cells unharmed because they get their blood supply from the portal vein.
Embolization is the option for some patients with tumors that can’t be removed by surgery, It can be used for people with tumors that are too large to be treated with ablation (usually larger than 5 cm across) and who also have an adequate liver function.
Transarterial embolization (TAE)
The catheter (a thin, flexible tube) is put into the artery in the inner thigh through a small cut and eased up into the hepatic artery in the liver, The dye is injected into the bloodstream to help the doctor watch the path of the catheter, When the catheter is in place, small particles are injected into the artery to plug it up, blocking oxygen and key nutrients from the tumor.
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE)
Trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the first type of embolization used for large liver cancers that cannot be treated with surgery or ablation, It combines embolization with chemotherapy (chemo), and the Interventional radiologist gives chemotherapy through the catheter directly into the artery, and plugging up the artery, so the chemo can stay close to the tumor.
Drug-eluting bead chemoembolization (DEB-TACE)
Drug-eluting bead chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) combines TACE embolization with drug-eluting beads (tiny beads that contain a chemotherapy drug), The procedure is the same as TACE except that the artery is blocked after drug-eluting beads are injected, Because the chemo is close to cancer and because the drug-eluting beads slowly release the chemo, the cancer cells are more likely to be damaged and die. The most common chemo drugs used for TACE or DEB-TACE are mitomycin C, cisplatin, and doxorubicin.
Chemoembolization
Chemoembolization is known as Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE), It adds the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to the blockade of the tumor, It is used to treat primary liver cancer [hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)] and liver metastases through the local delivery of cytotoxic chemotherapy to the tumor and blocking of its blood supply.
Chemoembolization is a minimally invasive procedure performed by an interventional radiologist, First, cytotoxic chemotherapy is injected via a delivery catheter into the hepatic artery, the feeding blood supply for the tumor, This exposes the tumor to a much higher concentration of chemotherapy, Local delivery of chemo reduces the toxicity and side effects associated with chemotherapy such as hair loss and nausea.
Chemoembolization delivers chemotherapy drugs to tumors such as doxorubicin for liver cancer cells, or irinotecan for colon cancer that has metastasized or spread to the liver, Chemoembolization allows the chemotherapy drug to stay in contact with the tumor for up to several weeks, increasing the medication’s effectiveness, With chemoembolization, the concentration of the drug can be targeted to the tumor.
Radioembolization (RE)
Radioembolization (RE) combines embolization with radiation therapy, It is done by injecting small beads (called microspheres) that have a radioactive isotope (yttrium-90 or Y-90) attached to them into the hepatic artery, When infused, the beads lodge in the blood vessels near the tumor, where they give off small amounts of radiation to the tumor site for several days, The radiation travels a very short distance, so its effects are limited to the tumor.
Advantages of Chemoembolization
Embolization is the procedure that injects substances directly into the artery in the liver to block or reduce the blood flow to the tumor in the liver. The tumor is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, Because the drugs are injected directly into the tumor site, the dosage can be 20 to 200 times greater than standard systemic chemotherapy, and the artery is blocked, so, the blood does not wash through the tumor allowing the drugs to persist in the tumor for as long as a month.
Possible side effects of embolization
Possible complications after embolization include Abdominal pain, Fever, Nausea, Infection in the liver, and Blood clots in the main blood vessels of the liver.
How can you care for yourself at home?
You can go home the same day, Or you might need to stay in the hospital overnight or longer, The area where the catheter was put through your skin into your artery (the puncture site) may be sore for a day or two after the procedure, You will have a bruise for at least a week. You will have a dressing or bandage over the puncture site, The dressing helps the site heal and protects it.
You can rest when you feel tired, Getting enough sleep will help you recover. You should not do hard exercise and do not lift, pull, or push anything heavy (more than 4.5 kg or 10 lb.) until your doctor says it is okay, This may be for a day or 2, You can walk around the house and do light activity.
When the catheter was placed in your groin, try not to use stairs for the first couple of days. When the catheter was placed in your arm, be careful of activities that can keep the blood from flowing well in your arm, For 24 hours after the procedure, You should avoid repetitive arm or wrist movements, bending your arm, or having your blood pressure checked or an intravenous (IV) start on your arm.
You should avoid strenuous activities, such as bicycle riding, jogging, weight lifting, or aerobic exercise, for at least 2 days or until your doctor says it is okay. For 2 to 3 days, You should avoid lifting anything that would make you strain. You can eat your normal diet, When your stomach is upset, try bland, low-fat foods like plain rice, broiled chicken, toast, and yogurt, You should drink plenty of fluids (unless your doctor tells you not to).
Medicines
Your doctor will tell you if and when you can restart your medicines, Your doctor will also give you instructions about taking any new medicines, When you take aspirin or some other blood thinner, ask your doctor if and when to start taking it again, Be safe with medicines.
You should take pain medicines exactly as directed, If your doctor prescribed antibiotics, take them as directed, Do not stop taking them just because you feel better, You need to take the full course of antibiotics.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma) types, causes, symptoms and signs
Liver function, site, shape, lopes, Biliary system, Gall bladder & Biliary ducts
Robotic liver resection surgery review, advantages, disadvantages & treating liver cancer
Common procedures of Interventional Radiology and the best Interventional Radiologists
Interventional radiology types, Robotic endovascular systems advantages & disadvantages
Artificial intelligence in radiology decision support systems, Medical Imaging & Healthcare
Cone beam CT vs. Fan beam CT, CBCT advantages, disadvantages & uses
Thyroid nodules, Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy importance & risks
Uterine fibroid embolization risks, importance & Minimally invasive procedure specialists