Aging changes signs, Anti-Aging measures, and what are the common aging changes?
Aging brings about various changes in the body and mind, impacting physical, cognitive, and emotional aspects of life. These changes are a natural part of the aging process, though they can vary widely among individuals.
Aging changes in cells
- Cells become larger and are less able to divide.
- There is an increase in pigments inside the cell. A fatty brown pigment called lipofuscin collects in many tissues.
- Connective tissue becomes stiff, making organs, blood vessels, and airways more rigid. The exchange of gases, nutrients and wastes become difficult.
- Many tissues lose mass atrophy.
Body shape
- The human body is made up of fat, lean tissue (muscles and organs) bones, and water, as we age the amount and distribution of these materials will change.
- Fat is increasingly deposited toward the center of the body. The proportion of body fat increases by as much as 30%.
- Lean body mass decreases.
- Bones lose their minerals and become less dense.
- There is a reduction in total body water making old people more liable to dehydration.
Body Temperature
Body temperature in old people is lower by about 0.2-0.5 degree centigrade than adults; due to:
- Reduction in basal metabolic rate.
- Atrophy of skeletal muscles.
- Impairment of the circulation.
So a minimal rise of 0.5-1 degree has a grave significance in old age.
Water & electrolytes
- Total potassium is found to be reduced in old people, due to reduced lean body mass.
- Total body water declines, this may account for much of the weight loss seen in old. Thirst and thermoregulatory mechanisms are disturbed in the elderly. Encouraging old people to drink ample amounts of water is important to avoid dehydration.
- Total sodium increases with age, there is increased sensitivity to external sodium in diet.
- Total calcium decreases are related to decreased absorption and decreased vitamin D.
Skin
- Wrinkles of the skin, graying of hair. The outer layer thins. Large pigmented spots (age spots) of lentigos may appear. There is a reduction in skin strength and elasticity.
- Age spots or lentigos Appear old in the areas exposed to the sun. It can be prevented by avoiding exposure to the sun and using sunblock creams.
- Blood vessels of the dermis become more fragile, which results in easy bruising.
- Sebaceous glands produce less oil, making it harder to keep the skin moist, resulting in dryness and itching.
- The subcutaneous fat layer provides insulation, increasing the risk of injury and reducing the ability to maintain body temperature.
- Because there is less natural insulation, hypothermia can result when exposed to cold weather.
- The sweat glands produce less sweat. This makes it harder to keep cool, with an increasing risk of developing heat stroke when exposed to hot weather.
- The skin changes, thin subcutaneous fat, as well as nutritional deficiencies, contribute to pressure ulcers.
Musculoskeletal system
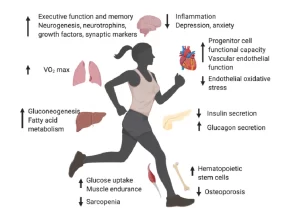
- There is a decrease in muscle cross-section area and the volume of contractile tissue resulting in decrease force production. There is evidence that exercise can have an impact on the size, strength, and aerobic capacity of skeletal muscle in old people.
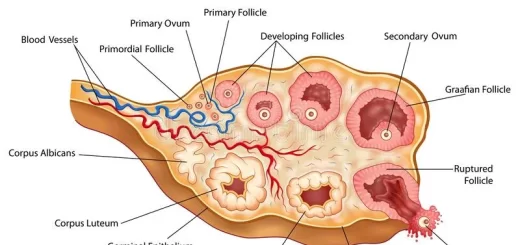
- Bone mass decreases as people age, especially in females after menopause. The trunk becomes shorter as disks lose fluid & become thinner
- Joints become stiffer & less flexible.
- Exercise is one of the best ways to slow changes in the musculoskeletal system.
Respiratory system
- There is a reduction and damage to the elastic tissue of the lungs. Alveoli become dilated and thin-walled.
- Decrease in ciliary transport system leading to decrease in mucous and foreign materials clearance.
- Decrease gag reflex leading to increased aspiration.
Digestive system
- Inadequate mastication, the absence of teeth, will allow large particles of food to reach the intestine, resulting in incomplete digestion, consequently, absorption is impaired, greater amount of food will reach the caecum giving rise to colonic disturbance.
- Salivary secretions: small in volume and enzyme content.
- Esophagus: high incidence of diaphragmatic hernia due to atrophy of connective tissue support. Patulous cardia leads to regurgitation of acid contents into the lower esophagus and heart burn.
- Stomach: basal secretion is reduced in volume and Hcl.
- The small intestine shows impaired absorption due to a reduction in enzymatic activity, a reduction in the number of absorptive cells, and a reduction in blood supply.
- Colon: There is a high incidence of constipation among the old, due to reduced intake of food and fluids, defective mastication, and due to irregular bowel habits. There is a high incidence of diverticulosis due to atrophy and decreased tone of musculature and diminished elasticity of the connective tissue layer of the wall of the colon.
Senescent Liver
- Liver. There is a decrease in the size and weight of the liver in aging, there is about a 50% reduction in liver blood flow.
- Functional derangements are slight: Serum bilirubin and prothrombin activity are within normal value. Serum transaminases are within normal indicating good cellular integrity. Serum albumin may be reduced in the elderly who have decreased mobility or who suffer from malnutrition.
- When prescribing drugs that are metabolized in the liver, we should decrease the dose in the elderly to avoid toxicity.
- Cholesterol saturation of bile increases with age due to enhanced hepatic secretion of cholesterol and decreased bile acid synthesis, this explains the increased incidence of cholesterol gallstones.
- Hepatic glucose output is found to be low in senescent liver due to a decrease in hepatic blood flow and decrease glycogen content.
- Hepatic urea output is reduced after a protein meal due to reduced liver cell mass in the elderly.
The Pancreas
There is a reduction in volume & enzyme activities due to decreased blood supply and increased incidence of chronic fibrosing pancreatitis.
Immune system
- There is a decrease in number of circulating lymphocytes.
- T cell response decrease in the elderly which leads to increase susceptibility to infection & malignancy.
- There is increase production of autoantibodies.
- We can preserve our immune system by good nutrition and increase protein intake and some trace elements like selenium and zinc and vit A, B,C,D.
Changes in the nervous system
- The intellectual functions are reduced. The speed of learning decreases, there is a gradual loss of memory specially for recent events.
- Posholoysal disturbances and emotional instability occur.
- Motor system reduction in muscle power, superficial reflexes may be absent. Deep reflexes may be absent in 50-70% of normal old. Senile tremors are present in 15-20% of old.
- Sensory system: decrease vibration sense & hypoesthesia.
- Special sanses: redaction in visual acuity, narrowing of the visual field, decrease in lacrymal secretions, decrease in lysozymes, decrease in blink reflex.
- There is reduction of hearing, smell and taste sensations making food less appealing, decrease appetite and weight loss. Sweet & salty tastes are lost first. followed by bitter & sour.
- Some brain exercises may promote the speed of learning and some components of the diet to improve memory like omega 3 which we get from fatty fish, nuts, and almonds.
- Sensory system function decrease due to decrease vitamins like B1, B6, and B12.
- To correct the dryness of the eye we use eye drops.
- To preserve the train you should use it and perform brain exercises and take a healthy diet.
Urinary system
- There is progressive sclerosis of the glomeruli with aging.
- There are atheromatous changes in renal vessels, leading to a reduction in GFR. Which is reduced by about 10mL/min/per decade after 40 years of age.
- Urinary tract infections are common in the elderly due to impaired bladder emptying.
- Serum creatinine should not be used as a test for renal function in old because there is a decrease in muscle mass which is the source of serum creatinine. If serum creatinine is normal we should assume that there is 40% reduction in renal function.
Endocrine System
- Decreased hormone secretion.
- Decreased efficacy of hormones on target tissues.
Anti-Aging measures
- Maintain ideal body weight.
- Eat breakfast every day.
- Avoid eating excess fat & sugary foods.
- Get regular exercise.
- Avoid stress
- Get seven to eight hours sleep/day.
- Avoid bad habits like smoking.
- Regular check-up for early detection of diseases.
Good Nutrition
- To maintain proper health, certain rules must be respected:
- Adequate water intake to maintain a healthy state of tissues, proper kidney function, digestive secretions & avoid constipation
- The type of food should be nourishing, containing mineral salts, trace elements, and vitamins.
- Total caloric intake better to be reduced to avoid obesity
- Fat: animal fat should be replaced by vegetable oil.
- Protein: protein intake is important to raise immune function, and should be reduced if there is impairment in kidney & liver functions.
- Fiber: increase intake of fiber, better from natural sources.
- Salt intake should be reduced
- Calcium intake should be increased together with vitamin D to help its absorption
- All items of nutrition should be supplied (increase fiber diet, fluid intake, omega 3, B complex, and vitamins with antioxidant activity) to preserve our memory.
You can follow science online on YouTube from this link: Science online
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Cephalosporins antibiotics types, examples, Carbapenems, Monobactams, and Glycopeptides
Antibacterial drugs definition, use and types, Penicillin classification and importance
Antimicrobial drug types, use, side effects, resistance and Empiric antimicrobial therapy
Vaccine types, Live vaccines, Inactivated vaccines, Subunit vaccines, Naked DNA, and mRNA vaccines