Artificial lift pump systems types, uses, advantages & disadvantages
The artificial lift system includes pumping systems and gas lift, It is a process used on oil wells to increase the pressure within the reservoir and encourage oil to the surface, If the natural drive energy of the reservoir is not strong enough to push the oil to the surface, The artificial lift is employed to recover more production, Although some wells contain enough pressure for oil to rise to the surface without stimulation, most don’t, requiring artificial lift.
Artificial lift pump systems
Artificial lift system refers to the use of artificial means to increase the flow of liquids, such as crude oil or water, from the production well, Artificial lift system can use a mechanical device inside the well that is known as pump or velocity string, It can decrease the weight of the hydrostatic column by injecting gas into the liquid some distance down the well.
It is needed in wells when there is insufficient pressure in the reservoir to lift the produced fluids to the surface, but it is used in naturally flowing wells to increase the flow rate above what would flow naturally, The produced fluid can be oil, water or a mix of oil and water, It is typically mixed with some amount of gas.
Methods of Artificial Lift
The most popular type of artificial lift pump system applied is beam pumping, which engages equipment on and below the surface to increase pressure and push oil to the surface, beam pumps are familiar jack pumps seen on onshore oil wells, Hydraulic pumping equipment applies a downhole hydraulic pump, rather than sucker rods, which lift oil to the surface.
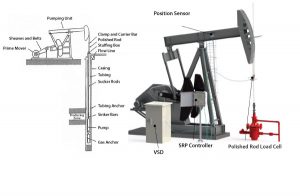
Rod Pumping
Rod Pumping has a relatively simple system design, The units are easily changed to other wells with minimum cost, It is efficient, simple, and easy for field people to operate, It is applicable to slim holes and multiple completions, It can pump a well down to very low pressure (depth and rate dependent), The system is naturally vented for gas separation and fluid level soundings.
Rod Pumping can lift high-temperature and viscous oils, It is analyzable, It can use gas or electricity as a power source, Corrosion and scale treatments are easy to perform, Hollow sucker rods are available for slim hole completions and ease of inhibitor treatment, Rod Pumping is applicable to pump-off control if electrified, It offers the availability of different sizes, It has pumps with double valving that pump on both upstroke and downstroke.
Rod Pumping disadvantages
Rod Pumping is depth limited, because of rod capability, It is obtrusive in urban locations, Crooked holes present a friction problem, It is heavy and bulky in offshore operations, It has limitations of downhole pump design in small diameter casing, It is susceptible to paraffin problems, H2S limits depth at which a large volume pump can be set, High solids production is troublesome, Gassy wells usually lower volumetric efficiency, and Tubing can’t be internally coated for corrosion.
Hydraulic piston pumping
Hydraulic piston pumping can lift from as deep as 18,000 feet (5486 m), It can produce 500 B/D (79.49 m3/d) from 15,000 feet (4572 m), Crooked holes present minimal problems depending on the model of the pump being used, Power source can be remotely located, and the installations can be analyzed.
Hydraulic piston pumping is unobtrusive in urban locations, It is flexible, It can match output to the delivery of well, It can use diesel, natural gas or electricity as power source, Downhole pumps can be installed /retrieved using the power fluid, Inhibitors can be mixed with the power fluid for the purposes of controlling corrosion, scale, emulsions, etc.
Hydraulic piston pumping can be used in a well that has low formation pressures (pumped off), It can be used on offshore platforms, It can use any liquid for power fluid, The liquid being produced from the well is used (water or oil), It is easy to pump in cycles depending on the model of the pump being used, Power fluid can be heated to reduce viscosity of produced fluid, Additional liquids can be mixed with the power fluid (such as diesel) for this purpose also.
Hydraulic piston pumping disadvantages
Hydraulic piston pumping can install a vented system, so, gas can by-pass pump but such systems are more expensive, It can maintain an oil inventory required for power oil system, and can’t be sold, Power oil systems are possible fire issue, Production end has the same problems with sand as does a rod pump, Qualified personnel are needed for troubleshooting in the field, as with other A/L systems, Surfactant is needed for lubrication of engine end when using water for power fluid, Any leaks when using power oil pose an environmental issue, The issues of a leak when using a power water system are much less.
Electric submersible pumping
Electric submersible pumping can lift a wide range of volumes from low volumes 750 B/D, to extremely high volumes, 20,000 B/D (19 078 m3/d) in shallow wells with large casing, Currently lifting ± 120,000 B/D (19 068 m3/d) from water supply wells in Middle East with 600 hp (448 kW) units, 720 hp (537 kW) available, 1,000 hp (746 kW) under development.
Electric submersible pumping is unobtrusive in urban locations, It is simple to operate, It is easy to install downhole pressure sensor for telemetering pressure to surface by cable, It is applicable in offshore, It is available in different sizes, Crooked holes have no problem, Corrosion & scale treatment is easy to perform, and lifting cost for high volumes is very low.
Electric submersible pumping disadvantages
Electric submersible pumping is not applicable to multiple completions, It is only applicable to electric power, It is impractical in shallow, low volume wells, It is expensive to change equipment to match declining well capability, High voltages (1,000 V) are necessary, Cables cause problems in handling tubulars, and cables deteriorate in high temperatures.
Electric submersible pumping has lack of production rate flexibility, it has casing size limitation, It comes with more downtime when problems are encountered because of the entire unit being downhole, System is depth limited, 10,000 ft (3048.0 m), because of cable cost and inability to install enough power downhole (depends on casing size).
Electric submersible pumping is not easily analyzable unless good engineering know-how, It can’t be set below fluid entry without a shroud to route fluid by the motor, Shroud also allows corrosion inhibitor to protect outside of motor, The production of gas and solids is troublesome.
Gas Lift
Gas Lift can handle large volume of solids with minor problems, It handles large volume in high-PI wells (continuous lift), 50,000 B/D (7949.37 m /d), It is fairly flexible-convertible from continuous to intermittent to chamber or plunger lift as well declines, It is unobtrusive in urban locations and power source can be remotely located, It is applicable to offshore, It is easy to obtain downhole pressures and gradients, It is serviceable with wireline unit, Crooked holes have no problem, and corrosion is not usually as adverse.
Gas Lift disadvantages
Gas Lift requires makeup gas in rotative systems, It has problems with dirty surface lines, It is not efficient in lifting small fields or one-well leases, It is difficult to lift emulsions and viscous crudes, It comes with some difficulty in analyzing without engineering supervision, It has a safety problem with high-pressure gas, It is not always available, Casing must withstand lift pressure, It comes with gas freezing and hydrate problems.
Hydraulic jet pump
Hydraulic jet pump can lift from as deep as 20,000 feet (5486 m), It can produce 25,000 B/D (3975 m3/d) from 5,000 feet (1520 m), It is unobtrusive in urban locations, Crooked holes present no problems, The power source can be remotely located, The installations can be analyzed, Downhole pumps can be installed /retrieved using the power fluid.
Hydraulic jet pump is flexible, It can match output to the delivery of well, It can use diesel, natural gas or electricity as a power source, It can use any liquid for power fluid, The liquid being produced from the well is used (water or oil) and it is easy to pump in cycles by qualified personnel, No record of plugging due to producing sand.
Hydraulic jet can be used on offshore platforms, Power fluid can be heated to reduce viscosity of produced fluid, Additional liquids can be mixed with the power fluid (such as diesel) for this purpose also, Inhibitors can be mixed with the power fluid for the purposes of controlling corrosion, scale, emulsions from reservoir, etc, and there is no record that a jet pump has ever created an emulsion.
Hydraulic jet pump disadvantages
Hydraulic jet pump uses momentum transfer as method for operation, and it is a very inefficient form of energy transfer, It requires approximately 10% submergence to prevent cavitation damage at low production rates, The total system has an efficiency of 10-30%, Pump will cavitate if more production than planned is forced through the pump, As with other A/L systems, the less the back pressure the better.
Hydraulic jet pump produces more free gas for a given nozzle/throat combination, So, it will reduce the amount of produced liquids and may cause cavitation damage, Pump must be retrieved and a larger throat installed, Power oil systems are a possible fire issue, and high surface power fluid lines are required.
Hydraulic jet pump can install a vented system so, gas can by-pass pump but such systems are more expensive, Any leaks when using power oil pose an environmental issue, The issues of a leak when using a power water system are much less, Maintaining an oil inventory required for power oil system, and can’t be sold, Qualified personnel are needed for troubleshooting in the field, as with other A/L systems.
Plunger Lift
Plunger lift automatically keeps tubing clean of paraffin and scale, It is retrievable without pulling tubing, It has very inexpensive installation, It is applicable for high GOR wells, It can be used with intermittent gas lift, and it can be used to unload liquid from gas wells.
Plunger Lift disadvantages
Plunger lift requires another lift method, It requires more engineering supervision to adjust properly, It is good for low-rate, normally less than 200 B/D (31.8 m/d) wells only, Danger exists in plunger reaching too high velocity and causing surface damage, Communication between tubing and casing is required for good operation unless used in conjunction with gas lift.
Progressive cavity pumps
Progressive cavity pumps can use downhole electric motors that handle sand and viscous fluid well, It comes with a moderate cost, It offers a low profile, It has high electrical efficiency, and some types are retrievable with rods.
Progressive cavity pumps disadvantages
Progressive cavity pumps lose efficiency with depth, Rod wind up and after the spin of rods increase with depth, Elastomers in stator swell due to some fluids in the well, Pump-off control is difficult, Rotating rods wear tubing, Sand and solids quickly wear off the rotor.
Continuous belt transportation
Continuous Belt Transportation (CBT) can use an oil absorbing belt to extract from marginal and idle wells, It can use downhole electric motors that handle sand and viscous fluid well, It is unobtrusive in urban locations, It offers a very low cost of operation, It has a low cost of installation, Oleophilic belt collects only heavy oil, It offers optimal application for high GOR, high viscosity, high sand and paraffin wells, It increases production of stripper, marginal, and orphaned wells, It offers minimal water reclamation, It has lower environmental impact, no disposal of radioactive rods or hazardous fluids.
Continuous belt transportation disadvantages
Continuous belt transportation is limited to 500B/D (79.2 m3/d) from 12123 feet (4000 m), It is not suitable for high volume production wells, It can’t be used on offshore platforms, It is optimal only for medium, heavy and very heavy oil, It is limited to wells deviated less than 5 deg, depending on well bore configuration.
Bulk diesel and fuel oil transfer pumps uses, features, types, advantages & disadvantages




Thank you for mentioning that sucker rods are used to lift oil to the surface. I would imagine that it would be important to make sure the proper protection is installed over a sucker rod so that it isn’t damaged during the pumping process. It seems like it would be easier to replace the protection rather than having to replace the entire rod itself.
You are welcome