Ultrasound therapy (US) features, types, advantages and disadvantages
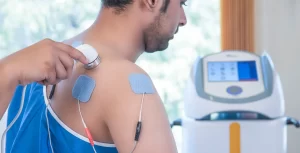
Ultrasound therapy is the most commonly used modality in physical therapy today, It is a form of physical therapy that uses high-frequency sound waves to transfer heat into specific injured areas of your body, It is a non-invasive way of administering medications to tissues below the skin, It is perfect for patients who are uncomfortable with injections and it can cause an increase in healing rates.
Ultrasound therapy (US)
Ultrasound therapy is a treatment method that uses sound waves to promote healing, reduce pain, and improve tissue mobility. It is used in physical therapy and rehabilitation settings. It helps improve flexibility in stiff joints and muscles. It can be adjusted for different conditions, such as chronic pain, acute injuries, or deep tissue issues.
Ultrasound therapy is used worldwide by physical therapists and occupational therapists to treat a variety of painful conditions such as tendonitis, arthritis, fibromyalgia, and musculoskeletal injuries, Ultrasound machines generate sound waves that are higher than the frequency we can hear, Cortisone is one of the most commonly used substances delivered in this way and it is used to reduce inflammation.
Ultrasound therapy uses the head of the ultrasound probe that is placed in direct contact with your skin via a transmission coupling gel, ultrasonic energy forces the medication through the skin, Ultrasound therapy can help stimulate the healing process by increasing blood flow and decreasing pain and inflammation.
The mechanical vibration at increasing frequencies is known as ultrasound, The frequencies used in therapy are between 1.0 and 3.0 MHz (1 MHz = 1 million cycles per second), Ultrasound therapy is a form of mechanical energy, it is not electrical, so, it is not electrotherapy at all, but does fall into the Electro Physical Agents grouping.
As the penetration (or transmission) of US is not the same in each tissue type, some tissues are capable of greater absorption of US than others, the tissues with a higher protein content and a lower water content will absorb US to a greater extent, The intensity or power density of the ultrasound can be adjusted depending on the desired effect.
Ultrasound therapy takes from 3-5 minutes, In cases where scar tissue breakdown is the goal, this treatment time can be much longer, The US beam is not uniform and changes in its nature with distance from the transducer, The US beam nearest the treatment head is called the NEAR field, the INTERFERENCE field or the Frenzel zone, The behaviour of the US in this field is far from regular.
With areas of significant interference, The US energy in parts of this field can be many times greater than the output set on the machine (possibly as much as 12 to 15 times greater), The size (length) of the near field can be calculated using r²/l where r= the radius of the transducer crystal and l = the US wavelength according to the frequency being used (0.5mm for 3MHz and 1.5mm for 1.0 MHz).
Ultrasound therapy advantages
Ultrasound therapy can be used to help reduce local swelling, chronic inflammation, and promote bone fracture healing, It is safe and commonly used to treat various conditions, It is used to examine and treat soft tissue injuries such as tendonitis, non-acute joint swelling and muscle spasm, Most muscle and ligament injuries can benefit from therapeutic ultrasound.
Ultrasound therapy can be absorbed into bones to accelerate fracture healing time, It is non-invasive, it is relatively inexpensive, it used for a quick procedure, fetus problems can be detected, Sound waves are used above the range of human hearing to treat injuries such as muscle strains or runner’s knee, Ultrasound therapy is used by physical therapists, It is used in healing dense collagenous tissues, it will require relatively high intensity, preferably in continuous mode to achieve this effect.
Ultrasound therapy is used to treat pain conditions and to promote tissue healing, Although ultrasound therapy is not effective for all chronic pain conditions, it can help reduce your pain if you have Osteoarthritis, Myofascial pain, Bursitis, Pain caused by scar tissue, Phantom limb pain, Sprains and strains.
Therapeutic ultrasound is used for treating chronic pain and promoting tissue healing, It may be recommended if you experience any of the following conditions: carpal tunnel syndrome, shoulder pain, including frozen shoulder, tendonitis, ligament injuries and joint tightness.
Therapeutic ultrasound offers deep heating to soft tissue to increase blood circulation to those tissues, This could promote healing and decrease pain, Therapeutic ultrasound can improve the flexibility of muscles to restore a full range of motion, and ultrasound energy can cause rapid contraction and expansion of microscopic gas bubbles (cavitation) around injured tissue, This, theoretically, speeds healing.
Ultrasound Therapy helps reduce pain by increasing blood flow and promoting tissue relaxation. It stimulates cell activity, enhancing tissue repair and regeneration. It decreases swelling and promotes the removal of inflammatory waste products. It improves Blood Circulation, It increases local blood flow, which aids in tissue healing.
Ultrasound Therapy is non-invasive, It is a safe and painless alternative to surgery or medication for pain management. It helps soften and break down adhesions and scar tissue in muscles and joints.
Types of Ultrasound Therapy
Types of ultrasound therapy are thermal and mechanical, they use sound waves generated by a transducer head (which looks a bit like a microphone) to penetrate soft tissues, The difference between the two types is the rate at which the sound waves penetrate the tissues.
Your therapist will use thermal ultrasound therapy, If you have myofascial pain, or have a muscle strain or sprain that has not healed, you will use mechanical ultrasound therapy, If your pain is caused by scar tissue or swelling, such as with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Thermal ultrasound therapy
Thermal ultrasound therapy uses a more continuous transmission of sound waves, It causes microscopic vibrations in the deep tissue molecules, it can increase heat and friction, The warming effect will encourage healing in the soft tissues by increasing the metabolism at the level of the tissue cells.
Mechanical ultrasound therapy
Mechanical ultrasound therapy has still a minor warming effect on the tissues, It can use pulses of sound waves to penetrate tissues, it can cause expansion & contraction in the tiny gas bubbles of the soft tissues, it helps decrease the inflammatory response, it can reduce tissue swelling & decrease pain.
Therapeutic Ultrasound: Contraindications and Precautions
Ultrasound therapy should not be used over the abdomen, pelvic regions or lower back in women who are menstruating or pregnant, over lesions, broken skin or healing fractures, over the breasts or sexual organs, over any areas with plastic implants, over or near areas with malignant tumors (history of malignancy is not a contraindication, You should not treat over tissue that is, or considered to be malignant), over areas with impaired sensations or blood flow.
You should not expose either the embryo or fetus to therapeutic levels of ultrasound by treating over the uterus during pregnancy, Tissues in which bleeding is occurring or could reasonably be expected (usually within 4-6 hours of injury but may be longer in some instances and for some patients).
You should not use ultrasound therapy over vascular abnormalities including deep vein thrombosis, emboli, and severe arteriosclerosis/atherosclerosis, You should not use ultrasound therapy over the eye, The stellate ganglion, The cardiac area in advanced heart disease & where pacemakers in situ, The gonads, Active epiphyses in children.
You should always use the lowest intensity which produces a therapeutic response, You should ensure that the applicator is moved throughout the treatment (speed and direction are not an issue), You have to ensure that the patient is aware of the nature of the treatment and its expected outcome.
Sound waves from ultrasound therapy must not come into contact with highly sensitive organs such as heart, kidneys, liver, lungs, stomach, spleen, bowels, eyes, ears, ovaries, testicles, brain and spinal cord, Sound waves must not come in contact over mucous membrane areas of the body, that include the mouth, nose, rectum & vagina.
Ultrasound therapy should not be used over any active growth plates (epiphyseal regions) in children as well as over areas of the body that have a metal implant embedded (e.g. pacemaker), Ultrasound therapy must not be used on patients who have certain diseases such as hemophilia (bleeding disorder), spina bifida, tissues or bones that have active infection (e.g. opens sores), cancerous or pre-cancerous cells, de-sensitized areas of the skin (diabetic neuropathy), untreated osteomyelitis (bone infection), deep vein thrombosis & cardiac disease.
The operator of the ultrasound device should check the calibration of the device at least once a week to make sure that the ultrasonic power and built-in timer are accurate, monthly maintenance and testing of the applicator (head of the transducer) should be done to see if it is providing a uniform and equal amount of power.
Disadvantages of Ultrasound therapy
Ultrasound therapy does not have as much detail as X-rays, it can’t be used in areas that contain gas (such as lungs), it doesn’t pass through bones, it can be wrong in detecting physical abnormalities, and it can affect the fetus brain development in mice, so could in humans.
While therapeutic ultrasound is considered generally safe in treating certain conditions, therapeutic ultrasound is not recommended over open wounds, with women who are pregnant, and near a pacemaker, Therapeutic ultrasound causes rapid pressure changes during cavitation that could cause a “microplosion” and damage cellular activity, This is unlikely to occur in most uses of the treatment.
Ultrasound Therapy is not suitable for people with pacemakers, metal implants, infections, or pregnancy (on the abdomen). It is not effective for all pain types, It may not work well for certain chronic pain conditions or deeply embedded injuries. The effectiveness of ultrasound therapy for certain conditions remains debated.
Ultrasound Therapy is not a standalone treatment, It works best when combined with other therapies like exercise or manual therapy. Improper use such as keeping the ultrasound head stationary can cause burns or tissue damage.
Ultrasound Therapy provides symptom relief rather than a permanent cure, requiring multiple sessions. It can be expensive and may not always be covered by insurance. It must be applied correctly by a trained professional for optimal results.
Heat therapy (Thermotherapy) and What are the clinical uses of heat?
X-ray properties, use and method of obtaining X-rays by using Coolidge tube
Sound intensity, Factors affecting Sound intensity and Applications of ultrasonic waves
Audible sounds, Doppler’s effect, Savart’s wheel importance, Sound properties & velocity