Periodic motion, Concept and examples of oscillatory motion
Periodic motion is a motion that is regularly repeated in equal periods, The oscillatory motion and the wave motion are examples of the periodic motion. Oscillatory motion is commonly observed in nature, physics, and engineering.
Oscillatory motion
The oscillatory motion is the motion of the oscillating body around its rest point, where the motion is repeated through equal intervals of time.
Oscillatory motion refers to the repetitive back-and-forth movement of an object about a central equilibrium position. It is commonly seen in systems where restoring forces act to return the object to its equilibrium state.
Examples of oscillatory motion
- The clock, The tuning fork, The spring, The stretched string, The motion of the swing, The rotary bee.
- The movement of the Earth’s crust during earthquakes.
- The movement of the atoms in the molecules.
- Simple pendulum.
- Electromagnetic waves (oscillating electric and magnetic fields).
Types of Oscillatory Motion
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) is a special type of oscillatory motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to displacement and acts in the opposite direction. Example: A mass on a spring, a simple pendulum (for small angles).
- Damped Oscillations: The amplitude of oscillations gradually decreases over time due to energy loss (e.g., friction or air resistance). Example: A pendulum swinging in the air.
- Forced Oscillations: External periodic force drives the system, sustaining the motion. Example: A child being pushed on a swing.
- Resonance: When the frequency of an external force matches the natural frequency of a system, leading to large amplitude oscillations. Example: A bridge vibrating due to wind (Tacoma Narrows Bridge disaster).
Some concepts related to oscillatory motion
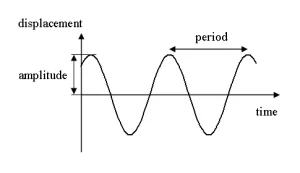
The amplitude: the amplitude is the maximum displacement done by the oscillating body away from its original position, The measuring unit of the amplitude is metre or centimetre.
The complete oscillation: the complete oscillation is the motion of an oscillating body when it passes by a fixed point on its path two successive times in the same direction.
The periodic time: the periodic time is the time taken by an oscillating body to make one complete oscillation, The measuring unit of the periodic time is the second.
The frequency: the frequency is the number of the complete oscillations made by an oscillating body in one second, The relation between the periodic time and the frequency is an inverse relation.
- Oscillatory Motion examplesSimple Pendulum: A small mass attached to a string swings back and forth under the influence of gravity. For small angles, it exhibits simple harmonic motion (SHM) with a time period:
- Mass-Spring System: A mass attached to a spring oscillates when stretched or compressed.
- Vibrating Tuning Fork: When struck, a tuning fork vibrates, producing sound waves. The prongs move back and forth about their equilibrium position, generating oscillations.
- Guitar Strings: Plucking a guitar string causes it to oscillate, producing sound waves. The frequency of oscillation determines the pitch of the sound.
- Swinging of a Playground Swing: A swing moves back and forth due to gravity and restoring forces. If undisturbed, it follows simple harmonic motion.
- Quartz Crystal in Clocks: Quartz crystals oscillate at a fixed frequency when subjected to an electric field. This property is used in quartz watches for precise timekeeping.
- Motion of a Floating Buoy: A buoy on the water surface oscillates up and down due to waves. This follows periodic motion driven by water displacement forces.
- Oscillations in LC Circuits: Electrical circuits containing inductors (L) and capacitors (C) undergo oscillatory charge and voltage variations.
- Vibrations of a Drum Membrane: When struck, a drum’s surface oscillates, producing sound waves. Different modes of vibration create various frequencies.
- Heartbeat: The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart are examples of biological oscillations.
You can download Science online application on google play from this link: Science online Apps on Google play
Role of waves in transferring energy, Wave Motion, Transverse waves & Longitudinal waves
Oscillatory Motion definition, examples, applications & properties




Quiet helpiful. Thanks
Thank you very much
It’s very good article
Thanks
You are welcome
Thanks 😊
You are welcome
Thank you very much . This is very helpful .
You are welcome
Very helpful. Thank you so much. 🙂 Can u give me some more Examples pls
You are welcome
You can read these articles
Types of motion, Relative motion, Applications of Mechanical waves & Electromagnetic waves
Static objects, Moving objects, Types of Motion and Velocity
Properties of Mechanical waves and Electromagnetic waves
this is very helpful for people…
Great Work