Physical and chemical properties of carbon dioxide gas, and uses of carbon dioxide
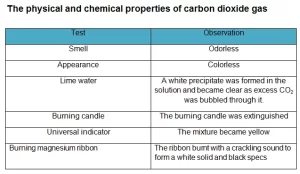
Carbon dioxide gas is produced from the breathing of humans and animals, It is produced from the combustion of coal or hydrocarbons, and the fermentation of liquids, It is a colorless, tasteless, and odorless gas.
Carbon dioxide gas
Carbon dioxide gas (CO2) is one of the most stable of all molecules as it consists of a single carbon atom covalently bonded to two atoms of oxygen, this bond is very strong, and it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure.
Carbon dioxide gas can change the pH of the water and it dissolves slightly in the water to form a weak acid called carbonic acid, and it is a greenhouse gas as it transmits visible light but it absorbs strongly in the infrared and near-infrared. Carbon dioxide gas does not burn and does not help in burning, so it is used in extinguishing fires, it is heavier than the air, so it is collected by upward displacement of air.
Most carbon dioxide units are slightly acidic by nature, the level of acidity can be modified by dissolving the molecules in the water, it is soluble in ethanol and in acetone, It is easily dissolved in the water, so it is not collected by the displacement of water.
Carbon dioxide gas reacts with alkalis to give carbonates and bicarbonates, it is a linear covalent molecule, it is an acidic oxide, and it reacts with the water to give carbonic acid. Carbon dioxide gas reacts with magnesium to form magnesium oxide (white powder) and carbon or coal (black substance) that deposits on the wall of the cylinder.
Carbon dioxide gas is prepared by adding dilute hydrochloric acid to calcium carbonate, it is prepared by upward displacement of air because it is heavier than the air, and it is not collected by displacement of water as it easily dissolves in the water, and it is also prepared by adding lemon juice or vinegar to sodium bicarbonate (the backing powder).
Carbon dioxide gas forms a solid substance at temperatures below -70 degrees Celsius (-94° Fahrenheit), It may also transform into a liquid when it is dissolved in the water under constant pressure, it is very stable, and it is largely unaffected as it interacts with many other materials in the atmosphere.
When we inhale carbon dioxide gas at concentrations much higher than the usual atmospheric levels, it can produce a sour taste in the mouth and a stinging sensation in the nose and throat, as carbon dioxide gas dissolves in the mucous membranes and saliva, and it forms a weak solution of carbonic acid.
Carbon dioxide gas molecule is moderately reactive and is non-flammable, but it will support the combustion of metals such as magnesium, it contains two double bonds and it has a linear shape, It has no electrical dipole, and it is fully oxidized.
Physical properties of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide gas (CO₂) is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature. The molecular weight of Carbon dioxide gas is 44.01 g/mol. Carbon dioxide gas is a gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP), which is 0°C (273.15 K) and 1 atm pressure.
Density: As a gas at 0°C and 1 atm: approximately 1.98 kg/m³. As a solid (dry ice) at -78.5°C: approximately 1.56 g/cm³.
Boiling Point: Carbon dioxide gas does not have a normal boiling point because it sublimates directly from a solid to a gas at atmospheric pressure, The sublimation point is at -78.5°C (-109.3°F) at 1 atm.
Melting Point: Carbon dioxide gas does not melt under standard atmospheric pressure but sublimates directly to gas. Under higher pressures (5.1 atm or above), Carbon dioxide gas can melt into a liquid phase at around -56.6°C (-69.9°F).
Critical Temperature: 31.0°C (87.8°F). Critical Pressure: 7.38 MPa (72.8 atm).
Carbon dioxide gas is moderately soluble in water, forming carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) in a reversible reaction. The solubility of Carbon dioxide gas in the water decreases with increasing the temperature.
Viscosity: As a gas, Carbon dioxide gas has a viscosity of about 14.8 µPa·s at 0°C.
Specific Heat Capacity: Gas (constant pressure, Cp): approximately 0.844 J/g·K. Gas (constant volume, Cv): approximately 0.655 J/g·K.
Thermal Conductivity: Carbon dioxide gas has a thermal conductivity of about 0.0146 W/m·K at 0°C.
These properties make Carbon dioxide gas useful in various applications, including refrigeration (as dry ice), carbonation of beverages, fire extinguishers, and as a supercritical fluid for extraction processes.
Chemical properties of carbon dioxide
Composition and Structure: Carbon dioxide gas CO₂ consists of one carbon atom covalently bonded to two oxygen atoms, The molecule is linear and symmetrical, with a bond angle of 180°. The carbon atom is in the +4 oxidation state, while each oxygen atom is in the -2 oxidation state.
Reactivity with Water: Carbon dioxide gas reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), a weak acid: CO₂ + H2O ⇌ H2CO3
Carbonic acid partially dissociates in water to produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) and bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻): H2CO3 ⇌ H⁺ + HCO₃⁻
Acidity: The carbonic acid formed in the water makes carbon dioxide gas an acidic oxide, It lowers the pH of water when dissolved.
Reactivity with Bases: Carbon dioxide gas reacts with bases to form carbonates and bicarbonates, When carbon dioxide gas is bubbled through sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution, it forms sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) depending on the CO₂ concentration:
CO₂ + 2NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
CO₂ + NaOH → NaHCO3
Carbon dioxide gas is non-flammable and does not support combustion, So, Carbon dioxide gas is used in fire extinguishers.
Carbon dioxide gas can react with reactive metals like magnesium (Mg) at high temperatures to produce metal oxides and carbon (C):
2Mg + CO₂ → 2MgO + C
Carbon dioxide gas can react with certain organic compounds, it can be used in carboxylation reactions where Carbon dioxide gas is introduced into a molecule, such as in the synthesis of carboxylic acids.
Carbon dioxide gas is a key reactant in photosynthesis, where plants, algae, and some bacteria use it, along with sunlight, to produce glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and oxygen (O₂):
6 CO₂ + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Under specific conditions, Carbon dioxide gas can form solid clathrate hydrates with water, where the CO₂ molecules are trapped within a lattice of water molecules, This occurs at high pressure and low temperature.
In biological systems, Carbon dioxide gas binds with hemoglobin in the blood to form carbaminohemoglobin, which plays a role in the transport of Carbon dioxide gas from tissues to the lungs for exhalation.
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Carbon monoxide emissions, sources, effects, uses, poisoning symptoms