Atmospheric envelope, Characteristics and importance of Troposphere layer
The troposphere is a critical layer for life on Earth. It’s the home of our weather, and the air we breathe, and it influences our climate. The troposphere is the closest layer to Earth, and it’s where most of the weather happens.
Atmospheric envelope
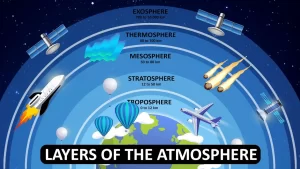
The atmospheric envelope consists of four layers above the sea level which are the troposphere layer, the stratosphere layer, the mesosphere layer, and the thermosphere layer.
There is a region between each successive layer, In these regions, the temperature remains constant, There is the tropopause which is the region between the troposphere layer and the stratosphere layer.
There is the stratopause which is a region between the stratosphere layer and the mesosphere layer, There is the mesopause which is the region between the mesosphere layer and the thermosphere layer.
Characteristics of the Troposphere Layer
The troposphere layer is the first layer of the atmospheric envelope. The troposphere layer is the disturbed layer because all the weather changes take place in it.
The troposphere layer extends for 13 km above the sea level to the tropopause, The thickness of the troposphere layer is 13 km, and it contains 99 % of the atmospheric water vapour that organizes the Earth’s temperature.
The troposphere layer is the lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere, where nearly all weather conditions take place, The average height of the troposphere is 18 km in the tropics, 17 km in the middle latitudes, and 6 km in the polar regions in winter.
The temperature decreases with a rate (6.5 degree Celsius) for each (1 km) height until it reaches the lowest value of about (- 60 degree Celsius) at the tropopause, The air movement in this layer is vertical where, the hot air currents move upwards, while the cold air currents move downwards.
As you move up in the troposphere, it gets colder. This happens because the Earth’s surface warms the air below, and the heat transfers upwards. Air quality in the troposphere is directly affected by human activities, pollution sources, and natural processes.
The temperature difference between the bottom and top of the troposphere is what drives most weather phenomena. Warm air rises, cooler air sinks, and water vapor condenses to form clouds – all within the troposphere. This constant movement of air creates wind, rain, snow, thunderstorms, and other weather events we experience.
The atmospheric pressure in the troposphere layer decreases as we go up until it becomes 100 mb at its top, It contains about 75 % of the mass of the atmospheric air and aerosols, All the atmospheric phenomena such as rains, wind, clouds, ………take place in this layer.
Almost all of the water vapor and the dust particles in the atmosphere are in the troposphere, The water vapor is key for weather formation, as it condenses to form clouds and precipitation, So, most clouds are found in this lowest layer, the bottom of the troposphere, right next to the surface of Earth, is called the boundary layer.
The lowest part of the troposphere, where the friction with the Earth’s surface influences airflow, is the planetary boundary layer, This layer is a few hundred meters to 2 km deep depending on the landform and time of day, A top of the troposphere is the tropopause, which is the border between the troposphere and stratosphere.
Importance of Troposphere layer
The temperature change with altitude in the troposphere is what drives most weather phenomena. Warm air rises, cooler air sinks, and water vapor condenses to form clouds. This circulation of air creates wind, rain, snow, thunderstorms, and all the other weather events we experience.
The troposphere plays a big role in Earth’s climate. The greenhouse effect, where certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun, mainly occurs in the troposphere. Tropospheric processes like the greenhouse effect and water cycle significantly influence Earth’s climate. Understanding them is essential for addressing climate change.
The troposphere contains the air we breathe, which contains the oxygen we need to survive, Air is a mixture of gases including nitrogen, oxygen, and small amounts of other elements. The troposphere contains the water vapor for rain, and the moderate temperatures that allow life to thrive. The troposphere is the Earth’s atmosphere’s lowest layer, where we live and breathe.
Since weather happens in the troposphere, studying its conditions allows us to forecast weather patterns and prepare for potential hazards. Understanding the troposphere is essential for weather forecasting and climate studies. Scientists focus on conditions in this layer to predict weather patterns and understand how climate change might affect them.
The troposphere acts as a kind of natural filter for the Earth. It traps dust particles, ash, and some harmful gases from reaching the surface, protecting us from some of the harsh elements.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google play
Atmospheric layers & pressure, Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere & Thermosphere
The characteristics and the importance of the mesosphere layer
The characteristics and the importance of the thermosphere layer
The characteristics and the importance of the stratosphere layer