Characteristics and importance of Stratosphere layer, What is stratosphere layer known for?
The stratosphere layer is the second layer of the atmospheric envelope, It is called the ozonic atmospheric envelope, The atmospheric pressure in the stratosphere layer decreases as we go up until it becomes 1 mb at its top ( 0.001 of the normal atmospheric pressure at sea level).
Stratosphere layer
The stratosphere plays a vital role in protecting life on Earth, regulating climate, and influencing weather patterns, making it an essential part of the atmospheric system.
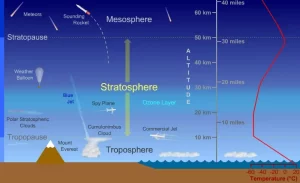
The stratosphere layer extends from the tropopause (at a height of 13 km above sea level) to the stratopause (at a height of 50 km above sea level), The thickness of the stratosphere is 37 kilometers.
The temperature in the stratosphere layer increases gradually from (- 60° Celsius), at the lower part until it reaches (0° Celsius) at the top of the layer.
The temperature increases gradually due to the absorption of the ultraviolet rays emitted from the Sun by the ozone layer which is present in the upper part of the stratosphere layer.
The stratosphere layer contains most of the ozone gas found in the atmospheric envelope at a height of 20 to 40 km above sea level. So, the stratosphere layer is called the ozonic atmospheric envelope.
The lower part of the stratosphere layer does not contain clouds or weather disturbances, and the air movement is horizontal. So, the pilots prefer to fly their planes in the stratosphere layer.
So, the stratosphere layer is important for human life as it contains the ozone layer, which absorbs the harmful ultraviolet radiation emitted from the Sun, and also it is convenient for flying planes.
The stratosphere layer is stratified in temperature, with warmer layers higher and cooler layers closer to the Earth. This increase in temperature with altitude is due to the absorption of the Sun‘s ultraviolet radiation by the ozone layer.
The stratospheric temperatures vary within the stratosphere as the seasons change, reaching low temperatures in the polar night (winter). Winds in the stratosphere can far exceed those in the troposphere.
The stratosphere layer is a region of intense interactions between the radiative, dynamic, and chemical processes, in which the horizontal mixing of gaseous components proceeds much more rapidly than the vertical mixing.
Importance of the Stratosphere layer
It contains the ozone layer, which absorbs the majority of the Sun‘s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Without this protection, life on Earth would be exposed to dangerous levels of UV, leading to increased risks of skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues for humans, as well as harmful effects on ecosystems, particularly marine life.
The stratosphere exhibits a temperature inversion, meaning it warms with altitude due to the absorption of UV radiation by ozone. This warming stabilizes the layer, preventing significant vertical mixing of air, which helps maintain global weather patterns.
Commercial jet aircraft often fly in the lower stratosphere to avoid the turbulence common in the troposphere. The air is stable in this layer, providing smoother flight conditions and better fuel efficiency.
The strong winds, known as jet streams, occur near the boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere. These winds are important for aviation and affect weather systems, as they steer storms and influence weather patterns globally.
Although weather primarily occurs in the troposphere, the stratosphere still has an indirect effect on weather and climate. Variations in stratospheric temperature, ozone levels, and circulation patterns can influence surface weather, including sudden stratospheric warming events that can impact winter weather in the Northern Hemisphere.
The stratosphere, along with the mesosphere above it, helps burn up meteoroids as they enter Earth’s atmosphere. Although most meteoroids burn up in the mesosphere, the stable, relatively thick air of the stratosphere also contributes to slowing down incoming debris.
Do planes fly in the stratosphere?
Yes, planes fly in the stratosphere — particularly jetliners at cruising altitude and high-altitude military or research aircraft.
The troposphere is the lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere, extending from the surface up to about 8–15 kilometers (5–9 miles), depending on latitude and weather. This is where most commercial airliners operate, usually at altitudes of 30,000 to 40,000 feet (9–12 km).
The stratosphere begins just above the troposphere and extends up to about 50 kilometers (31 miles). So, the lower stratosphere starts around 33,000 feet (10 km) — right around the cruising altitude of many jets.
Planes that fly in the stratosphere:
- Commercial jets (e.g., Boeing 747, Airbus A380) often cruise at the lower edge of the stratosphere, especially to avoid weather and turbulence in the troposphere.
- Military aircraft, like the U-2 spy plane, fly well into the stratosphere — up to 70,000 feet (21 km).
- Supersonic jets like the now-retired Concorde also flew in the stratosphere at altitudes of about 60,000 feet (18 km).
Why fly in the stratosphere?
- Less turbulence.
- Lower air resistance (improved fuel efficiency).
- Above most weather systems.
You can subscribe to Science Online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
Atmospheric layers and pressure, Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, and Thermosphere
The characteristics and the importance of the mesosphere layer
The characteristics and the importance of the thermosphere layer
The characteristics and the importance of the troposphere layer



This is very helpful, thank you
You are welcome
Heh this was useful for my home work
Thank you
you are welcome
Much needed.
Thank you
You are welcome