Solutions of electrolytes & non-electrolytes and Degree of saturation
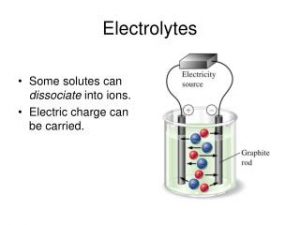
Solutions of substances are divided into two types according to the ability to conduct the electricity which are Solutions of electrolytes and Solutions of non-electrolytes , Electrolytes are the substances in which their solutions or moltens can conduct the electricity by the free ions movement .
Solutions of electrolytes
Solutions of substances that are ionized or dissociated , when dissolving in the water , These solutions contain free ions , So , they conduct the electricity such as the table salt solution .
Electrolytes are divided into Strong electrolytes and Weak electrolytes .
Strong electrolytes
They are the substances which are completely ionized and strongly conduct the electricity , like Ionic compounds and the polar covalent compounds .
Ionic compounds like sodium chloride NaCl and sodium hydroxide NaOH, which are completely dissociated into ions when they dissolve in the water , Polar covalent compounds like Hydrogen chloride HCl , which is completely ionized when it dissolves in the water .
Weak electrolytes
They are substances which are partially ionized and weakly conduct the electricity , like Ionic compounds and the polar covalent compounds .
Ionic compounds like ammonium hydroxide NH4OH , which is partially dissociated into ions when it dissolves in the water , Polar covalent compounds like Acetic acid CH3COOH , which is partially ionized when it dissolves in the water .
HCl (g) is bad conductor of electricity , because the gases generally are non-conductors , HCL ( aq ) is aqueous solution, It is a good conductor of electricity, because it is a strong electrolyte .
Free protons H+ ions can not exist as free ions in aqueous solutions of acids such as Dissolution of HCl ( g ) in the water that can be expressed in this chemical equation :
H2O ( ℓ ) + HCl ( g ) → H3O+( aq ) + Cl−( aq )
Due to the bonding of H+ ions with the water molecules to form hydronium ions H3O+(aq) .
H2O ( ℓ ) + H+ ( aq ) → H3O+( aq )
Solutions of non-electrolytes
Solutions of substances that are not ionized or dissociated, when dissolving in the water, These solutions do not contain free ions , So, they do not conduct the electricity such as sugar solution .
Non-electrolytes
They are the substances in which their solutions or moltens can not conduct the electricity as they have no free ions or hydrated ions , such as Ethyl alcohol and sugar solution.
Ethyl alcohol is one of the non-electrolytes because it is non-ionized and does not conduct the electricity .
Degree of Saturation
Solutions are divided according to the degree of saturation into unsaturated solution , saturated solution and supersaturated solution.
Unsaturated solution is the solution which contains less amount of solute and can accept more amount of solute at a certain temperature.
Saturated solution is the solution which contains the maximum amount of the solute at a certain temperature, The saturated solution can be obtained from the unsaturated solution by adding an excess amount of solute at a certain temperature.
Supersaturated solution is the solution that accepts more amount of solute substance after reaching the state of saturation , The supersaturated solution can be obtained by heating the saturated solution and adding more of the solute to it.
How can you prepare a saturated solution from a supersaturated solution by two methods ?
Cooling : Cool the supersaturated solution and leave it for a short time, the excess solute will be separated ( precipitate ) from the solution .
Crystallization : Put small crystals from the solute in the supersaturated solution and leave it for a short time , the solute molecules will be precipitated as crystals on the surface of seeding crystals .
You can read this article about Mechanism of dissolving process and factors affecting solubility