Oxidation and reduction reactions according to Traditional concept and Electronic concept
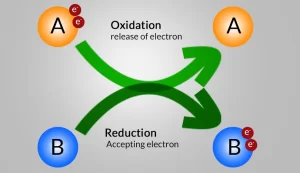
Most metals are strong reducing agents, while most nonmetals are strong oxidizing agents because metals tend to lose electrons during the chemical reaction, while nonmetals tend to gain electrons during the chemical reaction. Oxidation and reduction are concurrent processes that happen at the same time because the number of gained electrons in the reduction process equals number of lost electrons in the oxidation process.
Oxidation and reduction reactions
Oxidation and reduction according to:
- Traditional concept.
- Electronic concept.
Oxidation and reduction according to the traditional concept (by giving and taking away oxygen or hydrogen)
Oxidation and reduction processes can be understood according to the traditional concept by studying the following chemical reaction:
Reaction of hot copper oxide with dry hydrogen gas
On passing hydrogen through hot copper oxide, hydrogen takes the oxygen away from copper oxide forming water vapour and black copper oxide turns into red copper. The previous reaction is expressed by the following equation:
H2 + CuO → Cu + H2O
Hydrogen
An oxidation process occurs to hydrogen because it combines (unites) with oxygen. therefore, Hydrogen is considered as a reducing agent because it took oxygen away from copper oxide.
Copper oxide
A reduction process occurs to copper oxide because oxygen is taken away from it, therefore, copper oxide is considered as an oxidizing agent because it gave oxygen to hydrogen.
From the previous example, we can conclude the following concepts according to the traditional concept:
A reducing agent (factor) is a substance that takes oxygen away or gives hydrogen during a chemical reaction. →occurs to it, Oxidation: A chemical process that causes the increase in the oxygen percentage or the decrease in the hydrogen percentage in a substance.
Oxidizing agent (factor) is a substance that gives oxygen or takes hydrogen away during a chemical reaction. occurs to it → Reduction: A chemical process that causes a decrease in the oxygen percentage or an increase in the hydrogen percentage in a substance.
Oxidation and reduction according to the electronic concept
The modern electronic theory introduces a more accurate concept for oxidation and reduction, where there are oxidation and reduction reactions don’t include oxygen or hydrogen as in the following example:
Reaction of sodium atom and chlorine atom to form sodium chloride molecule (table salt)
The previous reaction is expressed by the following equation:
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
Sodium
An oxidation process occurs to sodium because it loses an electron and changes into a positive sodium ion.
2Na → 2Na+ + 2e−
Sodium is considered as a reducing agent because it loses an electron during the chemical reaction and changes into a positive sodium ion.
Chlorine
A reduction process occurs to chlorine because it gains an electron (which is lost by sodium) and changes into a negative chloride ion.
Cl2 + 2 e−→ 2Cl−
Chlorine is considered as an oxidizing agent because it gains an electron during the chemical reaction and changes into a negative chloride ion.
On the reaction between sodium with chlorine form sodium chloride, oxidation and reduction processes occur, although the absence of oxygen because this reaction occurs by losing and gaining electrons.
From the previous example, we can conclude the following concepts according to the electronic concept:
A reducing agent (factor) is a substance that loses an electron or more during a chemical reaction. occurs to it, Oxidation: A chemical process where the atom loses an electron or more.
Oxidizing agent (factor) is a substance that gains an electron or more during a chemical reaction. occurs to it, Reduction: A chemical process where the atom gains an electron or more.
Oxidation and reduction are concurrent processes as they occur at the same time because the number of gained electrons in the reduction process equals the number of lost electrons in the oxidation process.
Most metals are strong reducing agents, while most nonmetals are strong oxidizing agents because metals tend to lose electrons during the chemical reaction, while nonmetals tend to gain electrons during the chemical reaction.
Any chemical process includes:
Losing of electrons is known as an oxidation process.
Cu → Cu+2 + 2e−
F− → F + e−
Gaining of electrons is known as a reduction process.
Ag+ + e−→ Ag
Br + e−→ Br −
Exercise 1
2Al + 3Cl2 → 2AlCl3, [Al=13 & Cl= 17]
Reducing agent: Aluminium Al, 2Al → 2Al+3 + 6e−
Oxidizing agent: Chlorine Cl2, 3Cl2 + 6e−→ 6Cl −
Exercise 2
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 , [Mg=12 & H=1]
The type of this reaction is a simple substitution reaction (oxidation & reduction).
Reducing agent: Magnesium atom (Mg), because it loses two electrons during the chemical reaction and changes into positive magnesium ion (Mg+2).
Mg → Mg+2 + 2e−
Oxidizing agent: Hydrogen ion (H+), because it gains two electrons during the chemical reaction and changes into hydrogen molecule (H₂).
2H+ + 2e−→ H2
You can follow science online on YouTube from this link: Science online
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Speed of chemical reactions, Types of catalytic reactions & Catalytic converter
Substitution reactions, Chemical activity series, types of simple & double substitution reactions
Chemical reactions, Types of thermal decomposition reactions & Air bags importance
Simple and double substitution reactions, Reaction between an acid & a salt
Chemical activity series, Chemical properties of metals & nonmetals
Types, importance, negative effects of chemical reactions, Sulphur & Carbon oxides harms