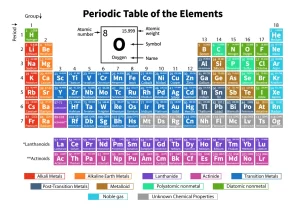
Modern periodic table and classification of Elements
The modern periodic table consists of 7 periods (horizontal rows), and 18 groups (vertical columns), The elements are arranged ascendingly according to their atomic numbers and the way to fill their atomic energy sublevels by electrons according to the Aufbeau (building-up) principle, where each element has one electron more than the element precedes it.
Modern periodic table
The atomic number of each element increases than the element precedes it in the same period by a whole one, Each period begins by filling a new energy level with one electron, then filling the atomic energy sublevels lying in the same period successively, until we reach the last element in the period which is a noble gas that has completely filled energy levels.
The elements of the same vertical group are identical in the electronic composition of the highest (outermost) energy level, different in the principal quantum number (n).
Both of sodium 11Na and potassium 19K have similar properties, Because they are identical in the electronic composition of the highest (outermost) energy level (ns¹).
Elements blocks of the modern periodic table
The table is divided into four main blocks, these blocks are s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block
s-block elements
They are placed in the left-hand block of the table, The s-block contains the elements whose outermost electrons occupy the s sub-level, The s-block consists of two groups of elements, they are :
1A whose electronic configuration ends with ns¹, 2A whose electronic configuration ends with ns², where n is the number of the outer energy level and the number of periods at the same time.
p-block elements
They occupy the right-hand block of the table, The p-block contains the elements whose outermost electrons occupy the p sublevel except for helium, The p-block consists of six groups, characterized by symbol A except for zero groups.
d-block elements
They occupy the middle block of the table, The d-block contains the elements with the outermost electrons occupying the d sublevel, The d-block consists of 10 vertical columns representing 8 groups which are characterized by the symbol B except the eighth group which consists of 3 vertical columns.
The d-block elements are classified according to the number of the outer energy level and the period number into three series which are :
- The first transition series: It includes the elements in which the 3d sub-level is filled successively, It lies in the fourth period and includes the elements from scandium (21Sc) to zinc (30Zn).
- The second transition series: It includes the elements in which the 4d sub-level is filled successively, It lies in the fifth period and includes the elements from yttrium (39Y) to cadmium (48Cd).
- The third transition series: It includes the elements in which the 5d sub-level is filled successively, It lies in the sixth period and includes the elements from lanthanum (57La) to mercury (80Hg), excluding lanthanides.
f-block elements
They are separated down the table, to avoid being a very wide table, In which the f sub-level is filled successively, The f-block is divided into series – each of them includes 14 elements – which are :
- The lanthanides series: It is placed in the sixth period, in which the 4f sub-level is filled successively, The elements of this series were named -wrong- by rare Earth’s elements because they are quite similar in behavior and very difficult to be separated as the outermost energy level for all of them 6s².
- The actinides series: It is placed in the seventh period, in which the 5f sub-level is filled successively, All the elements of this series are radioactive and their nuclei are unstable.
The number of elements of any series of the f-block is 14 elements, while the d-block contains 10 elements because f-block elements in which the f-sublevel is successively filled and consists of 7 orbitals, while d-block elements in which the d-sublevel consists of 5 orbitals and each orbital is occupied by 2 electrons.
Types of the periodic table elements
It is possible to classify the elements in the periodic table into four types which are:
- Noble gases.
- The representative elements.
- The main transition elements.
- The inner transition elements.
Noble gases
They are the elements of the zero group 18 which is the last column of the p-block, They are characterized by having energy levels completely filled by electrons and their electronic structure is np6, except that of helium 2He which is 1s².
Noble gases may form compounds, but with great difficulty, because they are very stable elements as their energy levels are completely filled by electrons.
The representative elements
They are the elements of s and p-blocks, except that of zero group, They occupy the groups from 1 A: 7 A, These elements are characterized by the complete filling of all the energy levels with electrons, except for the highest level.
They are active elements because their highest level tends to reach the completed configuration similar to the nearest noble gas (ns², np6) by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons.
Ex: 11Na → Na+ (loses 1 electron)
1s², 2s², 2p6, 3s¹ → 1s², 2s², 2p6 (similar to the electronic configuration of neon gas 10Ne)
16S → S– – (gains 2 electrons)
1s² , 2s² , 2p6 , 3s² , 2p4 → 1s² , 2s² , 2p6 , 3s² , 3p6 (similar to the electronic configuration of argon gas 18Ar)
1H + 1H → H2 (sharing)
1s¹ + 1s¹→ 1s² (similar to the electronic configuration of helium gas 2He)
The main transition elements
They are the elements of the d-block, They are characterized by having energy levels completely filled by electrons, except the two outermost levels.
21Sc : 1s² , 2s² , 2p6 , 3s² , 3p6 , 4s² , 3d1
The inner transition elements
They are the elements of the f-block, They are characterized by having energy levels completely filled with electrons, except the three outermost levels.
64Gd : 1s² , 2s² , 2p6 , 3s² , 3p6 , 4s² , 3d10 , 4p6 , 5s² , 4d10 , 5p6 , 6s2 , 4f7, 5d1
The elements configuration in the light of the modern periodic table
The periodic table shows a method to express the electronic configuration of the elements according to the nearest noble gas that precedes the element in the periodic table and this is considered the fourth method for the electronic configuration of elements.
Determination of the element location in the periodic table
Periodic number: It is determined by the greatest principal quantum number ( n ) in the electronic configuration of the element.
Group number and symbol: They are determined by the type of element
The type of element is Representative, block (s): The number of electrons of the last sublevel (s), Group symbol is A.
The type of element is Representative, block (p): The sum of the numbers of electrons in the last two sublevels (s) and (p), Group symbol is A.
The type of element is noble gases, block (p): Zero group (the p-sublevel is completely filled by electrons).
The type of element is the main transition, block (d): The sum of the numbers of electrons in the last (s) sub-level and the penultimate (d) sublevel, Group symbol is B.
If the sub-level (n − 1) d contains 6, 7, 8 electrons, the element is located in group 8, If the electronic configuration of the element ends with :
ns1, ( n− 1 ) d10: the electron is located in 1B group.
ns2, ( n− 1 ) d10: the electron is located in 2B group.
Ex: A representative element contains four principal energy levels, the last level has three unpaired electrons.
- Its electronic configuration → [ 18Ar ] , 4s² , 3d10 , 4p3
- Its atomic number → 33
- Number of full-filled orbitals in the outermost energy level → 1 orbital.
- Number of valence electrons → 5 electrons.
The quantum numbers and principles of distributing electrons
Radius property, Ionization potential, Electron affinity and Electronegativity
Metallic and nonmetallic properties, Acidic and basic properties in the periodic table


Nice content
Thank you for your comment