Elements of p-block, General properties of group 5A elements (group 15)
Group 5A (group 15) consists of five elements which are nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony & bismuth, Elements of this group are not abundant in nature, except nitrogen which represents about 80 % of atmospheric air (4/5) of air volume, We can’t detect both nitrogen & phosphorus by flame test, because both of them are nonmetals.
Group 5A (group 15)
The forms of these elements which are found in nature:
- Phosphorus is the most abundant element of this group (5A) in Earth’s crust, The form found in nature: Calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2, Apatite CaF2.Ca3(PO4)2 ” the salt of calcium fluoride and calcium phosphate “.
- Arsenic: The form found in nature is Arsenic sulphide As2S3.
- Antimony: The form found in nature is Antimony sulphide Sb2S3.
- Bismuth: The form found in nature is Bismuth sulphide Bi2S3.
General properties of group 5A elements (group 15)
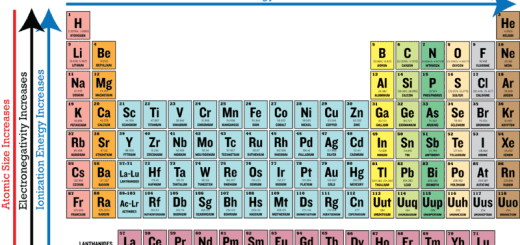
The properties of group 5A elements graduate regularly depending on the increase in atomic number and atomic size as illustrated in the following:
- Graduation of the metallic and nonmetallic properties.
- Different number of molecules atoms of each element.
- Several oxidation numbers.
- Oxides of group 5A elements.
- Hydrides of group 5A elements.
The graduation of the metallic and nonmetallic property
The metallic property increases by increasing the atomic number (downward the group), The properties of this group elements tend to be those of the nonmetals, even bismuth – is a metal – but its ability to conduct electricity is weak.
Different number of molecule atoms of each element
The number of molecule atoms of each element of this group differs as the following:
- Nitrogen: The molecule contains two atoms, Symbol of the molecule is N2.
- Phosphorus: its vapour has a molecule which contains four atoms, Symbol of the molecule is P4.
- Antimony: its vapour has a molecule which contains four atoms, Symbol of the molecule is As4.
- Arsenic: its vapour has a molecule which contains four atoms, Symbol of the molecule is Sb4.
- Bismuth: It forms a metallic crystal lattice & its vapor consists of diatomic molecules, Symbol of the molecule is Bi2.
Although bismuth is a metal, it has different properties than that of the other metals, because of its low electric conductivity relative to the other metals and it has a diatomic structure in its vapor state, whereas the other metals have mono-atomic structure.
Several oxidation numbers
Elements of this group are characterized by having several oxidation numbers in their different compounds from (− 3) to (+ 5), because through covalent sharing they may gain till 3 electrons or lose till 5 electrons, The oxidation numbers of nitrogen in some of its compounds:
The oxidation numbers of nitrogen in the oxygenated compounds are positive, while that in the hydrogenated compounds are negative because the electronegativity of nitrogen is less than that of oxygen and higher than that of hydrogen.
Several allotropic forms
Allotropy is the presence of the element in more than one form which has different physical properties and similar chemical ones, The allotropic phenomenon appears in the solid nonmetals only, Due to the presence of the solid nonmetal element in different crystalline forms, each form differs in the number of atoms and in their arrangement.
- Phosphorus: Allotropic forms are white (waxy), red, violet.
- Arsenic: Allotropic forms are black, grey, yellow (waxy yellow).
- Antimony: Allotropic forms are yellow, black.
Allotropy exists in phosphorus, but not in nitrogen and bismuth because phosphorus is a solid nonmetal, while nitrogen is a gaseous nonmetal and bismuth is a metallic element, in which gases and metals do not have allotropic forms.
Oxides of group 5A elements
All elements of this group form oxides have the formula: X2O3, X2O5, Some of these oxides are acidic, others are amphoteric and others are basic, The basic property of these oxides increases (the acidic property decreases) with increasing the atomic number.
- Element is 7N: Its oxide is N2O3, N2O5, Type of oxide is Acidic oxide.
- Element is 15P: Its oxide is P2O3, Type of oxide is Acidic oxide.
- Element is 33As: Its oxide is As2O3, Type of oxide is Acidic oxide.
- Element is 51Sb: Its oxide is Sb2O3, Type of oxide is Amphoteric oxide.
- Element is 83Bi: Its oxide is Bi2O3, Bi2O5, Type of oxide is Basic oxide.
Hydrides of group 5A elements
Most of the elements of this group react with hydrogen forming hydrides, the oxidation number of the element is −3, as in Ammonia NH3, Phosphine PH3, and Arsine AsH3.
The central atom in these compounds still has a lone pair of electrons in its valence shell (outer energy level), so, it can give this pair of electrons to other atoms or ions making coordinate bonds.
Based on that the basicity of the hydride depends on the ability of its central atom to lose one pair of electrons or gain a proton from another substance, ammonia is more basic than phosphine.
NH3 + H2O → NH+4 + OH−
PH3 + H2O → PH+4 + OH−
The properties of hydrides of the group 5A elements:
- Their thermal stability decreases, so, they decompose even by gentle heating.
- The polarity of hydrogen compounds in this group decreases with increasing atomic number of the element attached to hydrogen, thus their solubility in water decreases.
The solubility degree of phosphine in water is less than that of ammonia because the polarity of phosphine is less than the polarity of ammonia.
The most famous elements in 5A group (Nitrogen properties, Preparation & compounds)
Nitric acid properties, Passivity phenomenon & Economic importance of the 5A group elements
Graduation of the properties of the elements in the modern periodic table