Chemical Equilibrium, Chemical reactions types, complete reactions and reversible reactions
Chemical Equilibrium is a dynamic system, which takes place when the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of backward reaction, where the concentration, temperature, pressure, and equilibrium position are unchanged, Types of equilibrium are dynamic equilibrium, chemical equilibrium & ionic equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium is a stationary system apparently, but a dynamic system in reality.
The equilibrium system
It is the system that is a stationary system on the visible level, but in reality, a dynamic system on the invisible level, Equilibrium does not mean that the change has stopped, but it means that the change is continued in two directions (forward and backward), the Equilibrium state is the state at which the apparent properties of the mixture are unchanged (stable).
Evaporation and condensation of water
If the water in a closed vessel is heated, we notice that two reversible or opposite processes happen, these are vaporization and condensation processes, At the beginning of heating, vaporization predominates which is associated with an increase in the vapour pressure (vapour pressure is the pressure produced due to water vapour in air at a certain temperature).
The vaporization process continues until the vapour pressure equals saturated water vapour pressure which is the maximum water vapour pressure (which is the maximum water vapour pressure in the air at a certain temperature).
Eventually, a state of equilibrium is reached between the rate of vaporization and condensation, At this time, the number of water molecules which evaporate from the liquid is equal to the number of water molecules in the condensed vapour.
Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical reactions can be divided into two types which are complete (irreversible) reactions and reversible reactions.
- Instantaneous reactions are reactions that end in a very short time as soon as the reactants are mixed.
- Comparatively slow reactions are the reaction between oil and caustic soda (NaOH) to give soap and glycerol.
- Reactions need several months to take place such as iron rusting.
Complete (irreversible) reactions
The irreversible reaction is the reaction that proceeds in one direction because one of the products escapes from the system in the form of a gas or a precipitate.
It is called the instantaneous reaction, this reaction proceeds in one direction “Forward Direction only”, The products do not react once more with each other to reform the reactants under the conditions of the reaction, These reactions are irreversible as one of the products escapes from the medium of the reaction in the form of gas or ppt.
On adding of sodium chloride solution to a silver nitrate solution, a white precipitate of silver chloride is formed.
NaCl + AgNO3 → NaNO3 + AgCl ↓
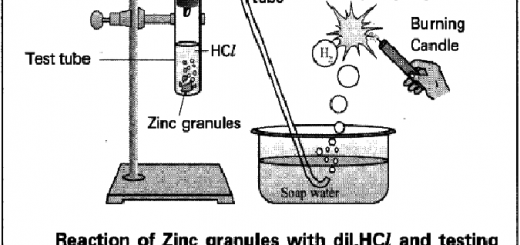
When a strip of magnesium metal is placed in a hydrochloric acid solution, hydrogen gas evolves.
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 ↑
These reactions are considered as complete or irreversible reactions because one of the products escapes from the system, the silver chloride precipitates in the first reaction and hydrogen gas evolves in the second reaction, these reactions proceed in one direction because the products can’t be combined with each other once more reforming the reactants, under the conditions of the experiment.
Reversible reactions “Incomplete Reaction” (simultaneous processes)
This reaction proceeds in both directions (Forward and Backward), The products recombine to form the reactants until a state of equilibrium is reached when the rate of forward reaction equals to the rate of backward reaction.
When one mole of acetic acid (ethanoic acid) is added to one mole of ethanol, it is expected according to the following equation that one mole of ethyl acetate (ethyl ethanoate) ester and one mole of water should be formed.
Forward direction:
CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
Backward direction:
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O → CH3COOH + C2H5OH
When a blue litmus paper is placed in the solution, it turns red, although the products are neutral (have no action on litmus), the previous reaction does not proceed to completion (in one direction towards the formation of the products only), it is a reversible reaction, which proceeds in both directions, forward and backward.
Accordingly, both the reactants and products are always found in the reaction medium, this explains the acidity of the ester solution due to the presence of acetic acid.
The chemical equilibrium takes place in reversible reactions and it takes place when the rate of forward reactions is equal to the rate of backward reactions.
During chemical equilibrium:
- The concentration of reactions and products remains constant.
- All the reactants and products are still found in the medium of the reaction (No gas evolves and no ppt. is formed).
- Conditions of the reaction, such as concentration, temperature and pressure are constant.
Chemical equilibrium in reversible reactions is a dynamic system that takes place when the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of backward reaction and the concentration of the reactants and products are not changed, the equilibrium position remains unchanged and products are still found in the system and as long as the reaction conditions are not changed.
The rate of the chemical reaction is the rate of change in the concentration of the reactants or products per time unit, The concentration unit is expressed as mole/liter, The time unit is expressed as second or minute.
In irreversible (complete) reactions, the concentration of the reactants decreases and the concentration of the products increases, the concentration of the reactant is the minimum and the concentration of the product is the maximum.
In reversible (complete) reactions, the increase in the concentration of the products and decrease in the concentration of the reactants proceeds until an equilibrium state is established, the concentration of the product equals the concentration of reactant, the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of backward reaction.
The thermal decomposition of copper II nitrate is a complete reaction due to the escaping of NO2 and O2 gases from the reaction medium.
2Cu(NO3)2 → 2CuO + 4NO2 ↑ + O2 ↑
The reaction of sodium chloride solution with silver nitrate solution is a complete reaction due to the escaping of silver chloride precipitate from the reaction medium.
AgNO3 + NaCl → NaNO3 + AgCl ↓
The blue litmus paper turns red when it is placed in a container that contains one mole of ethanol and one mole of acetic acid although the products are neutral because acetic acid is always found in the medium of this reversible reaction.
The chemical equilibrium is a dynamic system, not a stationary system although the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of backward reaction, the reaction continues in both of two directions.
Balanced chemical equations, Law of conservation of matter (mass) & Law of constant ratios