Chemical combination, Properties of Metals, Nonmetals and Noble (inert) gases
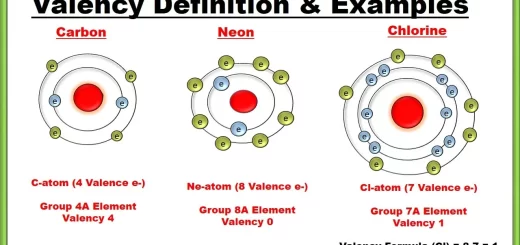
The number of well-known elements up till now is 118 elements, These elements can be classified according to their properties and electronic structure into metals, nonmetals and noble (inert) gases, In the 19th century, Berzelius (1779-1848) was the first scientist who classified elements into metals and nonmetals.
Metals
Metals are the elements that contain 1 or 2 or 3 elements in the outermost energy level. The metals form positive ions (cations), they can be hammered into thin sheets (malleable) and they can be drawn into wires (ductile). The electric wires are manufactured of copper because copper is a metal that is a good conductor of electricity.
Properties of metals
- They are the elements that contain less than 4 electrons (1 or 2 or 3 electrons) in the outermost energy level.
- They are solids except mercury (Hg) which is the only liquid metallic element.
- They have a metallic luster.
- They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- They are malleable and ductile.
The behaviour of atoms of metals during the chemical reaction
During the chemical reaction, atoms of metals tend to give their outermost electrons to other atoms to complete their outermost energy level with electrons, the atom becomes a positive ion when it loses an electron or more because the number of positive protons becomes more than the number of negative electrons.
The positive ion
The positive ion is an atom of the metallic element which loses an electron or more during the chemical reaction, The number of protons in its nucleus is greater than the number of electrons revolving around it, The number of energy levels around its nucleus is less than the number of energy levels in the atom, The positive ion carries a number of positive charges equals to the number of lost electrons from the neutral atom.
Examples of atoms of metals and their behaviour during the chemical reaction
During the chemical reaction, the magnesium atom (Mg) loses two electrons and changes into a positive ion (Mg+2), which carries two positive charges, Neutral magnesium atom (Mg) contains 12 electrons, 12 protons, 12 neutrons & 3 energy levels, Positive magnesium ion (Mg+2) contains 10 electrons, 12 protons, 12 neutrons & 2 energy levels.
During the chemical reaction, the aluminium atom (Al) loses three electrons and changes into a positive ion (Al+3), which carries three positive charges, Neutral aluminium atom (Al) contains 13 electrons, 13 protons, 14 neutrons & 3 energy levels, Positive aluminium ion (Al+3) contains 10 electrons, 13 protons, 14 neutrons & 2 energy levels.
Nonmetals
Nonmetals are the elements that contain 5 or 6 or 7 electrons in the outermost energy level. When you hammer a piece of carbon, It will be fragmented easily, because carbon is from nonmetals which are not malleable. A hydrogen (1H) atom & a carbon (6C) atom are considered from nonmetals although the outermost energy level of a hydrogen atom contains 1 electron and that of a carbon atom contains 4 electrons.
Properties of nonmetals
- They are the elements which contain more than 4 electrons (5 or 6 or 7 electrons) in the outermost energy level.
- Some of them are solids and others are gases except bromine (Br) which is the only liquid nonmetallic element.
- They have no luster.
- They are bad onductors of heat and electricity except graphite (carbon) which is a good conductor of electricity.
- They are not malleable or ductile (brittle).
The behaviour of atoms of nonmetals during the chemical reactions
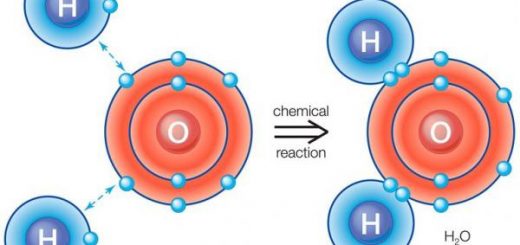
During the chemical reaction, atoms of nonmetals tend to gain electrons from other atoms to complete their outermost energy level with electrons. The atom becomes a negative ion when it gains an electron or more because the number of electrons becomes more than the number of protons.
Negative ion
The negative ion is an atom of a nonmetallic element that gains an electron or more during the chemical reaction. The number of protons in its nucleus is less than the number of electrons revolving around it, the number of energy levels around its nucleus is equal to the number of energy levels in the atom, The negative ion carries a number of negative charges equal to the number of gained electrons.
Examples of atoms of nonmetals and their behaviour during the chemical reaction:
During the chemical reaction, the chlorine atom (Cl) gains one electron and changes into a negative ion (Cl−), which carries one negative charge, Neutral chlorine atom (Cl) contains 17 electrons, 17 protons, 18 neutrons & 3 energy levels, Negative chlorine ion (Cl−) contains 18 electrons, 17 protons, 18 neutrons & 3 energy levels.
During the chemical reaction, the oxygen atom (O) gains two electrons and changes into a negative ion (O−2), which carries two negative charges, Neutral oxygen atom (O) contains 8 electrons, 8 protons, 8 neutrons & 2 energy levels, Negative oxygen ion (O−2) contains 10 electrons, 8 protons, 8 neutrons & 2 energy levels.
Both a sodium ion and an oxygen ion have the same number of electrons because a sodium ion is formed when a sodium atom loses one electron and changes into (Na+) which contains 10 electrons, while an oxygen ion is formed when an oxygen atom gains two electrons and changes into (O−2) which contains 10 electrons too.
The ion
The ion is the atom of an element that loses or gains an electron or more during the chemical reaction. When an atom changes into an ion, the mass number remains as the same without change, while the number of electrons changes. The number of electrons of an ion differs from that of its atom because the number of electrons in ion is less than or more than its number in the same atom by the number of lost or gained electrons.
The positive ion diameter is smaller than its atomic diameter when the atom loses an electron or more, its diameter decreases, and consequently, its volume decreases due to lack of the electrons rather than the protons, and the attraction of nucleus to the remaining electrons increases.
The negative ion diameter is bigger than its atomic diameter, By gaining an electron or more, the atom diameter increases and its volume increases due to the increase in the number of the electrons rather than the protons and the occurrence of repelling.
When an atom gives an electron or more, it becomes a positive ion because the number of electrons becomes less than the number of protons. When an atom gains an electron or more, it becomes a negative ion because the number of electrons becomes more than the number of protons.
The number of energy levels in the ion of a metallic element is less than the number of energy levels in its atom because the atom of a metallic element loses the outermost electrons forming a positive ion.
A sodium atom (11Na) tends to form a positive ion, while oxygen atom (8O) tends to form a negative ion because sodium atom loses its outermost electron and changes into a positive ion, while oxygen atom gains two electrons to complete its outermost level and changes into a negative ion.
Comparison between the atom & ion
The atom is electrically neutral in its ordinary state, The number of electrons equals the number of protons, its outermost energy level is not completely filled with electrons except atoms of noble gases.
The ion is a positive or negative electric charge, The number of electrons is more or less than the number of protons, its outermost energy level is completely filled with electrons.
Noble (inert) gases
Noble gases are elements in which the outermost electron shells are completely filled with 8 electrons (except helium which has 2 electrons in its outermost electron shell). Therefore: They don’t participate in any chemical reaction in ordinary conditions, their molecules consist of one single atom (monoatomic), they don’t form positive or negative ions in ordinary conditions.
Noble (inert) gases are the elements that don’t participate in any chemical reaction in ordinary conditions due to the completeness of their outermost energy levels with the electrons.
You can follow science online on YouTube from this link: Science online
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Modern periodic table and classification of Elements
Metallic & nonmetallic property, Acidic & basic property in the periodic table
The properties of the noble (inert) gases
Chemical bonds, Ionic bonds, Properties & types of covalent bonds
Radius property, Ionization potential, Electron affinity & Electronegativity
The classification of metals according to their chemical activity