Chemical activity series, Chemical properties of metals and nonmetals
Nonmetal oxides are known as acidic oxides because they dissolve in water forming acidic solutions, we can use water to differentiate between calcium and zinc because calcium can react with cold water, while zinc reacts with hot water vapour at high temperature only.
Chemical properties of metals
Reaction of metals with dilute acids
When you put a piece of magnesium strip in a test tube and add some dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl), gas bubbles are evolved. Active metals such as magnesium (Mg) and zinc (Zn) react with dilute acids (as hydrochloric acid) forming a salt of an acid and hydrogen gas which burns with a pop sound on approaching a burning match to it.
Active metal + Acid → Salt of acid + Hydrogen gas
Mg + 2HCl→ MgCl2 + H2 ↑
Reaction of metals with oxygen
Ignite one end of a magnesium strip until it burns then put it inside a jar filled with oxygen gas, Magnesium strip burns with a bright light and changes into a powder (magnesium oxide).
Add some water to the produced substance (magnesium oxide) with shaking, then add drops of violet litmus solution. Magnesium oxide dissolves in water. The solution turns into blue.
Metals such as magnesium (Mg) react with oxygen forming metal oxides, which are known as Basic oxides. Basic oxides are metallic oxides, some of them dissolve in water forming alkaline solutions.
Metal + oxygen → Basic oxide
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Some basic oxides (such as magnesium oxide) dissolve in water forming alkaline solutions that turn litmus solution into blue.
Basic oxide + Water → Alkali
MgO + H2O→ Mg(OH)2
A mixture of MgO, MgCl2, and H2O is used in making stones for making blades of knives which are very thin (sharpening knives). All bases aren’t considered alkalis because alkalis are bases dissolve in water, but not all bases dissolve in water.
Chemical activity series
Metals are arranged according to the degree of their chemical activity in a table known as “Chemical activity series”. Chemical activity series is the arrangement of metals in a descending order according to the degree of their chemical activity. The difference in the behavior of some metals with water according to their location in the chemical activity series:
- (K) Potassium, (Na) Sodium: They react instantly with water and hydrogen gas evolves which burns with a pop sound.
- (Ca) Calcium, (Mg) Magnesium: They react very slowly with cold water.
- (Zn) Zinc, (Fe) Iron: They react with hot water vapor (boiling water) at high temperatures only.
- (Cu) Copper, (Ag) Silver: They don’t react with water.
The rise in sodium ion concentration (Na+) in the body causes a rise in blood pressure. so high blood pressure patients are advised to reduce table salt in their food.
Steps to clean silver tools
- Cover the bottom of a plastic plate with aluminum paper (foil), whereas the bright surface is upward.
- Pour the boiling water into the plate and then add 3 spoons of baking powder.
- Immerse the silver tools which you want to clean in water, then leave the tools for 15 minutes.
- Dry the tools after rinsing them with boiling water, then polish them with a piece of wool.
Chemical properties of nonmetals
Reaction of nonmetals with dilute acids
Put a piece of coal (carbon) in a test tube then add some dilute HCl to it. No reaction takes place. so, Nonmetals (such as carbon) don’t react with dilute acids (such as HCl).
Reaction of nonmetals with oxygen
Burn a piece of coal in a burning spoon and put it after complete burning in a jar filled with oxygen. Add some water to the jar with shaking and drops of violet litmus solution. so, The glow increases. The produced substances from burning (carbon dioxide) dissolves in water and the solution turns into red.
Nonmetals such as carbon (C) react with oxygen forming nonmetal oxides, most of them are known as Acidic oxides. Acidic oxides are nonmetallic oxides, which dissolve in water forming acidic solutions.
Nonmetal + Oxygen →Acidic oxide
C + O2 → CO2
Acidic oxides (such as carbon dioxide) dissolve in water forming acidic solutions that turn litmus solution into red.
Acidic oxide + Water → Acid
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
Some oxides as aluminum oxide (Al2O3) are known as “Amphoteric oxides” because they can react with acids as basic oxides and also react with bases as acidic oxides giving in the two cases salt and water.
We can use dilute HCl to differentiate between carbon and magnesium because magnesium is a metal that reacts with dilute HCl and hydrogen gas evolves, while carbon is a nonmetal that doesn’t react with HCl.
The solution of magnesium oxide in water turns the violet litmus solution into blue because magnesium oxide dissolves in water forming magnesium hydroxide (alkaline solution) which turns the litmus solution into blue
The solution of carbon dioxide in water turns the violet litmus solution into red because it dissolves in water forming carbonic acid which turns litmus solution into red
Comparison between metals and nonmetals
Metals are elements, which have less than four electrons in their outermost energy levels, They tend to lose electrons and change into positive ions, They are characterized by the largest atomic sizes, some of them react with dilute acids forming a salt of an acid and hydrogen gas. They react with oxygen forming basic oxides.
Nonmetals are elements, which have more than four electrons in their outermost energy levels, They tend to gain electrons and change into negative ions, They are characterized by the smallest atomic sizes, They don’t react with dilute acids. They react with oxygen forming acidic oxides.
Comparison between basic oxides and acidic oxides
Basic oxides are metal oxides, they are formed by the reaction of metal with oxygen, some of them dissolve in water forming alkaline solutions, their solutions turn litmus solution into blue, such as Na2O & MgO.
Acidic oxides are nonmetal oxides, they are formed by the reaction of nonmetal with oxygen, They dissolve in water forming acidic solutions, their solutions turn litmus solution into red, such as CO2 & SO2.
Graduation of the properties of the elements in the modern periodic table
Modern periodic table and classification of Elements
Elements classification, Mendeleev’s, Moseley’s & Modern periodic table
Classification of elements in Long-form periodic table, Ionization Energy & Oxidation numbers
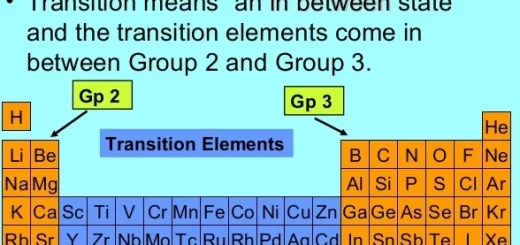
Transition elements & Economic importance of elements of the first transition series
Radius property, Ionization potential, Electron affinity & Electronegativity