Importance and Chemical structure of Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids
They are biological macromolecules ( polymers ) made up of many smaller molecules ( monomers ) called nucleotides , Nucleic acids are composed of hydrogen , oxygen , nitrogen , carbon and phosphorus atoms .
Molecular structure of nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are made up of building units which are the nucleotides that bind together by covalent bounds to form the polynucleotide ( the nucleic acid ).
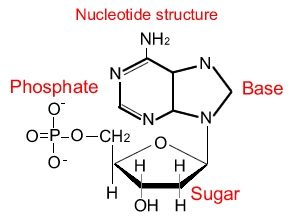
The nucleotide
The nucleotide is the basic building unit of the nucleic acid , It consists of three units which are a pentose sugar molecule , a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base, A pentose sugar molecule contains five carbon atoms, A phosphate group is connected to the carbon atom no.5 of the sugar molecule.
A nitrogenous base is connected to the carbon atom no.1 of the sugar molecule, There are five types of nitrogenous bases, which are Adenine ( A), Guanine ( G), Uracil ( U ), Cytosine ( C ) and Thymine ( T), Uracil is found in RNA only instead of thymine in DNA , Nucleic acids differ according to the difference of the type of sugar and nitrogenous bases forming them .
Classification of Nucleic acids
There are two types of nucleic acids , which are Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA ) , Ribonucleic acid ( RNA ) .
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA )
The type of pentose sugar in the nucleotide is Deoxyribose sugar ( which lacks an oxygen atom than ribose sugar ), Nitrogenous bases are Adenine ( A ) , Guanine ( G ) , Thymine ( T ) and Cytosine ( C ), Number of strands in each molecule is two strands of nucleotides .
Location: Inside the nucleus of the cell where it is involved in the structure of chromosomes .
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA ) importance
It carries the genetic information passing from a generation to another when the cells divide and these information are responsible for appearing the distinctive characteristics of the living organisms and organizing all vital activities of the cells .
Ribonucleic acid ( RNA )
The type of pentose sugar in the nucleotide is Ribose sugar, Nitrogenous bases are Adenine ( A ) , Guanine ( G ) , Uracil ( U ) and Cytosine ( C ), Number of strands in each molecule is single strand of nucleotides, It is transcribed ( formed ) from the nucleic acid DNA inside the cell nucleus then transferred into the cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus .
Ribonucleic acid ( RNA ) importance
Building ( synthesizing ) proteins which the cell needs, These proteins are responsible for appearing the genetic traits and organizing the vital activities .
Bio computer
It was possible to use deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ) in making Biochips that can be used to make the computers much faster than the current devices that rely on silicon chips , Also , their storage capacity will be million greater than the current devices .
Genes, Chromosomes, Proteins, Bacteriophages & Quantity of DNA in the cells
Human karyotype, Chromosomes and Genetic information
Classification of Acids according to its strength (degree of ionization), Its source & Basicity
Classifications of bases according to strength ( degree of ionization ) and molecular structure
Regulation of the cell cycle, DNA synthesis phase, Interphase & Mitosis
Importance of Nucleosides, Nucleotides, Purines, Pyrimidines & Sugars of nucleic acids