Genes interaction ( Non-mendelian characteristics )
Mendelian characteristics are complete dominance characteristics , The factor ( gene ) of dominant character dominates over the factor of recessive one and completely obscures its effect , as the flower colour , seeds colour and shape in pea plant .
But, with a continuation of observations and carrying out experiments on other plants and animals, It is found that some of their characteristics were not inherited according to Mendel’s law and called non-mendelian characteristics , They include cases in which the emergence of genetic traits is affected by the interactions of genes .
Genes interaction ( Non-mendelian characteristics )
Some of these genetic cases such as Lack of dominance , Complementary genes and Lethal genes.
Lack of dominance
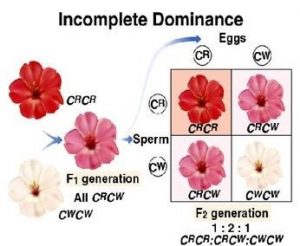
It is a genetic case in which the character is controlled by a pair of genes , no one of them dominates over the other and this happens due to the gene interaction where each one of these genes has an effect in the appearance of a new character .
The ratio in this case is :
In the first generation ( F1 ) : 100 % new character .
In the second generation ( F2 ) : 1 : 2 : 1
1 ( Character of one parent ) : 2 ( New character ) : 1 ( Character of the other parent ) .
Such as Inheritance of flower colour character in Antirrhinum plant and Inheritance of blood group ( AB ) in humans .
Inheritance of flower colour character in Antirrhinum plant
When crossing a red-flowered plant ( RR ) with a white-flowered plant ( WW ) , the plants of first generation ( F1 ) are purple-flowered (RW ) , new character appeared where the red colour gene does not dominate over the white colour gene due to the interaction of genes , as each gene of the allelmorphic genes has an effect in emergence of the new character .
The genes of characters of lack of dominance are symbolized by capital letters because no character of them dominates over the other .
When the plants of first generation are self-pollinated and their seeds are cultivated , the plants of second generation ( F2 ) have red , purple and white flowers in ratio 1 : 2 : 1 , respectively .
In scientific references , it is mentioned that crossing a red-flowered plant with a white-flowered one will produce generation of pink-flowered plants not purple .
Complete dominance
Genes of one character dominate over the genes of the other character , The dominant character appear in all members in ratio 100 % in the first generation ( F1 ) .
Ratio of F2 individuals : F2 generation includes two groups of individuals , A group has the dominant character , The other group has the recessive character in ratio 3 : 1 , respectively .
Phenotype does not include the genotype in case of the dominant character and indicates it in case of recessive character , such as Flower colour in pea plant .
Lack of dominance
Genes of one character do not dominate over the genes of other character , A new character appear in all members in ratio 100 % in the first generation ( F1 ) .
Ratio of F2 individuals : F2 generation includes three groups of individuals , The first has character of one parent , The second has a new character , The third has the character of the other parent in ratio 1 : 2 : 1 , respectively .
Phenotype indicates the genotype , such as Flower colour in Antirrhinum plant .
Complementary genes, Lethal genes and Effect of environmental conditions on action of some genes
Inheritance of blood group ( AB ) in humans and Steps of determining of a blood group type