Complementary genes, Lethal genes & Effect of environmental conditions on action of some genes
Complementary genes
They are genes that work together to emerge a specific trait where the inheritance of this trait is controlled by two pairs of genes and the emergence of dominant character depends on the presence of a dominant gene at least in each pair.
Whereas absence of any pair of dominant genes or both will lead to disappearance of the dominant character and the recessive character appears , The ratio in the first generation ( F1 ) is 100 % dominant and in the second generation ( F2 ) is 9 ( dominant ) : 7 ( recessive ) .
Example : Inheritance of flower colour in pea flower plant , where pink colour is the dominant character , while the white colour is the recessive one .
When crossing a white-flowered plant ( AAbb ) with a white- flowered plant ( aaBB ) , the plants of F1 have pink flowers ( AaBb ) in ratio 100 % , where they gather a dominant gene from each pair .
When F1 plants were self-pollinated and their seeds were cultivated , the F2 plants have pink flowers and white flowers in ratio 9 : 7 , respectively .
In scientific references , it is mentioned that crossing a white-flowered plant ( AAbb ) with a white-flowered one ( aaBB ) will produce a generation of purple-flowered plants not pink .
Explanation : The appearance of the dominant character requires the gathering of a dominant gene or more from both pairs because both dominant genes participate to produce the dominant character where each of them controls the production of a specific enzyme that affects the formation of the pigment of colour.
This indicates the complement of genes action , where in this case the dominant character can be obtained from two parents , each carries the recessive character .
It is noticed that the ratio of second generation ( F2 ) in case of complementary genes ( non-mendelian characters ) is 9: 7, whereas the ratio of the second generation in case of law of independent assortment of genes ( Mendelian characters ) is 9 : 3 : 3: 1.
Lethal genes
They are genes when found in pure state ( dominant or recessive ) cause harms to the living organism resulting in disruption of some vital processes and leading to the death of organism in different stages of life.
Types of lethal genes are Dominant lethal genes ( such as Gene of yellow fur colour in mice and Gene of bulldog strain in cattles ) and Recessive lethal genes ( Gene of chlorophyll absence in corn plant and Gene of infantile dementia in humans ) .
Dominant lethal genes
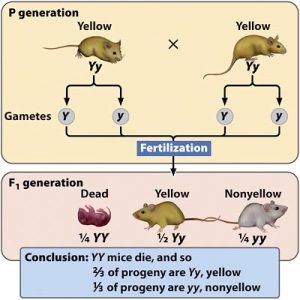
Example : Inheritance of fur colour in mice :
The gene of yellow fur color in mice ( Y ) dominates over the gene of gray fur colour ( y), The presence of a pair of pure ( homozygous ) dominant genes of yellow fur colour causes the death of yellow mice inside their mother’s uterus.
The dead mice represent about ¼ of the resulted generation ( 25 % ) , The inheritance of this character takes place through heterozygous parents in their genotype .
Example : what is the percentage of loss of mice when a yellow male mice is mated with a gray female mice ?
There is no loss in mice due to the lack of a pair of dominant pure ( homozygous ) lethal genes converted together ( there are no pure yellow mice among the individuals of the resulted generation ) .
Recessive lethal genes
Example: Inheritance of chlorophyll absence character in corn plant :
The gene of chlorophyll presence ( C ) in corn plants is dominant over the gene of chlorophyll absence ( c).
When some corn plants were self-pollinated and their seeds were cultivated , some seedlings free of chlorophyll ( white coloured ) were shortly grown , then wilt and die due to the presence of a recessive lethal gene , This gene is the chlorophyll absence gene .
The convergence of a pair of chlorophyll absence recessive genes ( in a pure state ) in some seedlings leads to the prevention of formation of chlorophyll substance that acquires plants their green colour and responsible for absorbing light energy needed for photosynthesis .
The seedlings that wilt and die represent ¼ of the resulted generation ( 25 % ) , The inheritance of this character takes place through heterozygous parents in their genotype .
Effect of environmental conditions on action of some genes
Modern researches have proven that the action of some genes is affected by the factors surrounding the living organism, Studying these factors helps in avoiding risks that may arise from them, such as Air pollutants, Oxygen deficiency, Exposure to rays, Some environmental factors as light and temperature.
Effect of light on appearance of chlorophyll character in green plants :
The gene responsible for chlorophyll formation in green plants needs the light factor to show its effect.
In absence of the gene causing the appearance of chlorophyll , the plant can not form chlorophyll pigment even if it was placed in light.
The internal cabbage leaves are coloured white because they are not exposed to light needed for appearing the effect of the gene of green chlorophyll pigment, on contrast the external leaves are characterized by the green colour due to their continuous exposure to light which helps the formation of chlorophyll .
When exposing internal cabbage leaves to light , they are changed to the green due to the appearance of the effect of chlorophyll gene .