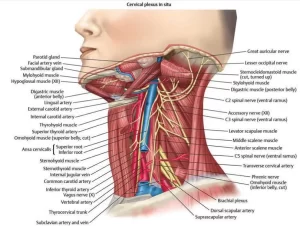
Triangles of the neck contents, Structure of Anterior and Posterior triangle of the neck
Neck triangles are the topographic areas of the neck bounded by the neck muscles, The sternocleidomastoid muscle divides the neck into the two major neck triangles; which are the anterior triangle and the posterior triangle of the neck, each of them containing a few subdivisions, The neck triangles house all the neck structures, including glands, nerves, vessels, and lymph nodes.
Triangles of the neck
The side of the neck is divided by the sternomastoid muscle into:
- Anterior triangle in front of the muscle.
- Posterior triangle behind the muscle.
Sternomastoid (sternocleidomastoid) muscle
Origin:
- The sternal head: anterior surface of the manubrium.
- Clavicular head: medial 3/1 of the upper surface of the clavicle.
Insertion: lateral surface of the mastoid process and lateral 2/1 of the superior nuchal line.
Action:
- Acting on one side, it tilts the head to the same side and rotates the face to the opposite side.
- Acting together, the muscles of the two sides flex the neck forwards.
Nerve supply: spinal accessory nerve (XI), with sensory supply from C2 and C3 (for proprioception).
Digastric muscle
Origin:
- The anterior belly: arises from a depression on the inner side of the lower border of the mandible (digastric fossa).
- The posterior belly: arises from the mastoid notch of the temporal bone.
Insertion: the two bellies meet in an intermediate tendon which perforates the stylohyoid muscle and runs in a fibrous sling attached to the body of the hyoid bone.
Action: elevates the hyoid bone; depresses the mandible.
Nerve supply:
- The anterior belly is supplied by the mylohyoid nerve because it is a muscular derivative of the first pharyngeal arch.
- The posterior belly is supplied by the facial nerve (VII) because it is a muscular derivative of the second pharyngeal arch.
Omohyoid muscle
Origin:
- Superior belly: from the lower border of the body of the hyoid bone.
- Inferior belly: from the upper border of the scapula and suprascapular ligament.
Insertion: by an intermediate tendon that lies on the internal jugular vein and is held in position by a fascial sling connecting it to the clavicle.
Nerve supply: ansa cervicalis.
Posterior triangle of the neck
I. Boundaries:
- Anterior: posterior border of the sternomastoid muscle.
- Posterior: anterior border of trapezius muscle.
- Base: intermediate third of the clavicle.
- Apex: at the superior nuchal line.
- Roof: the investing layer of deep cervical fascia.
- Floor: is formed of the following muscles covered with prevertebral fascia; (muscles are arranged from below upwards): Scalenus medius. Levator scapulae. Splenius capitis. Semispinalis capitis.
II. Contents of the posterior triangle
1. Arteries:
- Subclavian artery (3rd part).
- Suprascapular artery.
- Transverse cervical artery.
- Occipital artery.
Notice that the suprascapular and the transverse cervical arteries are branches from the thyrocervical trunk of the first part of the subclavian artery.
2. Veins:
- Subclavian vein.
- External jugular vein & its tributaries.
3. Nerves:
- Roots and trunks of the brachial plexus & their branches: From the roots (nerve to rhomboids & nerve to serratus anterior muscle). From the upper trunk (suprascapular nerve & nerve to subclavius muscle).
- Spinal part of the accessory nerve.
- Cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus: Great auricular nerve. Transverse cervical (cutaneous) nerve. Lesser occipital nerve. Supraclavicular nerve.
4. Muscles: the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle.
5. Lymph node: occipital and supraclavicular lymph nodes.
Suboccipital triangle
I. Boundaries:
- Superomedial: rectus capitis posterior major
- Superolateral: superior oblique of head.
- Inferolateral: inferior oblique of head.
- Floor: posterior atlanto-occipital membrane and posterior arch of atlas.
- Roof: semispinalis capitis & splenius capitis. The roof is traversed by the greater occipital nerve.
II. Contents: vertebral artery, suboccipital nerve and suboccipital plexus of veins.
Anterior triangle of the neck
1. Boundaries:
- Anteriorly: midline of the neck.
- Posteriorly: anterior border of sternomastoid muscle.
- Base: formed by the lower border of the body of the mandible.
Subdivisions of the anterior triangle
- Submental triangle.
- Digastric triangle.
- Carotid triangle.
- Muscular triangle.
1. Submental triangle
Boundaries:
- Anterior belly of the right digastric muscle.
- Anterior belly of the left digastric muscle.
- Hyoid bone Inferiorly.
Floor: is formed by the two mylohyoid muscles & their raphe.
Contents:
- Submental lymph nodes.
- Submental plexus of veins.
- Submental branch of the facial artery.
- Nerve to mylohyoid
2. Carotid triangle
Boundaries:
- Anterior border of sternomastoid.
- Posterior belly of the digastric muscle.
- Superior belly of Omohyoid.
Floor: is formed by hyoglossus, thyrohyoid, and middle and inferior constrictor muscles of the pharynx.
Contents:
- Carotid sheath and its contents.
- External carotid artery (lower part) and some of its branches.
- Sympathetic trunk.
- Upper and lower deep cervical lymph nodes.
- Last three cranial nerves (X, XI, XII).
- Ansa cervicalis.
3. Digastric triangle
Boundaries:
- Lower border of the mandible.
- Anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle.
Floor: is formed by mylohyoid and hyoglossus muscles.
Contents:
- Submandibular salivary gland.
- Submandibular lymph node.
- Facial artery and anterior facial vein.
- Hypoglossal nerve and nerve to mylohyoid.
4. Muscular triangle
Boundaries:
- Superior belly of Omohyoid.
- Anterior border of sternomastoid.
- The midline of the neck.
Contents: infrahyoid muscles which are arranged in two layers:
- The superficial layer formed of the superior belly of the omohyoid laterally and sternohyoid muscle medially.
- Deep layer formed of thyrohyoid & sternothyroid muscles.
All infrahyoid muscles are supplied by ansa cervicalis (C1, C2 & C3) except thyrohyoid muscle (supplied by C1 only).
You can subscribe to science online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science Online Apps on Google Play
Cranial nerves anatomy, function, Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal and Abducent
Facial muscles function, anatomy, arteries, veins, names and expressions
Skull function, anatomy, structure, views and Criteria of neonatal skull
Anatomy of the circulatory system, Vascular system, Arteries of head and neck