Computer technology in dentistry (Digital dentistry) uses, types, cons and pros
Dentistry relies heavily on technology and highly implements new techniques, It is a branch of medicine that involves research, teaching, and administration, Patient care is based on the generation, storage, and manipulation of information, and computers can handle a large amount of such data, The use of computer graphics has enabled simulation of the cosmetic changes to be presented to the patient with before & after possibilities.
Digital dentistry
If you use digital dentistry, You can carry out dental procedures more efficiently than using mechanical or electrical tools, It can range from CAD/CAM (computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing) to those that may not be recognized, such as the computer-controlled delivery of nitrous oxide.
Many areas are used in digital dentistry such as CAD/CAM and intraoral imaging ( both laboratory- and clinician-controlled), Caries diagnosis, Computer-aided implant dentistry (such as design and fabrication of surgical guides), Digital radiography (The intraoral and extraoral, including cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)).
There are many other areas of digital dentistry available, such as the electric and surgical/implant hand-pieces, Lasers, Occlusion and TMJ analysis and diagnosis, Photography including digital patient education, and Shade matching, digital dentistry contains three things, which are Improved efficiency, both cost and time, Improved accuracy in comparison to previous methods and a high level of predictability of outcomes.
Special software is provided by the manufacturers for the design of various kinds of dental restorations, With such software, crown & fixed partial dentures (FPD) frameworks can be constructed, Some systems offer the opportunity to design full anatomical crowns, partial crowns, inlays, inlay retained FPDs, as well as adhesive FPDs and telescopic primary crowns.
Digital dentistry applications
Computers are used for many purposes in the field of dentistry, They can be broadly classified as Administrative applications, Clinical applications and other applications, There are many administrative applications, The computers are used in the administration field, They are aimed at the smooth running of dental clinics, hospitals, and dental institutions.
There are many activities in the administrative applications such as Patient appointments and recalls, Correspondence, Billing and Accounting, Inventory controls and supply orders, Dental insurance claims, Document preparation and word processing, Referral information, Missed appointments, and follow-ups.
There are many clinical applications, The computers are very useful for dentists in their professional practice, Such as Patient records storage and retrieval, Patient evaluation, examination and treatment planning, Patient motivation and awareness, and Appliance designing using CAD, and CAM techniques.
The computers are very useful in Radiovisuography (RVG) techniques, Clinical diagnosis and treatment planning, Storage of patient photographs, radiographs, and study models, Computerized imaging techniques, and Computerized Cephalometrics and Growth prediction.
There are many other applications, Besides administrative purposes and clinical uses, The other applications include creating a database of survey information, Case presentations, Conference presentations, Reviewing literature and Continuing medical education.
Technological advances in industrial manufacturing have contributed to the improvement in productivity and quality of dental care, There are many benefits such as collecting, sorting, and searching the data, The efficiency and productivity are increased through computer appointments, recall, and practice analysis programs.
Digital Radiography
The digital images can be stored on the computer easily and they can be transferred to different dentists or orthodontists for referrals, You can enhance the digital image (such as altering brightness and contrast) with a series of processing techniques, Digital Radiography helps you in Digital archiving, It produces larger photos to better source hard-to-see cavities.
Digital radiography provides you with improved comfort of intra-oral X-rays, performed by intra-oral dental assistants and less cranial exposure to radiation, It is more environmentally friendly in the long run and it is cheaper, Grey-scale of digital X-rays has 256 shades of grey versus 16-25 shades in conventional radiography.
Film sensors are less thick and rigid than digital sensors, So, They offer the patient better comfort when the X-ray sensors go into their mouths, Film presents superb picture quality, You do not need extra training to use conventional X-ray machines and it is standard in most dental offices.
Unlike digital X-ray sensors that must use plastic disinfectant covers, conventional film sensors can withstand heat sterilization, Film X-ray photos cannot be altered, whereas digital ones can, The possibility of alteration exposes digital radiography to fraudulent use and legal issues.
The main benefits of digital radiography include lower radiation (when following the ALARA principle), significant time reduction, ease of storage and organization, and image enhancements for quick and improved viewing.
There are many new and existing developments such as wireless sensors (both CCD/CMOS and PSP), caries diagnosis (Logicon by Carestream Dental), an Intelligent Positioning System for quick and easy digital alignment of the tube head to the sensor (Carestream Dental) and integration with the tablets and voice activation.
Cone-beam computed tomography
Cone-beam computed tomography is a superb technology, It has seen rapid growth due to decreased costs, It offers many options to choose from, an increased number of general dentists placing implants, and decreased radiation, It is quickly adopted by most specialties and becoming the proposed standard for many surgical procedures, Such as implant placement, third-molar removal and endodontics.
Lasers
Advances in lasers contain the expanded use in every field of dentistry, Many users have integrated lasers very effectively into their practices and their observations, Diode laser offers lower-cost areas of digital dentistry to adopt and it is very easy to use, It is used in periodontics, endodontics, surgery and prosthodontics.
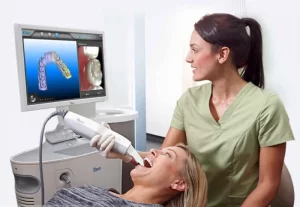
CAD/CAM and intraoral imaging
The term CAD/CAM in dental technology is used as a synonym for prostheses produced by milling technology, CAD is the abbreviation for computer-aided design, and CAM stands for computer-aided manufacturing, The term CAD/CAM does not offer any information on the method of fabrication.
All CAD/CAM systems consist of three components, which are the digitization tool/scanner that transforms geometry into digital data that can be processed by the computer, Software that processes data and depending on the application, It produces the data set for the product to be fabricated and a production technology that transforms the data set into the desired product.
CAD/CAM for dental manufacturing and the dental laboratory profession is faster, more economical, predictable, consistent and relatively accurate, All components of the CAD/CAM system are located in the dental surgery, and Fabrication of dental restorations can take place at the chairside without a laboratory procedure.
The digitization instrument is an intra-oral camera, which replaces a conventional impression in most clinical situations, This saves time and offers the patient indirectly fabricated restorations at one appointment, One of the benefits of this very mature system is the software that has been supplemented by a very exact three-dimensional reconstruction of the occlusal surface.
Laboratory production
The dentist sends the impression to the laboratory where the master cast is fabricated first, These data are processed by means of dental design software, After the CAD process, the data will be sent to a special milling device that produces the real geometry in the dental laboratory.
The exact fit of the framework can be evaluated and corrected based on the master cast, The ceramist carries out the veneering of the frameworks in a powder layering or over-pressing technique.
Moving dental data into the cloud
One benefit is lower computer costs, You can use any brand of computer such as a Mac or PC, You won’t need as much processing power, Your computer can be less expensive, It has less memory and a more economical and efficient processor.
There are instant software updates, You never install software, Every time you access the system you’re using the latest version, You won’t experience downtime due to hardware and servers that must be shut down to install an update.
There is unlimited storage capacity, No matter how big your practice grows, you will not need to buy more memory in the form of hard drives and disks to accommodate the expanding patient database.
You can log on from any computer and update your notes or schedule wherever you are, The documents and applications are the same no matter what computer or device you are using.
Cloud computing offers high reliability on the data, If your practice burns to the ground or your computers are stolen, your practice data is unaffected, It will be stored in the cloud, and there will not be any downtime to retrieve your patient and practice-management data.
The main drawback of moving all of your dental information into the cloud is the security, There is a fear that when your practice information is moved to the cloud that you lose control of security, Although, dental software companies who host Web-based software have better security measures than what a dentist can achieve internally, they should incorporate the latest security measures continually to keep your data safe.
If you use web-based dental software, It requires a constant data connection, but good Internet connections are still difficult to find, So, Web-based dental software will work with low-speed connections.
Digital dentistry disadvantages
The main limitation of digital dentistry is cost, To adopt new technology often requires a higher capital investment, especially at the innovator or early adopter stage, Misunderstanding the new technology tends to foster slower adoption rates, This scenario can be easily avoided by greater attendance of basic and advanced hands-on courses in these areas of technology — not just the state’s minimum to maintain the dental license.
One of the popular pitfalls in adopting new dental technology is a lack of desire on the part of the clinician and the team to be adequately trained, Some clinicians will purchase new technology, but they never read the owner’s manual or seek advanced training on how to operate the technology efficiently, So, leading to high failure and abandonment.
Dental Robotics uses, advantages, disadvantages, types & Yomi robot
Nanobots in dentistry, Dental Implantology, Micromachine for automatic endodontic treatment
Cone beam CT vs. Fan beam CT, CBCT advantages, disadvantages & uses
The importance and uses of computer technology in pharmacy
Computers in Medicine uses, advantages and disadvantages
Biological computers mechanism, uses, pros and cons
You can subscribe to science online on YouTube from this link: Science Online
You can download Science Online application on Google Play from this link: Science Online Apps on Google Play