Radioactivity, Nuclear reactions (Natural transformation of elements) & Half-Life time
Nuclear reactions are different from the chemical reactions , Since chemical reactions occur between the atoms of the reactant elements by the binding between the electrons of the outermost energy levels & no change occurs to the nuclei of these atoms , Whereas, nuclear reactions include the change in the composition of the nuclei & formation of atoms’ nuclei of new elements .
Nuclear reactions
Nuclear reactions are the reactions that include the change in the composition of the nuclei of the reactants elements and the formation of new nuclei when the nuclei of the reacting atoms interact , The nuclear reactions can be classified into four types :
- Natural transformation of elements ( Natural Radioactivity )
- Nuclear transformation .
- Nuclear fission reactions .
- Nuclear fusion reactions.
First : Natural transformation of elements
Discovery of radioactivity phenomenon : In 1896 the scientists , Henri Becquerel discovered – coincedently – a kind of invisible radiations produced from one of the uranium compounds leading to form a shadow on a sensitive photographic film .
In 1898 Marie Curie named this phenomenon by Radioactivity , Researchers paid their attention to know the nature of these emitted rays and compare their properties by the following two methods which are :
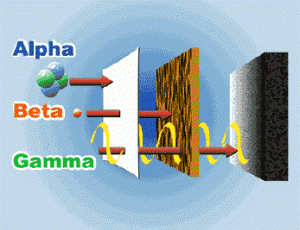
Testing the ability of rays to penetrate substances , testing the deviation of rays by the effect of both the magnetic and electric fields , The experiments inferred that there are three different radiations , which are Alpha radiation ( α ) , Beta radiation ( β ) and Gamma rays ( γ ) .
Alpha radiation ( α )
It consists of the nucleus of helium atom ( 2 protons + 2 neutrons ) , The emission of an α – particle from the nucleus of a radioactive element atom leads to from a new element which has an atomic number ( Z ) less than the original element by 2 and a mass number ( A ) smaller by 4 .
The nuclear equation is considered a balanced equation because the sum of mass and atomic numbers of reactions and products are equal , α – particle differs than helium atom , although they have the same symbol because α – particle is a nucleus of helium which carries a positive charge , while helium is a neutral atom .
Emission of α – particles accompanied by formation of a new element ( elemental transformation ) because by the emission of α – particle from the nucleus of a radioactive element , a new element nucleus is formed with an atomic number less than that of the parent nucleus by 2 .
Beta radiation ( particles ) ß−
Beta radiation are particles that carry the characteristics of electrons in terms of mass , charge and speed , The mass of beta particles is ignored ( negligible ) , compared to the atomic mass unit ( u ) , The charge of beta particle = –1 .
Emission of ß− – particle is accompanied by elemental transformation to form a new element nucleus whose atomic number is greater by one than the parent nucleus , while its mass number remains fixed , where beta particle is produced from of a neutron to proton .
The emission of beta particle is accompanied by elemental transformation because the emission of ß− – particle from the nucleus of a radioactive element , a new element nucleus is formed with atomic number higher than of the parent nucleus by 1 .
Emission of beta particle produces a new element , in which the atomic number of daughter nuclei is higher than that of parent nuclei by 1 , but no charge in the mass number ( A ) because the emission of ß− – particle is due to the transformation of a neutron into a proton .
Gamma rays ( γ )
They are electromagnetic waves with a very short wavelength , its speed equals the speed of light , It has no charge and no mass , So , its emission doesn’t lead to any change in atomic or mass numbers , The high energy of γ – rays is due to their frequency and their short wavelength .
Emission of γ – rays isn’t accompanied by change of atomic or mass numbers , this is attributed to the nature of γ – ray , it is photons that have no mass and no charge .
Half-Life ( t½ )
The scientists concluded from the studying of radioactivity that the radiation activity decreases with time and also found that the ratio between the number of the disintegrated atoms in a second to the number of atoms present at a certain moment is a constant ratio and this ratio is called Half-life time ( t½ ) .
Half-life time ( t½ )
It is the time required to disintegrate half the original number of the atoms’ nuclei of a radioactive element , The half-life ( t½ ) is repeated at equal periods of time , Half-life ( t½ ) is constant for each radioactive element , but it differs from one radioactive element to another and it might be seconds or millions of years .
The half-life ( t½ ) calculated from the following relation :
Half-life ( t½ ) = Total decay time ( t ) ÷ Number of periods ( D )
The half-life ( t½ ) phenomenon can be used to determine the age of rocks and mummies by using the half-life ( t½ ) of C-14 isotope , When the half-life of iodine – 131 = 8 days , This means that the time required for decaying half the number of the atoms’ nuclei of the radioactive iodine element equals 8 days .
Nuclear Transformation , Nuclear fission bomb and Nuclear fission reactor