Density of matter, Life applications of density, What does density mean?, How is density calculated?
Each substance has its density, The density is a physical property of the matter as each element and compound has its density, and it varies with the temperature and the pressure.
Density
It is a fundamental property of matter, It is defined as the mass of a substance per unit volume, It is expressed using the formula: Density=Mass/Volume.
The mass is the amount of the matter that the body contains, and its measuring unit is (kg) or (gm), The volume is the space that a substance occupies, and the density is the mass of a unit volume of the matter or it is the mass of one cubic centimeter of the matter.
The units of density are kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), Density helps describe how compact or spread out the matter within a substance is.
Equal masses of different substances have different volumes, and equal volumes of different substances have different masses as they have different densities, Some substances float on the water surface and others sink in the water due to the difference in their densities.
The materials which have a higher density than the water sink in it such as iron nails and metallic coins, while the materials which have a lower density than the water float on its surface such as the wood, the cork, the ice, and the drops of oil.
Density of Matter
In the context of different types of matter, density plays a vital role in various physical phenomena:
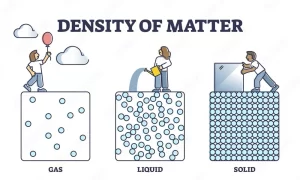
- Solids have high density because their particles are packed closely together, Metals such as iron or gold have much higher densities than non-metals like wood or plastic.
- Liquids have lower densities compared to solids, Water has a density of 1 g/cm³ at room temperature. However, some liquids such as mercury have unusually high densities.
- Gases have much lower densities because their particles are spread far apart, The density of a gas can change with temperature and pressure, as seen in the behavior of air at different altitudes or weather conditions.
- Plasma: This state of matter, like the sun’s core or fusion reactors, can have a wide range of densities depending on energy input and conditions, though it is less relevant for everyday life.
Life applications of the density
The water is not used to put out the petrol fires as the density of petrol is less than of the water so, the petrol floats on the water surface and the water does not put out the fire.
The balloons filled with hydrogen or helium rise up in the air carrying flags during the festivals as the densities of hydrogen and helium are less than the density of the air.
The determination of the change in the density of the matter is taken as evidence of the purity of the matter as the determination of the quality of the milk.
The principle of Floating is related to density. Objects float in a fluid (like water or air) if their density is less than that of the fluid, This is why boats float (even though they’re heavy) and why hot air balloons rise—because hot air is less dense than cool air.
Engineers and designers consider density when selecting materials for construction or manufacturing. aircraft and spacecraft must use materials that are strong yet lightweight, meaning they have low density but high strength, such as aluminum or carbon composites.
In medicine, the density plays a vital role in diagnostic imaging. X-rays or CT scans can differentiate tissues based on their densities (bone, which is dense, versus soft tissue or fat). Body Mass Index (BMI) indirectly relates to density, as it considers a person’s mass relative to their height.
Earth’s structure is understood through density variations. the Earth’s core is extremely dense (due to high-pressure iron and nickel), while the crust is less dense. These density differences also affect tectonic plate movements and seismic wave propagation.
In chemistry, density is used to identify substances. A hydrometer is an instrument used to measure the density of liquids and is commonly used in industries like brewing or dairy to check fluid quality.
The density of food can affect its texture and flavor. the density of dough in baking determines whether bread turns out light and fluffy or dense and chewy. It helps in determining calorie content, as more dense foods contain more energy.
The properties and the measuring devices of the mass
Properties of fluids, Factors affecting density and pressure
Matter, Properties & Kinds of molecules, Melting process & Vaporization process