The atomic structure of the matter
The atom
The atom is the fundamental building unit of the matter, and it is the smallest individual unit of the matter which can share in the chemical reactions, Boyle, Thomas, Rutherford and Bohr are from the scientists who contributed the discovery of the atom construction.
The atomic radius of an atom is measured by a unit called Angstrom, and one Angstrom equals a part of ten thousands million parts of one metre, The radius of hydrogen atom equals 0.3 Angstrom, and this indicates how much the atom is small.
The atomic construction
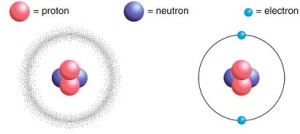
The atom consists of the nucleus and the electrons, and it is electrically neutral in its ordinary state, The nucleus is the central core of the atom, where the mass of the atom is concentrated in it.
The nucleus is positively charged as it contains the protons (positively charged particles) and the neutrons (electrically neutral particles), The atomic number and the mass number to express the atom of any element.
The atomic number is the number of the protons in the nucleus of an atom, and it is written below the symbol from the left, The mass number is the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom, and it is written above the symbol from the left side.
The electrons are negatively charged particles, they revolve around the nucleus with very high speed, The electrons have a negligible mass relative to that of the protons or the neutrons, so the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
The number of the negative electrons which revolve around the nucleus is equal to the number of the positive protons in the nucleus, so the atom is electrically neutral in its ordinary state.
Evolution concept of the atomic structure, Atomic theory & Properties of cathode rays
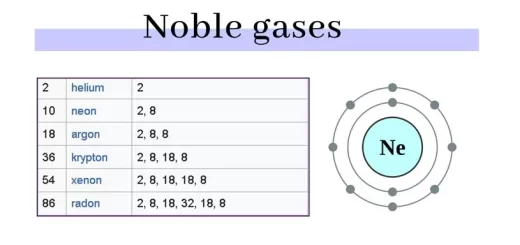
Atoms components, Rutherford and Bohr’s Atomic Models
Chemical combination, Types of bonds (Chemical bonds & Physical bonds)
Theories explaining the covalent bond, Octet rule & Overlapped orbitals concept