The structure and function of the brain in the central nervous system
The human brain
The central nervous system is composed of the brain and the spinal cord, the brain is a nerve block containing millions of the nerve cells (the neurons) and it is the main control center in your body.
The brain is located inside a bony box called the skull to protect it, It directs and coordinates all the processes ideas, the behaviours and the emotions, and it weighs about 1.5 kg in the adult human.
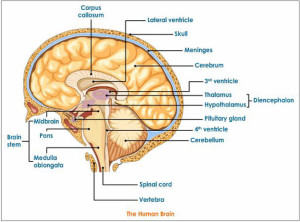
The brain of the human consists of three main parts which are the cerebrum (two cerebral hemispheres), the cerebellum and the medulla oblongata.
The cerebrum (the two cerebral hemispheres)
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain? It is divided into two halves (the right and the left) called the two cerebral hemispheres, The cerebral hemispheres are separated by a fissure and attached to each other through the nerve fibres.
The outer surface of the two hemispheres is called the cerebral cortex and it is a grey matter, but the inner surface is called the white matter, The two hemispheres have many convolutions and folds on their surface.
The function of the cerebrum
The cerebrum is a very important part in the brain as it controls the voluntary movements of the body such as running in the races, The cerebrum contains the centers of thinking and memory (the concentration).
The cerebrum receives the nerve impulses from the sense organs (the eyes, the ears, the nose, the tongue and the skin) and send the suitable responses to these impulses.
The cerebellum
The cerebellum lies at the back area of the brain below the two cerebral hemispheres, and it maintains the balance of the body during the movement.
The medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata lies in front of the cerebellum, and it connects the brain with the spinal cord.
The function of the medulla oblongata
Damage to the medulla oblongata causes death, and it is responsible for regulating the involuntary processes of the body as regulating the heartbeats.
The medulla oblongata regulates the movement of the respiratory system parts during the breathing, The medulla oblongata regulates the movements and functions of the digestive system.
Autonomic nervous system, Reflex action types & Autonomic ganglia function
Functions of Sympathetic nervous system & Role of the sympathetic in emergencies
Nervous system in man, Nerve cells types & Nature of nerve impulse
Nervous system (Central nervous system, Peripheral nervous system & Autonomic nervous system)
Human Transport system, Structure of human circulatory system (heart, blood vessels and blood)