The function of pharynx, esophagus and stomach in the digestive system
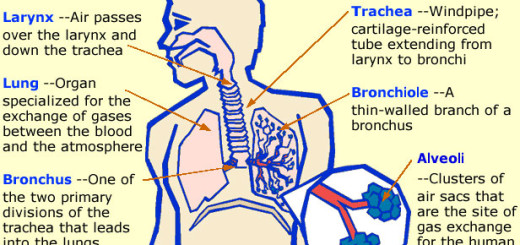
The pharynx is a cavity extending from the mouth to the esophagus, It is a common cavity between the esophagus and the trachea, and the pharynx is a common cavity between the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system.
The pharynx
The conducting zone includes the nose, the larynx, the trachea, the bronchi and the bronchioles, and their function is to filter, warm, and moisten the air and conduct it into the lungs, The human pharynx is divided into three sections which are the nasopharynx, the oropharynx and the laryngopharynx.
The esophagus
The esophagus is a muscular tube connecting to the stomach, and it allows food to pass from the mouth to the stomach, The esophagus is usually from 18 to 25 centimetres (cm) long, and it is behind the trachea and the heart, It passes through the diaphragm.
The esophagus empties into the cardia of the stomach, and during swallowing, the epiglottis prevents the food from going down the larynx.
The stomach
The stomach is a sac-like muscular organ, and it is a hollow, dilated part of the digestive system which located on the left side of the upper abdomen, The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine, and it has a relaxed near empty volume of about 45 to 75 millilitres, and it normally expands to hold about one litre of food.
The stomach secretes the gastric juice that makes the incomplete digestion of the proteins, The stomach receives the food from the esophagus, and enters the stomach through a muscular valve called the lower esophageal sphincter.
The stomach mixes the food with its gastric (digestive) juice to form a semi-liquid substance after a few hours that can be digested easily, The stomach is divided into four sections beginning at the cardia, and each of them has different cells and functions.
The cardia is where the contents of the esophagus empty into the stomach, and the cardia is defined as the region following the z-line of the gastroesophageal junction.
The fundus is formed by the upper curvature of the stomach, the body is the main central region and the pylorus is the lower section of the stomach that facilitates emptying the contents into the small intestine.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Digestion in man, Buccal digestion and Gastric digestion (digestion in stomach)
Small intestine, Absorption of digested food, Metabolism, Large intestine and defecation
Human Transport System, Structure of human circulatory system (Heart, blood vessels and blood)