Anesthesia types, use, advantages, disadvantages
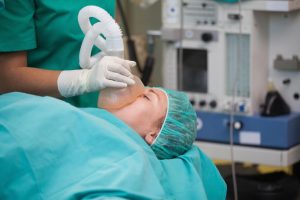
General anesthesia (GA) is the state of induced unconsciousness, It is the state produced when the patient receives the medications for amnesia, analgesia, muscle paralysis, and sedation, Anesthetized patient can be thought of as being in a controlled, reversible state of unconsciousness.
Advantages of Anesthesia
General anesthesia enables the patient to tolerate the surgical procedures that would otherwise inflict unbearable pain, the potentiate extreme physiologic exacerbations, There are three components to the anesthesia, They are Analgesia (the pain relief), Amnesia ( the loss of memory), and Immobilisation.
General anesthesia reduces intraoperative patient awareness and recall, It allows the proper muscle relaxation for the prolonged periods of time, It facilitates complete control of the airway, the breathing, and the circulation, It can be used in cases of sensitivity to the local anesthetic agent, It can be administered without moving the patient from the supine position.
General anesthesia can be adapted easily to procedures of unpredictable duration or extent, It can be administered rapidly and it is reversible, The patient is not unduly stressed during the procedure, It allows complete stillness over prolonged periods of time, and it permits the surgery in widely separated areas of the body at the same time.
The local anesthesia injection numbs just the part of your body requiring minor surgery or a procedure (numbing the small area), The side effects of local anesthesia injection are minimal and they are related to how much the anesthesia is injected.
Disadvantages of Anesthesia
General anesthesia requires the increased complexity of care and the associated costs, It requires some degree of preoperative patient preparation, It is associated with less serious complications such as nausea or vomiting, headache, shivering, and the delayed return to normal mental functioning.
General anesthesia is associated with malignant hyperthermia, the rare inherited muscular condition due to exposure to some general anesthetic agents that results in acute and potentially lethal temperature rise, hypercarbia, metabolic acidosis, and hyperkalemia.
General anesthesia causes the greatest number of side effects and complications, It causes sore throat (caused by the devices used to keep the airway open), It causes drowsiness or feeling tired hours after the surgery, dizziness, and vision problems, and damage to the teeth (caused by airway devices).
General anesthesia also carries the risk for serious complications such as stroke, heart attack, brain damage, The death, The patient’s risk depends on several factors including age, sex, allergies, overall health, underlying medical conditions, and the current use of tobacco, alcohol, and the drugs.
General anesthesia requires a special team of a doctor and technicians, It requires complex and costly machinery, It carries the major risk of the myocardial infarction or the stroke, and it causes the malignant hyperthermia, certain inhaled anesthetics can trigger the disorder called malignant hyperthermia in the people who carry the gene for it.
Regional anesthesia has a higher risk of side effects and complications, It may cause spinal fluid loss which occurs when the anesthetic is injected, The headache is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, light sensitivity, and a stiff neck, It causes Hypotension (low blood pressure).
Regional anesthesia causes an inability to urinate (usually temporary and relieved by catheterization), It causes backache, It causes much less frequently, infection, the nerve damage or the permanent paralysis can occur, It causes temporary weakness or paralysis of the affected area, It causes the headache following the spinal and the epidural anesthesia.
The side effects of the anesthesia can occur during the surgery or procedure, or afterward, The side effects vary, depending on what kind of anesthesia you have the general, the regional, or the local.
Antibiotics advantages, disadvantages, resistance & uses
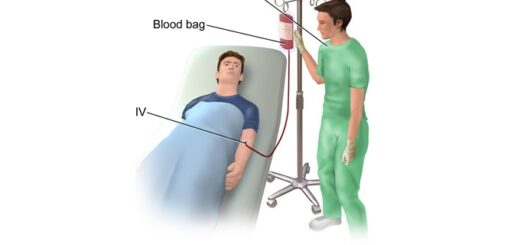
Blood transfusion causes, Haemolytic transfusion reaction & Acute renal failure
Lysis of blood clot, Factors that prevent clot extension & Role of platelets in hemostasis
Blood transfusion causes, Haemolytic transfusion reaction & Acute renal failure


Great idea
Thanks again
You are welcome