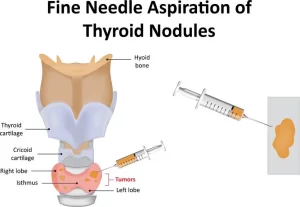
Thyroid nodules, Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy importance and risks
Nodules are more common in women than in men, Thyroid Nodules tend to grow during pregnancy, People who have had radiation treatments to their neck are also more likely to develop nodules. You should need the test to see whether your nodule is cancerous, You can notice the nodule yourself, or your healthcare provider can notice it during an exam or on another test.
Thyroid nodules
They are clumps of soft tissues within the thyroid gland, they can be cancerous or interfere with the proper functioning of the thyroid, so, the nodules need to be treated, Interventional radiologists perform fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB), an image-guided procedure to diagnose thyroid growths.
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the front of your neck, with 2 lobes connected by a narrow band of tissue, It is an endocrine gland, That makes thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism, These hormones affect heart rate, brain function, and other necessary bodily processes.
Hard nodules can be formed inside the gland, they are not dangerous, Thyroid nodules usually don’t cause any symptoms and are generally benign, In rare cases, thyroid nodules are cancerous and require medical intervention.
The most common form of treatment for thyroid nodules is “watchful waiting.” where doctors and patients work together to monitor the nodule with regular checkups, when the nodule needs treatment, your doctor may present common treatments including medication and surgery, but these will vary from patient to patient.
Diagnosing Thyroid Nodules
The thyroid nodule is identifiable as a lump on one side of the neck near Adam’s apple, When your doctor observes a bump that could be a nodule, the next step will be to run some tests to make an official diagnosis, There are four ways your doctor may test for thyroid nodules, These are blood tests, ultrasound, radiology scans, and fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB).
- Blood tests are used for thyroid nodules test for both thyroid hormones, The abnormal level of hormones could signal that the nodule is causing hormonal issues.
- Ultrasound is used to create images of the inside of the body using high-frequency sound waves, Your doctor will order the ultrasound of the bump to determine if it is a thyroid nodule.
- Depending on the nature of the nodule, your doctor may order the CT, MRI, or PET scan, The CT scan uses x-rays to create sectional scans of the thyroid, and MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of the thyroid, The PET scan uses radioactive tracers to help make images of organs and tissue more visible.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB) is performed by interventional radiologists, Interventional radiologists are doctors who perform minimally invasive procedures using medical imaging to provide real-time views inside their patients’ bodies, FNAB is one of the most accurate ways to diagnose thyroid nodules.
Ultrasound can be used to create an image of the growth, Imaging exams can detect nodules or abnormalities within the body, these imaging tests can’t always tell whether a nodule is benign (non-cancerous) or cancerous.
The interventional radiologist can use a small needle to extract the cell sample from the nodule, This sample is tested for cancer and abnormal levels of thyroid hormones, and they can be warning signs of the thyroid condition.
You should notify your physician if you are taking any blood thinning agents, such as aspirin, Lovenox®, Plavix® or Coumadin®, no special preparations are required for this procedure. The biopsy site may be sore and tender for one to two days, You can take nonprescription pain medicine, such as acetaminophen, to relieve any discomfort.
Thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB)
The thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy is the procedure that removes a small sample of tissue from your thyroid gland, Cells are removed through a small, hollow needle, and the sample is sent to the lab for analysis. Some people need medicine to help them relax before the procedure. your healthcare provider can inject a local anesthetic into the area before inserting the needle.
Your healthcare provider may perform the biopsy with the help of an ultrasound machine that uses high-frequency sound waves to offer an ongoing image of the nodule, This allows your healthcare provider to guide the needle to exactly the right spot, It prevents damage to other structures, The gel-like substance will be applied to your neck, where the ultrasound detector will be used.
After cleaning the area, your doctor will insert the thin, fine needle into your thyroid gland, This may hurt a little, He will slowly advance the needle into the nodule itself, moving it back and forth several times, The needle attaches to the syringe that can apply suction and remove some cells from the nodule, After the removal of the needle, these cells will be placed on a slide.
Your doctor may repeat this procedure a few times to obtain different samples from different parts of the nodule, Sometimes the lump will be all or mainly fluid, The fluid can be removed during the biopsy. After the procedure, the cells will be sent to a pathology lab, The pathologist will determine the exact nature of the nodule, and analyze for signs of cancer, A small bandage will be placed over the needle insertion site.
Most patients may experience pain and discomfort for about 48 hours after the biopsy, they have minimal discomfort after the procedure, Post-procedure discomfort is usually managed with over-the-counter pain medications.
What happens after a fine needle aspiration biopsy?
Most people will be able to resume their normal activities right away, You can remove your bandage within a few hours, The site of the biopsy might be sore for a day or two after the procedure, You can take over-the-counter pain medicines if you need to. Follow any other specific instructions that your healthcare provider gives you, It may take several days to get your test results from the pathology lab.
When your thyroid nodule is not cancerous, you might not need any further treatment, Your provider may want to monitor your nodule, and you might need another biopsy in the future, You will need surgical treatment if your nodule appears cancerous. Luckily, most thyroid cancers are curable.
Sometimes, the pathologist can’t determine whether your nodule is cancer, so, your healthcare provider might recommend a repeat biopsy or surgery, Whatever your test results, you can work with your healthcare provider to develop the best possible treatment plan for you.
Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy advantages
Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) is a simple, safe, and effective procedure to determine the nature of the thyroid nodule, When one of the other diagnosis methods is indeterminate, or when your doctor determines you are at a higher risk for thyroid cancer, FNAB can be the best option for you.
Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) is a highly accurate method of determining if the thyroid nodule is cancerous or not (95% accurate), It is quick and simple to perform, It usually lasts only 10-15 minutes, It is minimally invasive and non-surgical, It doesn’t require general anesthesia, only a topical anesthetic is used, Recovery time is minimal, most people are back to their normal activities after 48 hours.
During the procedure, The radiologist uses ultrasound to capture a real-time image of the thyroid nodule, He guides a very fine (thin) needle to the nodule and takes several tissue samples, that help aid the accuracy of diagnosis, The needle is very thin that Lidocaine, the topical anesthetic, is the only anaesthesia used.
A needle biopsy can obtain tissue samples that can help diagnose whether a nodule is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant, The needle biopsy is less invasive than open and closed surgical biopsies, but open and closed surgical biopsies involve a larger incision in the skin, and local or general anesthesia.
The patients can soon resume their usual activities, Needle biopsy is not painful, the results are as accurate as when a tissue sample is removed surgically, and the recovery time is short.
Risks of thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy
Thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy comes with some slight risks. These include Bleeding at the biopsy site, Infection, and damage to the structures near the thyroid, Because most healthcare providers use ultrasound to guide the procedure, this last complication is rare.
The specimens may be inadequate and the procedure may have to be repeated in order to obtain diagnostic results. There is a small risk that the fine needle aspiration biopsy will not show for sure whether the nodule is cancerous, so, you might need a repeat biopsy.
What are the uses of the procedure?
A thyroid biopsy is used to find the cause of a nodule in the thyroid gland, When your doctor finds a nodule, He may order imaging tests to help determine if it is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), When imaging exams can’t clearly define the abnormality, a biopsy may be necessary.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Histological structure of thyroid gland & Functions of Thyroid Hormones (T3 & T4)
Regulation of Thyroid hormones secretion, Effects of Hyperthyroidism & Hypothyroidism
Thyroid gland function, hormones, function, anatomy & Congenital anomalies
Common procedures of Interventional Radiology and the best Interventional Radiologists
Hepatic Artery Embolization, Importance & risks of Embolization therapy for Liver cancer
Enlarged prostate symptoms, Prostatic artery embolization (PAE) importance & risks
Uterine fibroid embolization risks, importance & Minimally invasive procedure specialists