Pancreas function, anatomy, parts, relations, ducts and blood supply
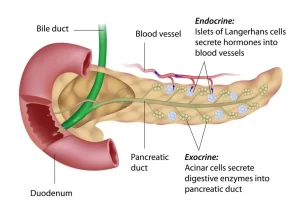
The pancreas plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into fuel for the body’s cells, It has two main functions: the exocrine function that helps in digestion and the endocrine function that regulates blood sugar, It is located behind the stomach in the upper left abdomen, It is surrounded by other organs including the small intestine, liver, and spleen.
Pancreas function
The pancreas has exocrine glands that produce enzymes important to digestion, These enzymes offer trypsin and chymotrypsin to digest proteins; amylase for the digestion of carbohydrates; and lipase to break down fats, The pancreas creates natural juices called pancreatic enzymes to break down foods, These juices travel through your pancreas via ducts.
Anatomy of Pancreas
Position of the pancreas:
- It is a combined exocrine & endocrine gland that lies transversely across the posterior abdominal wall.
- It extends from the concavity of the duodenum on the right side to the hilum of the spleen on the left side.
Parts of the pancreas:
It consists of the head, neck, body, and tail. The lower part of the head forms a projection called the uncinate process.
Relations of the pancreas
Head of the pancreas
It lies in the concavity of the duodenum. It is related to the 1st part of the duodenum superiorly, the 2nd part on the right side (separated from it by superior & inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries), and the 3rd part inferiorly.
- Anteriorly: it is related to the transverse colon.
- Posteriorly: it is related to IVC, renal veins, and common bile duct.
- The uncinate process lies between the abdominal aorta and superior mesenteric vessels.
The neck of the pancreas:
- Anteriorly: it is related to the gastro-duodenal junction.
- Posteriorly: it is related to the formation of portal veins from splenic and superior mesenteric veins.
Body (triangular in cross-section)
It has three surfaces (anterior, posterior, and inferior) and three borders (anterior, superior, and inferior).
Surfaces:
- Anterior surface: Related to the stomach, separated from it by the lesser sac.
- Inferior surface: Related to duodeno-jujenal flexure, loops of the ileum and end of the transverse colon (from right to left) are separated from them by the peritoneum of greater sac.
- Posterior surface: It is related to the posterior abdominal wall:
- Aorta and origin of sup. Mesenteric artery.
- Left kidney.
- Splenic and left renal vein.
- Left supra renal gland.
- Left psoas major.
- Left sympathetic chain.
- Left crus of the diaphragm.
Borders:
- Superior border: It is related to the splenic artery.
- Anterior border: It gives the attachment to transverse mesocolon and greater omentum.
- Inferior border: It separates the inferior from the posterior surfaces.
The tail of the pancreas
- It is related to the visceral surface of the spleen near its hilum.
- It reaches the hilum via the lieno-renal ligament.
Ducts of the pancreas
It has two ducts:
- Main pancreatic duct: It drains the upper part of the head, all of the body, and the tail of the pancreas. It runs from the tail to the head, then it unites with the common bile duct to form the ampulla of Vater which opens in the 2nd part of the duodenum. The ampulla of Vater opens into the apex of a mucosal elevation in the second part of the duodenum called the major duodenal papilla.
- Accessory pancreatic duct: It drains the uncinate process and lower part of the head. It opens in the 2nd part of the duodenum above the ampulla of Vater.
Blood supply
Arterial supply:
- Superior, inferior pancreatico-duodenal arteries: to the head.
- Pancreatic branches of splenic artery: to the rest of pancreas.
Venous drainage: To splenic vein and portal vein.
Lymphatic drainage:
- To the left of the neck: Drains into the pancreatico-splenic lymph nodes.
- The upper part of the head: Drains into the coeliac lymph nodes.
- The lower part of the head: Drains into the superior mesenteric lymph nodes.
You can download Science online application on Google Play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Histology of pancreas, Structure of islets of Langerhans, Insulin function & Metabolism
Small intestine function, anatomy, parts, Arterial supply of the duodenum, midgut & hindgut
Physiology & functions of Stomach, Composition of gastric secretion
Abdomen muscles, Blood Supply of Anterior Abdominal Wall & Rectus Sheath content
Stomach parts, function, curvatures, orifices, peritoneal connections & Venous drainage of Stomach