What are the kinds of molecules with examples?
The molecules of one substance are alike in properties, but they differ from other substance molecules, the molecule is composed of tiny structural units called the atoms, A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that stick together and they are very small that nobody can see them except with an electron microscope.
Molecules
The difference in the molecules of various substances is found as a result of the difference of the atoms which are involved in the structure of the molecule through the number of atoms, the kind of atoms and the way of combination together.
Kinds of molecules
1. Based on Composition
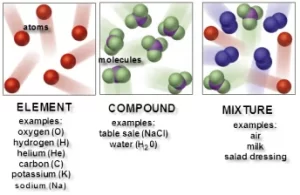
There are three types of molecules which are the element molecule, the compound molecule, and the mixture.
Element molecule
The element molecule is formed of similar atoms (one or more atoms) that combine together, The element is the simplest pure form of matter which can not be analyzed chemically into a simpler form. The elements molecules formed of an only atom (monoatomic) as solid (copper, iron, aluminum, sulphur, magnesium, carbon), liquid ( mercury), and Nobel gases (helium, neon, krypton, xenon and radon).
The element molecules formed of two atoms (diatomic) such as liquid (bromine), and active gases (oxygen, hydrogen, chlorine, nitrogen and fluorine). The molecules of active gases are diatomic such as oxygen molecules, while the molecules of inert gases are monoatomic, Mercury is the liquid element which is composed of one atom, while bromine is the liquid element which is composed of two atoms.
The elements molecules consist of only one kind of atom, they can’t be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either the physical or the chemical means, and they can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g. nitrogen).
Elements made of only one kind of atom, such as O₂ (oxygen), N₂ (nitrogen), H₂ (hydrogen).
Compound molecule
The compound molecule is formed of different atoms. the compound is a substance that is formed from the combination of atoms of two or more different elements with constant weight ratios, Some known compounds as sodium chloride molecule (table salt), water molecule, and ammonia molecule.
The compound molecule can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (the elements) by the chemical means but not by the physical means, It has properties that are different from its component elements, and it always contains the same ratio of its component atoms.
Compounds are made of two or more different elements bonded together, such as H₂O (water), CO₂ (carbon dioxide), and NaCl (salt).
Mixture molecule
The mixture molecule consists of two or more different elements or compounds physically intermingled, It can be separated into its components by physical means, and it often retains many of the properties of its components.
2. Based on the Bonding Type
- Covalent Molecules: Atoms share electrons, Usually formed between nonmetals, Example: CH₄ (methane), H₂O, O₂.
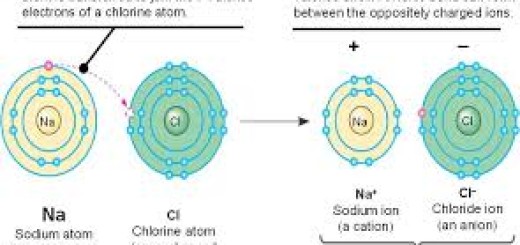
- Ionic Compounds (not always called “molecules,” but still worth noting), Atoms transfer electrons (creating ions). Typically between metals and nonmetals. Example: NaCl, MgO.
3. Based on the Number of Atoms
- Diatomic Molecules: Made of two atoms (same or different). Example: O₂, H₂, CO.
- Polyatomic Molecules: Made of three or more atoms. Example: H₂O (3 atoms), C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose — 24 atoms!).
4. Based on Origin
- Organic Molecules: Contain carbon (usually with hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen). Found in living things. Examples: Glucose, proteins, DNA.
- Inorganic Molecules: Often don’t contain carbon (or it’s not central). Example: H₂O, NaCl, CO₂ (yes, CO₂ is an exception — inorganic but carbon-containing).
5. Biological Molecules (Biomolecules)
These are crucial for life:
- Carbohydrates – sugars and starches
- Lipids – fats, oils
- Proteins – made of amino acids
- Nucleic Acids – DNA and RNA
Matter, Properties and Kinds of molecules, Melting process, and Vaporization process
Theories explaining the covalent bond, Octet rule and Overlapped orbitals concept
Chemical combination, Types of bonds (Chemical bonds and Physical bonds)
The coordinate bond, Physical bonds (hydrogen bond and the metallic bond)