General properties of halogens in the modern periodic table
The halogens
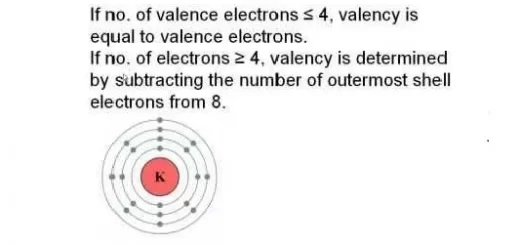
The halogens are located on the right side of the modern periodic table before the inert gases, The halogens are elements of group 7 A (17) in p-block, The halogens are mono-valent elements as their outermost energy levels have (7) electrons.
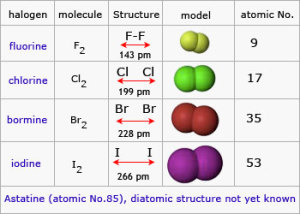
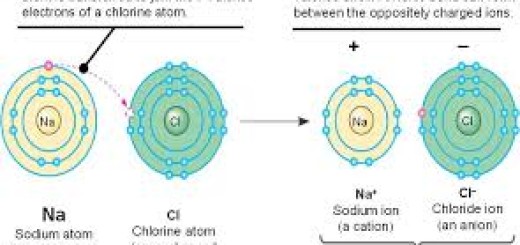
The halogens exist in the form of diatomic molecules (they are formed of two atoms), The halogens tend to gain one electron during the chemical reaction and convert into negative ion which has one negative charge.
The physical state of the halogens is graduated from the gas to the liquid to the solid. Fluorine and Chlorine are gases, Bromine is a liquid, and Iodine is solid.
The halogens react with the metals forming the salts, So, they are called the halogens which means “Forming the salts”.
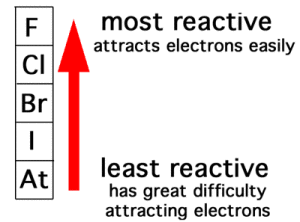
The halogens are the active elements, therefore, they do not exist in nature in the elementary state, but they are found combining with the other elements forming the chemical compounds (except Astatine (At) which is prepared artificially).
Each element of the halogens replaces the element below it in its salt solution.
You can download Science online application on google play from this link: Science online Apps on Google Play
Classification of elements in Long-form periodic table, Ionization Energy and Oxidation numbers
The graduation of the electronegativity of the elements in the periodic table
The lanthanides and actinides in the modern periodic table
Modern periodic table and classification of Elements
Graduation of the properties of the elements in the modern periodic table